Abstract
Rationale
Subchronic administration to rodents of the N-methyl-d-aspartate non-competitive antagonist, phencyclidine (PCP), impairs novel object recognition (NOR). Atypical antipsychotic drugs (APDs) reverse the effects of subchronic PCP on NOR. The effect of metabotropic glutamate2/3 receptor (mGlu2/3) agonists upon NOR is unknown.
Objectives and methods
We tested the hypotheses that the mGlu2/3 agonist, LY379268, by itself, or in combination with APDs or pimavanserin, a 5-HT2A inverse agonist, would reverse the deficit in NOR induced by subchronic treatment with PCP (2 mg/kg, b.i.d., for 7 days).
Results
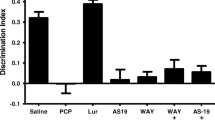
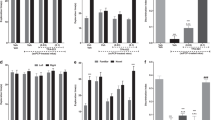
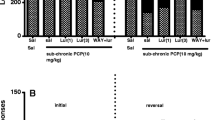
The mGlu2/3 agonist LY379268 (1 or 3 mg/kg) did not attenuate the PCP-induced NOR deficit. However, together with sub-effective dose of the atypical APDs, clozapine (0.1 mg/kg) or lurasidone (0.03 mg/kg), but not the typical APD, haloperidol (0.1 mg/kg), or pimavanserin (3 mg/kg), LY379268, 1 mg/kg, significantly reversed the PCP-induced NOR deficit. Moreover, the effect of clozapine was blocked by the mGlu2/3 antagonist, LY341495 (1 mg/kg).
Conclusions
These results indicate that mGlu2/3 agonism can potentiate the ability of atypical, but not typical APDs, to ameliorate the effect of subchronic PCP on NOR, that mGlu2/3 agonism may contribute to the ability of atypical APDs to acutely reverse the effect of subchronic PCP on NOR, but that by itself, mGlu2/3 agonism, is ineffective in this model of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia. These results suggest that mGlu2/3 receptor agonism should be investigated as an adjunctive treatment of cognitive impairment in schizophrenia rather than as monotherapy, which may be effective for control of psychosis, but not for cognitive impairment.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amitai N, Markou A (2010) Effects of metabotropic glutamate receptor 2/3 agonism and antagonism on schizophrenia-like cognitive deficits induced by phencyclidine in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 639(1–3):67–80
Aultman JM, Moghaddam B (2001) Distinct contributions of glutamate and dopamine receptors to temporal aspects of rodent working memory using a clinically relevant task. Psychopharmacology Berl 153(3):353–364
Bilder RM, Goldman RS, Volavka J, Czobor P, Hoptman M, Sheitman B, Lindenmayer JP, Citrome L, McEvoy J, Kunz M, Chakos M, Cooper TB, Horowitz TL, Lieberman JA (2002) Neurocognitive effects of clozapine, olanzapine, risperidone, and haloperidol in patients with chronic schizophrenia or schizoaffective disorder. Am J Psychiatry 159(6):1018–1028
Cartmell J, Schoepp DD (2000) Regulation of neurotransmitter release by metabotropic glutamate receptors. J Neurochem 75(3):889–907
Cartmell J, Monn JA, Schoepp DD (1999) The metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptor agonists LY354740 and LY379268 selectively attenuate phencyclidine versus d-amphetamine motor behaviors in rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 291(1):161–170
Chung YC, Li Z, Dai J, Meltzer HY, Ichikawa J (2004) Clozapine increases both acetylcholine and dopamine release in rat ventral hippocampus: role of 5-HT1A receptor agonism. Brain Res 1023:54–63
Coyle JT (2006) Glutamate and schizophrenia: beyond the dopamine hypothesis. Cell Mol Neurobiol 26(4–6):365–384
Critchlow HM, Maycox PR, Skepper JN, Krylova O (2006) Clozapine and haloperidol differentially regulate dendritic spine formation and synaptogenesis in rat hippocampal neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 32(4):356–365
Devivo M, Maayani S (1985) Inhibition of forskolin-stimulated adenylate cyclase activity by 5-HT receptor agonists. Eur J Pharmacol 119(3):231–234
Enomoto T, Ishibashi T, Tokuda K, Ishiyama T, Toma S, Ito A (2008) Lurasidone reverses MK-801-induced impairment of learning and memory in the Morris water maze and radial-arm maze tests in rats. Behav Brain Res 186(2):197–207
