Abstract
Aim
Excess consumption of alcohol leads to impaired cognition and decision making; hence, alcohol-containing products and advertising contain warning messages about the adverse effects of excess drinking. However, there is a need to understand how alcohol influences the processing of advisory messages.
Method
The current study used a computerised gambling simulation and investigated whether intoxication would affect the use of a decision aid. Using a double-blind repeated measures design, 16 adult males (aged 18–29) completed the Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test and the South Oaks Gambling Screen and played a computer blackjack program on two separate occasions, under differing doses of alcohol. On certain conditions, the computerised decision aid gave advice to participants as to whether the odds were in their favour.
Results
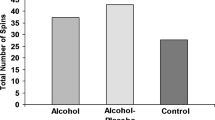
Participants were found to take longer to respond to the decision aid under higher risk conditions when they were losing.
Conclusion
Alcohol intoxication may lead to problems evaluating information pertaining to risk, and this has implications for the use of other decision aids designed to assist intoxicated individuals. The problems processing warning information were consistent with alcohol induced ‘myopia’ where intoxicated individuals had problems processing less salient cues.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alcohol Beverage Labeling Act (1988) Public Law 100-690, 27 USC 201-211, Nov. 18
Allen JP, Reinert DF, Volk RJ (2001) The alcohol use disorders identification test: an aid to recognition of alcohol problems in primary care patients. Prev Med 33:428–433
Andrews JC (1995) The effectiveness of alcohol warning labels: a review and extension. Am Behav Sci 38:622–632
Andrews JC, Netemeyer RG, Durvasula S (1991) Effects of consumption frequency on believability and attitudes toward alcohol warning labels. J Consum Aff 25:323–338
Balodis IM, MacDonald TK, Olmstead MC (2006) Instructional cues modify performance on the Iowa gambling task. Brain Cogn 60:109–117
Bechara A, Damasio H (2002) Decision-making and addiction (part I): impaired activation of somatic states in substance dependent individuals when pondering decisions with negative future consequences. Neuropsychologia 40:1675–1689
Bechara A, Dolan S, Denburg N, Hindes A, Anderson SW, Nathan PE (2001) Decision-making deficits, linked to a dysfunctional ventromedial prefrontal cortex, revealed in alcohol and stimulant abusers. Neuropsychologia 39:376–389
Casswell S, Thamarangsi T (2009) Reducing harm from alcohol: call to action. Lancet 373:2247–2257
Cohen LJ (1979) On the psychology of prediction: whose is the fallacy? Cognition 7:385–407
Cooper ML (2002) Alcohol use and risky sexual behavior among college students and youth: evaluating the evidence. J Stud Alcohol 14:101–117
Cummins LF, Nadorff MR, Kelly AE (2009) Winning and positive affect can lead to reckless gambling. Psychol Addict Behav 23:287–294
Davis KC, Hendershot CS, George WH, Norris J, Heiman JR (2007) Alcohol’s effects on sexual decision making: an integration of alcohol myopia and individual differences. J Stud Alcohol Drugs 68:843–851
Duhig AM, Maciejewski PK, Desai RA, Krishnan-Sarin S, Potenza MN (2007) Characteristics of adolescent past-year gamblers and non-gamblers in relation to alcohol drinking. Addict Behav 32:80–89
Ellery M, Stewart SH, Loba P (2005) Alcohol’s effects on video lottery terminal (VLT) play among probable, pathological and non-pathological gamblers. J Gambl Stud 21:299–324
Forster JL, Murray DM, Wolfson M, Wagenaar AC (1995) Commercial availability of alcohol to young people: results of alcohol purchase attempts. Prev Med 24:342–347
George S, Rogers RD, Duka T (2005) The acute effect of alcohol on decision making in social drinkers. Psychopharmacology 182:160–169
Hankin JR, Firestone IJ, Sloan JJ, Ager JW, Sokol RJ, Martier SS (1996) Heeding the alcoholic beverage warning label during pregnancy: multiparae versus nulliparae. J Stud Alcohol 57:171–177
Johnson MB, Voas RB (2004) Potential risks of providing drinking drivers with BAC information. Traffic Inj Prev 5:42–49
Julien RM (2005) A primer of drug action, 10th edn. Worth, New York
Kalant H (2004) Effects of food and body composition on blood alcohol levels. In: Reedy VR, Watson RR (eds) Comprehensive handbook of alcohol related pathology, vol 1. Elsevier, London, pp 87–101
Kausch O (2003) Patterns of substance abuse among treatment-seeking pathological gamblers. J Subst Abuse Treat 25:263–270
