Abstract
Rationale
Genetic inactivation or pharmacological antagonism of neurokinin 1 (NK1) receptors blocks morphine and alcohol reward in rodents, while NK1 antagonism decreases alcohol craving in humans. The role of the NK1 system for relapse-like behavior has not previously been examined.
Objective
Divergence between human and rodent NK1 receptors has limited the utility of NK1 antagonists developed for the human receptor species for preclinical studies of addiction-related behaviors in rats. Here we used L822429, an NK1 antagonist specifically engineered to bind at high affinity to the rat receptor, to assess the effects of NK1 receptor antagonism on alcohol-seeking behaviors in rats.
Methods
L822429 (15 and 30 mg/kg) was used to examine effects of NK1 receptor antagonism on operant self-administration of 10% alcohol in 30-min daily sessions, as well as intermittent footshock stress- and cue-induced reinstatement of alcohol-seeking after extinction of lever responding.
Results
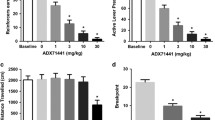
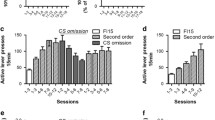
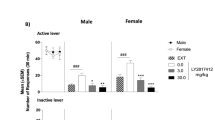
At the doses used, L822429 did not significantly affect alcohol self-administration or cue-induced reinstatement, but potently and dose dependently suppressed stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol seeking, with an essentially complete suppression at the highest dose. The effect of L822429 on stress-induced reinstatement was behaviorally specific. The drug had no effect on conditioned suppression of operant responding following fear conditioning, locomotor activity, or self-administration of a sucrose solution.
Conclusions
To the degree that the reinstatement model provides a model of drug relapse, the results provide support for NK1 antagonism as a promising mechanism for pharmacotherapy of alcoholism, acting through suppression of stress-induced craving and relapse.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Annau Z, Kamin LJ (1961) The conditioned emotional response as a function of intensity of the US. J Comp Physiol Psychol 54:428–432
Baek MN, Jung KH, Halder D, Choi MR, Lee BH, Lee BC, Jung MH, Choi IG, Chung MK, Oh DY, Chai YG (2010) Artificial microRNA-based neurokinin-1 receptor gene silencing reduces alcohol consumption in mice. Neurosci Lett 475:124–128
Belknap JK, Crabbe JC, Young ER (1993) Voluntary consumption of ethanol in 15 inbred mouse strains. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 112:503–510
Brownell KD, Marlatt GA, Lichtenstein E, Wilson GT (1986) Understanding and preventing relapse. Am Psychol 41:765–782
Bruijnzeel AW, Prado M, Isaac S (2009) Corticotropin-releasing factor-1 receptor activation mediates nicotine withdrawal-induced deficit in brain reward function and stress-induced relapse. Biol Psychiatry 66:110–117
Cippitelli A, Karlsson C, Shaw JL, Thorsell A, Gehlert DR, Heilig M (2010) Suppression of alcohol self-administration and reinstatement of alcohol seeking by melanin-concentrating hormone receptor 1 (MCH1-R) antagonism in Wistar rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 211:367–375
Conley RK, Cumberbatch MJ, Mason GS, Williamson DJ, Harrison T, Locker K, Swain C, Maubach K, O’Donnell R, Rigby M, Hewson L, Smith D, Rupniak NM (2002) Substance P (neurokinin 1) receptor antagonists enhance dorsal raphe neuronal activity. J Neurosci 22:7730–7736
Ebner K, Singewald N (2006) The role of substance P in stress and anxiety responses. Amino Acids 31:251–272
Ebner K, Rupniak NM, Saria A, Singewald N (2004) Substance P in the medial amygdala: emotional stress-sensitive release and modulation of anxiety-related behavior in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:4280–4285
Ebner K, Muigg P, Singewald G, Singewald N (2008) Substance P in stress and anxiety: NK-1 receptor antagonism interacts with key brain areas of the stress circuitry. Ann NY Acad Sci 1144:61–73
Epstein DH, Preston KL, Stewart J, Shaham Y (2006) Toward a model of drug relapse: an assessment of the validity of the reinstatement procedure. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 189:1–16