Gewirtz JC, Marek GJ (2000) Behavioral evidence for interactions between a hallucinogenic drug and group II metabotropic glutamate receptors. Neuropsychopharmacology 23(5):569–576
Goldman-Rakic PS, Selemon LD (1997) Functional and anatomical aspects of prefrontal pathology in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 23(3):437–458
González-Maeso J, Ang RL, Yuen T, Chan P, Weisstaub NV, López-Giménez JF, Zhou M, Okawa Y, Callado LF, Milligan G, Gingrich JA, Filizola M, Meana JJ, Sealfon SC (2008) Identification of a serotonin/glutamate receptor complex implicated in psychosis. Nature 452(7183):93–97
Gray JA, Roth BL (2007) Molecular targets for treating cognitive dysfunction in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 33(5):1100–1119
Grayson B, Idris NF, Neill JC (2007) Atypical antipsychotics attenuate a sub-chronic PCP-induced cognitive deficit in the novel object recognition task in the rat. Behav Brain Res 184(1):31–38
Gunduz-Bruce H (2009) The acute effects of NMDA antagonism: from the rodent to the human brain. Brain Res Rev 60(2):279–286
Hagger C, Buckley P, Kenny JT, Friedman L, Ubogy D, Meltzer HY (1993) Improvement in cognitive functions and psychiatric symptoms in treatment-refractory schizophrenic patients receiving clozapine. Biol Psychiatry 34:02–712
Hagiwara H, Fujita Y, Ishima T, Kunitachi S, Shirayama Y, Iyo M, Hashimoto K (2008) Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in mice are improved by subsequent subchronic administration of the antipsychotic drug perospirone: role of serotonin 5-HT1A receptors. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 18(6):448–454
Hajszan T, Leranth C, Roth RH (2006) Subchronic phencyclidine treatment decreases the number of dendritic spine synapses in the rat prefrontal cortex. Biol Psychiatry 60:639–644
Harich S, Gross G, Bespalov A (2007) Stimulation of the metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptor attenuates social novelty discrimination deficits induced by neonatal phencyclidine treatment. Psychopharmacology Berl 192(4):511–519
Harris SL, Cho K, Bashir ZI, Molnar E (2004) Metabotropic glutamate receptor signalling in perirhinal cortical neurons. Mol Cell Neurosci 25(2):275–287
Hashimoto K, Fujita Y, Shimizu E, Iyo M (2005) Phencyclidine-induced cognitive deficits in mice are improved by subsequent sub-chronic administration of clozapine, but not haloperidol. Eur J Pharmacol 519:114–117
Higgins GA, Ballard TM, Kew JN, Richards JG, Kemp JA, Adam G, Woltering T, Nakanishi S, Mutel V (2004) Pharmacological manipulation of mGlu2 receptors influences cognitive performance in the rodent. Neuropharmacology 46(7):907–917
Ichikawa J, Meltzer HY (1991) Differential effects of repeated treatment with haloperidol and clozapine on dopamine release and metabolism in the striatum and the nucleus accumbens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 256(1):348–357
Ichikawa J, Dai J, Meltzer HY (2002) Atypical antipsychotic drugs, quetiapine, iloperidone, and melperone, preferentially increase dopamine and acetylcholine release in rat medial prefrontal cortex: role of 5HT1A receptor agonism. Brain Res 956:349–357
Imre G, Fokkema DS, Ter Horst GJ (2006) Subchronic administration of LY354740 does not modify ketamine-evoked behavior and neuronal activity in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 544(1–3):77–81
Ishiyama T, Tokuda K, Ishibashi T, Ito A, Toma S, Ohno Y (2007) Lurasidone (SM-13496), a novel atypical antipsychotic drug, reverses MK-801-induced impairment of learning and memory in the rat passive-avoidance test. Eur J Pharmacol 572(2–3):160–170
Ishiyama T, Loebel A, Cucciaro J, Horisawa T, Tokuda K, Ishibashi T, Stahl S (2009) Receptor binding profile of lurasidone: a novel psychotropic agent under development for schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. ACNP 48th Annual Meeting Poster Abstr 75
Javitt DC, Zukin SR (1991) Recent advances in the phencyclidine model of schizophrenia. Am J Psychiatry 148(10):1301–1308