Keppel G (1982) Design and analysis: a researcher’s handbook. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Kozup J, Burton S, Creyer E (2001) A comparison of drinkers’ and nondrinkers’ responses to health-related information presented on wine beverage labels. J Cons Pol 24:209–230
Kyngdon A, Dickerson M (1999) An experimental study of the effect of prior alcohol consumption on a simulated gambling activity. Addiction 94:697–707
Ladd GT, Petry NM (2003) A comparison of pathological gamblers with and without substance abuse treatment histories. Exp Clin Psychopharm 11:202–209
Lane SD, Cherek DR, Pietras CJ, Tcheremissine OV (2004) Alcohol effects on human risk taking. Psychopharmacology 172:68–77
Lane SD, Yechiam E, Busemeyer JR (2006) Application of a computational decision model to examine acute drug effects on human risk taking. Exp Clin Psychopharmacol 14:254–264
Lesieur HR, Blume SB (1987) The South Oaks Gambling Screen (SOGS): a new instrument for the identification of pathological gamblers. Am J Psychiatry 144:1184–1188
Lesieur HR, Cross J, Frank M, Welch M, White CM, Rubenstein G, Moseley K, Mark M (1991) Gambling and pathological gambling among university students. Addict Behav 16:517–527
Maccallum F, Blaszczynski A (2002) Pathological gambling and comorbid substance use. Aust NZ J Psychiatry 36:411–415
MacDonald TK, Fong GT, Zanna MP, Martineau AM (2000) Alcohol myopia and condom use: can alcohol intoxication be associated with more prudent behaviour? J Pers Soc Psychol 78:605–619
Malouff J, Schutte N, Wiener K, Brancazio C, Fish D (1993) Important characteristics of warning displays on alcohol containers. J Stud Alcohol 54:457–461
Maylor EA, Rabbitt PMA, Sahgal A, Wright C (1987) Effects of alcohol on speed and accuracy in choice reaction-time and visual search. Acta Psychol 65:147–163
Mazis MB, Morris LA, Swasy JL (1991) An evaluation of the alcohol warning label: initial survey results. J Public Policy Mark 10:229–241
National Health and Medical Research Council (2009) Australian guidelines to reduce health risks from drinking alcohol. Commonwealth of Australia, Canberra
Norstrom T, Skog O (2005) Saturday opening of alcohol retail shops in Sweden: an experiment in two phases. Addiction 100:767–776
Orford J, Morison V, Somers M (1996) Drinking and gambling: a comparison with implications for theories of addiction. Drug Alcohol Rev 15:47–56
Phillips JG, Amrhein PC (1989) Factors influencing wagering in simulated blackjack. J Gamb Behav 5:99–111
Phillips JG, Ogeil RP (2007) Alcohol consumption and computer blackjack. J Gen Psychol 134:333–353
Rajaratnam SMW, Redman JR, Lenné MG (2000) Intoxication and criminal behaviour. Psychiatry Psych Law 7:59–69
Ramirez LF, McCormick RA, Russo AM, Taber JI (1983) Patterns of substance abuse in pathological gamblers undergoing treatment. Addict Behav 8:425–428
Roberts C, Robinson SR (2007) Alcohol concentration and carbonation of drinks: the effect on blood alcohol levels. J Forensic Leg Med 14:398–405
Seidl S, Jensen U, Alt A (2000) The calculation of blood ethanol concentrations in males and females. Int J Legal Med 114:71–77
Shields AL, Caruso JC (2003) Reliability generalization of the alcohol use disorders identification test. Educ Psychol Meas 63:404–413
Smith DI (1986) Comparison of patrons of hotels with early opening and standard hours. Int J Addict 21:155–163
Steele CM, Josephs RA (1990) Alcohol myopia: its prized and dangerous effects. Am Psychol 45:921–933
Stockley CS (2001) The effectiveness of strategies such as health warning labels to reduce alcohol-related harms—an Australian perspective. Int J Drug Policy 12:153–166
Stockwell T (2006) A review of research into the impacts of alcohol warning labels on attitudes and behaviour. Report Commissioned by Health Canada. Centre for Addictions Research of BC, Feb. 2006. University of Victoria, British Columbia, Canada
Thorp E (1966) Beat the dealer. Vintage, New York
Wagenaar WA (1988) Paradoxes of gambling behaviour. LEA, Hillsdale
Welte JW, Barnes GM, Wieczorek WF, Tidwell MC (2004) Simultaneous drinking and gambling: a risk factor for pathological gambling. Subst Use Misuse 39:1405–1422
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the Monash University Strategic Grant Scheme.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phillips, J.G., Ogeil, R.P. Alcohol influences the use of decisional support. Psychopharmacology 208, 603–611 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1762-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-009-1762-6