Abstract
Rationale
Cognitive deficits have been reported in recreational 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, “ecstasy”) users. In rats and other animal species, acute MDMA administration produces an impairment in passive avoidance and other learning tasks. Different studies have shown that this learning deficit is not strictly related to the pronounced serotonin (5-HT) depletion induced by the drug.
Objectives
This study was aimed at determining if acute MDMA administration induces in the rat hippocampus early molecular changes related to memory impairment in a passive avoidance task. The membrane expression of key molecules in memory consolidation, such as the NR1 and NR2B subunits of the N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptor, Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) and protein phosphatase 1 (PP1) was measured. Some of these studies were also performed after 5-HT depletion induced by the 5-HT synthesis inhibitor p-chlorophenylalanine (PCPA).
Methods
Neurochemical studies were performed in rats treated with MDMA and killed 90 min later and also in rats subjected to passive avoidance 30 min after MDMA treatment. Western blotting was used for measuring the levels of NMDA receptor subunits, CAMKII and PP1. Enzyme activity assays were also performed.
Results
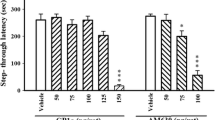
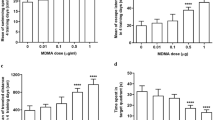
In hippocampal membrane extracts, passive avoidance training increased NMDA receptor NR1 subunit expression as well as CaMKII levels and phosphorylated CaMKII. In untrained rats, MDMA reduced NR1 and NR2B protein levels, membrane CaMKII levels and enzyme activity, and enhanced PP1 levels and activity. In trained rats, MDMA prevented the learning-specific increase in NR1 subunit expression and membrane CaMKII/pCaMKII levels. After pronounced 5-HT depletion by PCPA, MDMA impaired passive avoidance retention to a similar extent and also prevented the training-associated changes in NR1 levels and CaMKII activity.
Conclusions
Diminished function of hippocampal CaMKII and reduced levels of synaptic NMDA receptor subunits appear to be involved in the impairment of passive avoidance learning induced in rats by acute MDMA treatment.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre N, Frechilla D, García-Osta A, Lasheras B, Del Río J (1997) Differential regulation by methylenedioxymethamphetamine of 5-hydroxytryptamine1A receptor density and mRNA expression in rat hippocampus, frontal cortex and brainstem: the role of corticosteroids. J Neurochem 68:1099–1105
Artaiz I, Romero G, Zazpe A, Monge A, Calderó MM, Roca J, Lasheras B, Del Río J (1995) The pharmacology of VA21B7: an atypical 5-HT3 receptor antagonist with anxiolytic-like properties in animal models. Psychopharmacology 117:137–148
Artaiz I, Del Río J, Lasheras B (1996) Impairment of passive avoidance behaviour in rats by MDMA (“ecstasy”). A comparison of acute and chronic treatments. Meth Find Exp Clin Pharmacol 18 (suppl B):160
Barria A, Muller D, Derkach V, Griffith LC, Soderling TR (1997) Regulatory phosphorylation of AMPA-type glutamate receptors by CaM-KII during long-term potentiation. Science 276:2042–2045
Barrionuevo M, Aguirre N, Del Río J, Lasheras B (2000) Serotonergic deficits and impaired passive-avoidance learning by MDEA: a comparison with MDMA. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 65:233–240
Bayer K-U, Koninck PD, Leonard AS, Hell JW, Schulman H (2001) Interaction with the NMDA receptor locks CaMKII in an active conformation. Nature 411:801–805
Bolla KI, McCann UD, Ricaurte GA (1998) Memory impairment in abstinent MDMA (“ecstasy”) users. Neurology 51:1531–1537
Byrne T, Baker LE, Poling A (2000) MDMA and learning: effects of acute and neurotoxic exposure in the rat. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 66:501–508
Cammarota M, Bernabeu R, Levi de Stein M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (1998) Learning-specific, time-dependent increases in hippocampal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II activity and AMPA GluR1 subunit immunoreactivity. Eur J Neurosci 10:2669–2676
Cammarota M, de Stein ML, Paratcha G, Bevilaqua LR, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (2000) Rapid and transient learning-associated increase in NMDA NR1 subunit in the rat hippocampus. Neurochem Res 25:567–572
Clayton DA, Mesches MH, Alvarez E, Bickford PC, Browning MD (2002) A hippocampal NR2B deficit can mimic age-related changes in long-term potentiation and spatial learning in the Fischer 344 rat. J Neurosci 22:3628–3637
Cole JC, Sumnall HR (2003) The pre-clinical behavioural pharmacology of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA). Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:199–217
Dunah AW, Wang Y, Yasuda RP, Kameyama K, Huganir RL, Wolfe BB, Standaert DG (2000) Alterations in subunit expression, composition and phosphorylation of striatal N-methyl-D-aspartate glutamate receptors in a rat 6-hydroxydopamine model of Parkinson’s disease. Mol Pharmacol 57:342–352
Endo S, Zhou X, Connor J, Wang B, Shenolikar S (1996) Multiple structural elements define the specificity of recombinant human inhibitor-1 as a protein phosphatase-1 inhibitor. Biochemistry 35:5220–5228
Fink CC, Meyer T (2002) Molecular mechanisms of CaMKII activation in neuronal plasticity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:293–299
Frechilla D, García-Osta A, Del Río J (1999) Effect of p-chloroamphetamine and 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine on CRE- and TRE-binding activity in rat frontal cortex and hippocampus. Soc Neurosci Abstr 174