Jentsch JD, Dazzi L, Chhatwal JP, Verrico CD, Roth RH (1998) Reduced prefrontal cortical dopamine, but not acetylcholine, release in vivo after repeated, intermittent phencyclidine administration to rats. Neurosci Lett 258(3):175–178
Jones CA, Brown AM, Auer DP, Fone KC (2010) The mGluR2/3 agonist LY379268 reverses post-weaning social isolation-induced recognition memory deficits in the rat. Psychopharmacology Berl. doi:10.1007/s00213-010-1931-7
Keefe RSE, Bilder RM, Davis SM, Harvey PD, Palmer BW, Gold JM, Meltzer HY, Green MF, Capuano G, Stroup TS, McEvoy JP, Swartz MS, Rosenheck RA, Perkins DO, Davis CE, Hsiao JK, Lieberman JA, CATIE Investigators and the Neurocognitive Working Group (2007) Neurocognitive effects of antipsychotic medications in patients with chronic schizophrenia in the CATIE trial. Arch Gen Psychiatry 64:633–647
Kinon BJ (2009) LY2140023 monohydrate: an agonist at the mGlu2/3 receptor for the treatment of schizophrenia. International Congress on Schizophrenia Research, San Diego
Krystal JH, D'Souza DC, Petrakis IL, Belger A, Berman RM, Charney DS, Abi-Saab W, Madonick S (1999) NMDA agonists and antagonists as probes of glutamatergic dysfunction and pharmacotherapies in neuropsychiatric disorders. Harv Rev Psychiatry 7(3):125–143
Krystal JH, Abi-Saab W, Perry E, D'Souza DC, Liu N, Gueorguieva R, McDougall L, Hunsberger T, Belger A, Levine L, Breier A (2005) Preliminary evidence of attenuation of the disruptive effects of the NMDA glutamate receptor antagonist, ketamine, on working memory by pretreatment with the group II metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist, LY354740, in healthy human subjects. Psychopharmacology Berl 179(1):303–309
Kuroki T, Meltzer HY, Ichikawa J (1999) Effects of antipsychotic drugs on extracellular dopamine levels in rat medial prefrontal cortex and nucleus accumbens. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 288:774–781
LaPorte DJ, Lahti AC, Koffel B, Tamminga CA (1996) Absence of ketamine effects on memory and other cognitive functions in schizophrenia patients. J Psychiatr Res 30(5):321–330
Li Q, Deng Z, Zhang Y, Zhou X, Nagerl V, Wong S (2011) A global spatial similarity optimization scheme to track large numbers of dendritic spines in time-lapse confocal microscopy. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 30(3):632–641
Liegeois JF, Ichikawa J, Meltzer HY (2002) 5-HT(2A) receptor antagonism potentiates haloperidol-induced dopamine release in rat medial prefrontal cortex and inhibits that in the nucleus accumbens in a dose-dependent manner. Brain Res 947:157–165
Lovenberg TW, Baron BM, de Lecea L, Miller JD, Prosser RA, Rea MA, Foye PE, Racke M, Slone AL, Siegel BW, Danielson PE, Sutcliffe JG, Erlander MG (1993) A novel adenylyl cyclase-activating serotonin receptor (5-HT7) implicated in the regulation of mammalian circadian rhythms. Neuron 11(3):449–458
Marek GJ, Wright RA, Schoepp DD, Monn JA, Aghajanian GK (2000) Physiological antagonism between 5-hydroxytryptamine(2A) and group II metabotropic glutamate receptors in prefrontal cortex. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 292(1):76–87
McKibben CE, Jenkins TA, Adams HN, Harte MK, Reynolds GP (2010) Effect of pretreatment with risperidone on phencyclidine-induced disruptions in object recognition memory and prefrontal cortex parvalbumin immunoreactivity in the rat. Behav Brain Res 208(1):132–136
Meltzer HY, Huang M (2008) In vivo actions of atypical antipsychotic drug on serotonergic and dopaminergic systems. Prog Brain Res 172:177–197
Meltzer HY, McGurk SR (1999) The effects of clozapine, risperidone, and olanzapine on cognitive function in schizophrenia. Schizophr Bull 25:233–255
Meltzer HY, Matsubara S, Lee JC (1989) The ratios of serotonin2 and dopamine2 affinities differentiate atypical and typical antipsychotic drugs. Psychopharmacol Bull 25:390–392
Meltzer HY, Arvanitis L, Bauer D, Rein W, Meta-Trial Study Group (2004) Placebo-controlled evaluation of four novel compounds for the treatment of schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Am J Psychiatry 161(6):975–984