Estes WK, Skinner BF (1941) Some quantitative properties of anxiety. J Exp Psychol 29:390–400
Gadd CA, Murtra P, De Felipe C, Hunt SP (2003) Neurokinin-1 receptor-expressing neurons in the amygdala modulate morphine reward and anxiety behaviors in the mouse. J Neurosci 23:8271–8280
George DT, Gilman J, Hersh J, Thorsell A, Herion D, Geyer C, Peng X, Kielbasa W, Rawlings R, Brandt JE, Gehlert DR, Tauscher JT, Hunt SP, Hommer D, Heilig M (2008) Neurokinin 1 receptor antagonism as a possible therapy for alcoholism. Science 319:1536–1539
Gobbi G, Cassano T, Radja F, Morgese MG, Cuomo V, Santarelli L, Hen R, Blier P (2007) Neurokinin 1 receptor antagonism requires norepinephrine to increase serotonin function. Eur Neuropsychopharmacol 17:328–338
Grant KA, Samson HH (1986) The induction of oral ethanol self-administration by contingent ethanol delivery. Drug Alcohol Depend 16:361–368
Guiard BP, Guilloux JP, Reperant C, Hunt SP, Toth M, Gardier AM (2007) Substance P neurokinin 1 receptor activation within the dorsal raphe nucleus controls serotonin release in the mouse frontal cortex. Mol Pharmacol 72:1411–1418
Hamke M, Herpfer I, Lieb K, Wandelt C, Fiebich BL (2006) Substance P induces expression of the corticotropin-releasing factor receptor 1 by activation of the neurokinin-1 receptor. Brain Res 1102:135–144
Heilig M, Egli M (2006) Pharmacological treatment of alcohol dependence: target symptoms and target mechanisms. Pharm Ther 111:855–876
Heilig M, Koob GF (2007) A key role for corticotropin-releasing factor in alcohol dependence. Trends Neurosci 30:399–406
Hutson PH, Patel S, Jay MT, Barton CL (2004) Stress-induced increase of cortical dopamine metabolism: attenuation by a tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonist. Eur J Pharmacol 484:57–64
Le A, Shaham Y (2002) Neurobiology of relapse to alcohol in rats. Pharmacol Ther 94:137–156
Le AD, Quan B, Juzytch W, Fletcher PJ, Joharchi N, Shaham Y (1998) Reinstatement of alcohol-seeking by priming injections of alcohol and exposure to stress in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 135:169–174
Le AD, Poulos CX, Harding S, Watchus J, Juzytsch W, Shaham Y (1999) Effects of naltrexone and fluoxetine on alcohol self-administration and reinstatement of alcohol seeking induced by priming injections of alcohol and exposure to stress. Neuropsychopharmacology 21:435–444
Le AD, Harding S, Juzytsch W, Watchus J, Shalev U, Shaham Y (2000) The role of corticotrophin-releasing factor in stress-induced relapse to alcohol-seeking behavior in rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 150:317–324
Le AD, Harding S, Juzytsch W, Fletcher PJ, Shaham Y (2002) The role of corticotropin-releasing factor in the median raphe nucleus in relapse to alcohol. J Neurosci 22:7844–7849
Liu X, Weiss F (2002) Additive effect of stress and drug cues on reinstatement of ethanol seeking: exacerbation by history of dependence and role of concurrent activation of corticotropin-releasing factor and opioid mechanisms. J Neurosci 22:7856–7861
Maubach KA, Martin K, Chicchi G, Harrison T, Wheeldon A, Swain CJ, Cumberbatch MJ, Rupniak NM, Seabrook GR (2002) Chronic substance P (NK1) receptor antagonist and conventional antidepressant treatment increases burst firing of monoamine neurones in the locus coeruleus. Neuroscience 109:609–617
McLellan AT, Lewis DC, O’Brien CP, Kleber HD (2000) Drug dependence, a chronic medical illness: implications for treatment, insurance, and outcomes evaluation. JAMA 284:1689–1695
Murtra P, Sheasby AM, Hunt SP, De Felipe C (2000) Rewarding effects of opiates are absent in mice lacking the receptor for substance P. Nature 405:180–183
Pickens CL, Golden SA, Adams-Deutsch T, Nair SG, Shaham Y (2009) Long-lasting incubation of conditioned fear in rats. Biol Psychiatry 65:881–886
Pickens CL, Navarre BM, Nair SG (2010) Incubation of conditioned fear in the conditioned suppression model in rats: role of food-restriction conditions, length of conditioned stimulus, and generality to conditioned freezing. Neuroscience 169:1501–1510