Frederick DL, Ali SF, Slikker W, Gilliam MP, Allen RR, Paule MG (1995) Behavioral and neurochemical effects of chronic methylenedioxymethamphetamine treatment in rhesus monkeys. Neurotoxicol Teratol 17:531–543
Genoux D, Haditsch U, Knobloch M, Michalon A, Storm D, Mansuy IM (2002) Protein phosphatase 1 is a molecular constraint on learning and memory. Nature 418:970–975
Green AR, Mechan AO, Elliott JM, O’Shea E, Colado MI (2003) The pharmacology and clinical pharmacology of 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, “ecstasy”). Pharmacol Rev 55:463–508
Hudmon A, Schulman H (2002) Neuronal Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: the role of structure and autoregulation in cellular function. Annu Rev Biochem 71:473–510
Izquierdo I, Medina JH (1997) Memory formation: the sequence of biochemical events in the hippocampus and its connection to activity in other brain regions. Neurobiol Learn Mem 68:285–316
Jequier E, Lovenberg W, Sjoerdsma A (1967) Tryptophan hydroxylase inhibition: the mechanism by which p-chlorophenylalanine depletes rat brain serotonin. Mol Pharmacol 3:274–278
Leonard AS, Lim IA, Hemsworth DE, Horne MC, Hell JW (1999) Calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II is associated with the N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:3239–3244
Loftis JM, Janowsky A (2003) The N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit NR2B: localization, functional properties, regulation and clinical implications. Pharmacol Ther 97:55–85
Lyles J, Cadet JL (2003) Methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, ecstasy) neurotoxicity: cellular and molecular mechanisms. Brain Res Rev 42:155–168
McCann UD, Mertl M, Eligulashvili V, Ricaurte GA (1999) Cognitive performance in 3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine (MDMA, “ecstasy”) users: a controlled study. Psychopharmacology 143:417–425
Misane I, Johansson C, Ögren SV (1998) Analysis of the 5-HT1A receptor involvement in passive avoidance in the rat. Br J Pharmacol 125:499–509
Morgan MJ (1999) Memory deficits associated with recreational use of “ecstasy” (MDMA). Psychopharmacology 141:30–36
Nihei MK, Desmond NL, McGlothan JL, Kuhlman AC, Guilarte TR (2000) N-Methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunit changes are associated with lead-induced deficits of long-term potentiation and spatial learning. Neuroscience 99:233–242
Otano A, García-Osta A, Ballaz S, Frechilla D, Del Río J (1999) Facilitation by 8-OH-DPAT of passive avoidance performance in rats after inactivation of 5-HT1A receptors. Br J Pharmacol 128:1691–1698
Pérez-Otaño I, Herrero MT, Oset C, De Ceballos ML, Luquin MR, Obeso JA, Del Río J (1991) Extensive loss of brain dopamine and serotonin induced by chronic administration of MPTP in the marmoset. Brain Res 567:127–132
Riedel G, Platt B, Micheau J (2003) Glutamate receptor function in learning and memory. Behav Brain Res 140:1–47
Rodgers J (2000) Cognitive performance amongst recreational users of “ecstasy”. Psychopharmacology 151:19–24
Santucci AC, Knott PJ, Haroutunian V (1996) Excessive serotonin release, not depletion, leads to memory impairments in rats. Eur J Pharmacol 295:7–17
Shen K, Meyer T (1999) Dynamic control of CaMKII translocation and localization in hippocampal neurons by NMDA receptor stimulation. Science 284:162–166
Shobe J (2002) The role of PKA, CaMKII, and PKC in avoidance conditioning: permissive or instructive? Neurobiol Learn Mem 77:291–312
Suemaru J, Akiyama K, Tanabe Y, Kuroda S (2000) Methamphetamine decreases calcium-calmodulin dependent protein kinase II activity in discrete rat brain regions. Synapse 36:155–166
Taffe MA, Davis SA, Yuan J, Schroeder R, Hadzidimitriou G, Parsons LH, Ricaurte GA, Gold LH (2002) Cognitive performance of MDMA-treated rhesus monkeys: sensitivity to serotonergic challenge. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:993–1005
Tang Y-P, Shimizu E, Dube GR, Rampon C, Kerchner GA, Zhuo M, Liu G, Tsien JZ (1999) Genetic enhancement of learning and memory in mice. Nature 401:63–69
Thomas KL, Davis S, Laroche S, Hunt SP (1994) Regulation of the expression of NR1 NMDA glutamate receptor subunits during hippocampal LTP. Neuroreport 6:119–123
Verkes RJ, Gijsman HJ, Pieters MS, Schoemaker RC, de Visser S, Kuijpers M, Pennings EJ, de Bruin D, Van de Wijngaart G, Van Gerven JM, Cohen AF (2001) Cognitive performance and serotonergic function in users of ecstasy. Psychopharmacology 153:196–202
Williams JM, Guévremont D, Kennard JTT, Mason-Parker SE, Tate WP, Abraham WC (2003) Long-term regulation of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor subunits and associated synaptic proteins following hippocampal synaptic plasticity. Neuroscience 118:1003–1013
Yoshimura Y, Sogawa Y, Yamauchi T (1999) Protein phosphatase 1 is involved in the dissociation of Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II from postsynaptic densities. FEBS Lett 446:239–242
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from EC (QLG3-CT-2002-00809) and MCyT, Spain (BFI-2001-1602). We thank Gobierno de Navarra for a fellowship to one of us (S.M.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moyano, S., Frechilla, D. & Del Río, J. NMDA receptor subunit and CaMKII changes in rat hippocampus induced by acute MDMA treatment: a mechanism for learning impairment. Psychopharmacology 173, 337–345 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1816-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00213-004-1816-8