Meltzer HY, Mills R, Revell S, Williams H, Johnson A, Bahr D, Friedman JH (2010) Pimavanserin, a serotonin(2A) receptor inverse agonist, for the treatment of parkinson's disease psychosis. Neuropsychopharmacology 35(4):881–892
Meyer JM, Loebel AD, Schweizer E (2009) Lurasidone: a new drug in development for schizophrenia. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 18(11):1715–1726
Moghaddam B, Adams BW (1998) Reversal of phencyclidine effects by a group II metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist in rats. Science 281(5381):1349–1352
Moghaddam B, Bunney BS (1990) Acute effects of typical and atypical antipsychotic drugs on the release of dopamine from prefrontal cortex, nucleus accumbens, and striatum of the rat: an in vivo microdialysis study. J Neurochem 54(5):1755–1760
Morgan CJ, Huddy V, Lipton M, Curran HV, Joyce EM (2009) Is persistent ketamine use a valid model of the cognitive and oculomotor deficits in schizophrenia? Biol Psychiatry 65(12):1099–1102
Nagai T, Murai R, Matsui K, Kamei H, Noda Y, Furukawa H, Nabeshima T (2009) Aripiprazole ameliorates phencyclidine-induced impairment of recognition memory through dopamine D1 and serotonin 5-HT1A receptors. Psychopharmacology Berl 202(1–3):315–328
Neill JC, Barnes S, Cook S, Grayson B, Idris NF, McLean SL, Snigdha S, Rajagopal L, Harte MK (2010) Animal models of cognitive dysfunction and negative symptoms of schizophrenia: focus on NMDA receptor antagonism. Pharmacol Ther 128(3):419–432
Newman-Tancredi A, Assié MB, Leduc N, Ormière AM, Danty N, Cosi C (2005) Novel antipsychotics activate recombinant human and native rat serotonin 5-HT1A receptors: affinity, efficacy and potential implications for treatment of schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 8(3):341–356
Palmer BW, Heaton RK, Paulsen JS, Kuck J, Braff D, Harris MJ, Zisook S, Jeste DV (1997) Is it possible to be schizophrenic yet neuropsychologically normal? Neuropsychology 11(3):437–446
Patil ST, Zhang L, Martenyi F, Lowe SL, Jackson KA, Andreev BV, Avedisova AS, Bardenstein LM, Gurovich IY, Morozova MA, Mosolov SN, Neznanov NG, Reznik AM, Smulevich AB, Tochilov VA, Johnson BG, Monn JA, Schoepp DD (2007) Activation of mGlu2/3 receptors as a new approach to treat schizophrenia: a randomized Phase 2 clinical trial. Nat Med 13(9):1102–1107
Pehrson AL, Moghaddam B (2010) Impact of metabotropic glutamate 2/3 receptor stimulation on activated dopamine release and locomotion. Psychopharmacology Berl 211(4):443–455
Prézeau L, Carrette J, Helpap B, Curry K, Pin JP, Bockaert J (1994) Pharmacological characterization of metabotropic glutamate receptors in several types of brain cells in primary cultures. Mol Pharmacol 45(4):570–577
Rasmussen H, Ebdrup BH, Erritzoe D, Aggernaes B, Oranjem B, Kalbitzer J, Pinborg LH, Baaré WFC, Svarer C, Lublin H, Knudsen GM, Glenthoj B (2010) Serotonin2A receptor blockade and clinical effect in first-episode schizophrenia patients treated with quetiapine. Psychopharmacology Berl. doi:10.1007/s00213-010-1941-5
Rauly-Lestienne I, Boutet-Robinet E, Ailhaud MC, Newman-Tancredi A, Cussac D (2007) Differential profile of typical, atypical and third generation antipsychotics at human 5-HT7a receptors coupled to adenylyl cyclase: detection of agonist and inverse agonist properties. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 376(1–2):93–105
Schlumberger C, Schäfer D, Barberi C, Morè L, Nagel J, Pietraszek M, Schmidt WJ, Danysz W (2009) Effects of a metabotropic glutamate receptor group II agonist LY354740 in animal models of positive schizophrenia symptoms and cognition. Behav Pharmacol 20(1):56–66
Schotte A, Janssen PF, Gommeren W, Luyten WH, Van Gompel P, Lesage AS, De Loor K, Leysen JE (1996) Risperidone compared with new and reference antipsychotic drugs: in vitro and in vivo receptor binding. Psychopharmacology Berl 124:57–73
Schreiber R, Lowe D, Voerste A, De Vry J (2000) LY354740 affects startle responding but not sensorimotor gating or discriminative effects of phencyclidine. Eur J Pharmacol 388(2):R3–R4