Renoldi G, Invernizzi RW (2006) Blockade of tachykinin NK1 receptors attenuates stress-induced rise of extracellular noradrenaline and dopamine in the rat and gerbil medial prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci Res 84:961–968
Ripley TL, Gadd CA, De Felipe C, Hunt SP, Stephens DN (2002) Lack of self-administration and behavioural sensitisation to morphine, but not cocaine, in mice lacking NK1 receptors. Neuropharmacology 43:1258–1268
Samson HH (1986) Initiation of ethanol reinforcement using a sucrose-substitution procedure in food- and water-sated rats. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 10:436–442
Santarelli L, Gobbi G, Debs PC, Sibille ET, Blier P, Hen R, Heath MJ (2001) Genetic and pharmacological disruption of neurokinin 1 receptor function decreases anxiety-related behaviors and increases serotonergic function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:1912–1917
Seneviratne C, Ait-Daoud N, Ma JZ, Chen G, Johnson BA, Li MD (2009) Susceptibility locus in neurokinin-1 receptor gene associated with alcohol dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:2442–2449
Shaham Y, Stewart J (1995) Stress reinstates heroin-seeking in drug-free animals—an effect mimicking heroin, not withdrawal. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 119:334–341
Shaham Y, Erb S, Leung S, Buczek Y, Stewart J (1998) CP-154, 526, a selective, non-peptide antagonist of the corticotropin-releasing factor (1) receptor attenuates stress-induced relapse to drug seeking in cocaine- and heroin-trained rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 137:184–190
Shaham Y, Erb S, Stewart J (2000) Stress-induced relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking in rats: a review. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 33:13–33
Shalev U, Grimm JW, Shaham Y (2002) Neurobiology of relapse to heroin and cocaine seeking: a review. Pharmacol Rev 54:1–42
Singewald N, Chicchi GG, Thurner CC, Tsao KL, Spetea M, Schmidhammer H, Sreepathi HK, Ferraguti F, Singewald GM, Ebner K (2008) Modulation of basal and stress-induced amygdaloid substance P release by the potent and selective NK1 receptor antagonist L-822429. J Neurochem 106(6):2476–88
Sinha R (2009) Modeling stress and drug craving in the laboratory: implications for addiction treatment development. Addict Biol 14:84–98
Steensland P, Simms JA, Nielsen CK, Holgate J, Bito-Onon JJ, Bartlett SE (2010) The neurokinin 1 receptor antagonist, ezlopitant, reduces appetitive responding for sucrose and ethanol. Plos One 5(9):e12527
Thorsell A, Schank JR, Singley E, Hunt SP, Heilig M (2010) Neurokinin-1 receptors (NK1R:s), alcohol consumption, and alcohol reward in mice. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 209:103–111
Vickers AJ, Altman DG (2001) Statistics notes—analysing controlled trials with baseline and follow up measurements. Br Med J 323:1123–1124
Waddell J, Morris RW, Bouton ME (2006) Effects of bed nucleus of the stria terminalis lesions on conditioned anxiety: aversive conditioning with long-duration conditional stimuli and reinstatement of extinguished fear. Behav Neurosci 120:324–336
Walker BM, Koob GF (2008) Pharmacological evidence for a motivational role of kappa-opioid systems in ethanol dependence. Neuropsychopharmacology 33:643
Walker D, Yang Y, Ratti E, Corsi M, Trist D, Davis M (2009) Differential effects of the CRF-R1 antagonist GSK876008 on fear-potentiated, light- and CRF-enhanced startle suggest preferential involvement in sustained vs phasic threat responses. Neuropsychopharmacology 34:1533–1542
Weiss F (2005) Neurobiology of craving, conditioned reward and relapse. Curr Opin Pharmacol 5:9–19
Acknowledgments
We thank Andrea Goldstein, Michelle Zook, and Lauren Bell for technical assistance, and Dr. Andrea Cippitelli for advice concerning methodological procedures.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schank, J.R., Pickens, C.L., Rowe, K.E. et al. Stress-induced reinstatement of alcohol-seeking in rats is selectively suppressed by the neurokinin 1 (NK1) antagonist L822429. Psychopharmacology 218, 111–119 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2201-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-011-2201-z