Senogles SE, Amlaiky N, Berger JG, Caron MG (1988) Biochemical properties of D1 and D2 dopamine receptors. Adv Exp Med Biol 235:33–41
Snigdha S, Horiguchi M, Huang M, Li Z, Shahid M, Neill JC, Meltzer HY (2010) Attenuation of phencyclidine-induced object recognition deficits by the combination of atypical antipsychotic drugs and pimavanserin (ACP 103), a 5-hydroxytryptamine(2A) receptor inverse agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 332(2):622–631
Stefanovic A, Brandner B, Klaassen E, Cregg R, Nagaratnam M, Bromley LM, Das RK, Rossell SL, Morgan CJ, Curran HV (2009) Acute and chronic effects of ketamine on semantic priming: modeling schizophrenia? J Clin Psychopharmacol 29(2):124–133
Swanson CJ, Schoepp DD (2002) The group II metabotropic glutamate receptor agonist (−)-2-oxa-4-aminobicyclo[3.1.0.]hexane-4,6-dicarboxylate (LY379268) and clozapine reverse phencyclidine-induced behaviors in monoamine-depleted rats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303(3):919–927
Turetsky BI, Moberg PJ, Roalf DR, Arnold SE, Gur RE (2003) Decrements in volume of anterior ventromedial temporal lobe and olfactory dysfunction in schizophrenia. Arch Gen Psychiatry 60(12):1193–1200
Uslaner JM, Smith SM, Huszar SL, Pachmerhiwala R, Hinchliffe RM, Vardigan JD, Hutson PH (2009) Combined administration of an mGlu2/3 receptor agonist and a 5-HT 2A receptor antagonist markedly attenuate the psychomotor-activating and neurochemical effects of psychostimulants. Psychopharmacology Berl 206(4):641–651
Vales K, Svoboda J, Benkovicova K, Bubenikova-Valesova V, Stuchlik A (2010) The difference in effect of mGlu2/3 and mGlu5 receptor agonists on cognitive impairment induced by MK-801. Eur J Pharmacol 639(1–3):91–98
Vanover KE, Weiner DM, Makhay M, Veinbergs I, Gardell LR, Lameh J, Del Tredici AL, Piu F, Schiffer HH, Ott TR, Burstein ES, Uldam AK, Thygesen MB, Schlienger N, Andersson CM, Son TY, Harvey SC, Powell SB, Geyer MA, Tolf BR, Brann MR, Davis RE (2006) Pharmacological and behavioral profile of N-(4-fluorophenylmethyl)-N-(1-methylpiperidin-4-yl)-N'-(4-(2-methylpropyloxy)phenylmethyl) carbamide (2R,3R)-dihydroxybutanedioate (2:1) (ACP-103), a novel 5-hydroxytryptamine(2A) receptor inverse agonist. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 317(2):910–918
Wang HD, Deutch AY (2008) Dopamine depletion of the prefrontal cortex induces dendritic spine loss: reversal by atypical antipsychotic drug treatment. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:1276–1286
Winters BD, Forwood SE, Cowell RA, Saksida LM, Bussey TJ (2004) Double dissociation between the effects of peri-postrhinal cortex and hippocampal lesions on tests of object recognition and spatial memory: heterogeneity of function within the temporal lobe. J Neurosci 24(26):5901–5908
Woodward ND, Purdon SE, Meltzer HY, Zald DH (2005) A meta-analysis of neuropsychological change to clozapine, olanzapine, quetiapine, and risperidone in schizophrenia. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol 8(3):457–472
Woolley ML, Pemberton DJ, Bate S, Corti C, Jones DN (2008) The mGlu2 but not the mGlu3 receptor mediates the actions of the mGluR2/3 agonist, LY379268, in mouse models predictive of antipsychotic activity. Psychopharmacology Berl 196(3):431–440
Yassa MA, Stark CE (2008) Multiple signals of recognition memory in the medial temporal lobe. Hippocampus 18(9):945–954
Acknowledgements
This research was supported, in part, by a grant from Dainippon Sumitomo Pharma Co., Ltd. HYM is supported, in part, by contributions from the Ritter and Weisman Family Foundations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horiguchi, M., Huang, M. & Meltzer, H.Y. Interaction of mGlu2/3 agonism with clozapine and lurasidone to restore novel object recognition in subchronic phencyclidine-treated rats. Psychopharmacology 217, 13–24 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2251-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2251-2