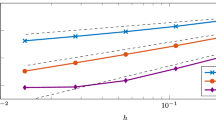
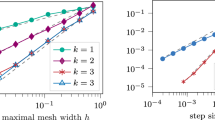
Abstract
We apply mixed finite element approximations to the first-order form of the acoustic wave equation. The semidiscrete method exactly conserves the system energy. A fully discrete method employing the symplectic Euler time method in time exactly conserves a positive-definite pertubed energy functional that is equivalent to the actual energy under a CFL condition. In addition to proving optimal-order \(L^\infty (L^2)\) estimates, we also develop a bootstrap technique that allows us to derive stability and error bounds for the time derivatives and divergence of the vector variable beyond the standard under some additional regularity assumptions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Geveci, T.: On the application of mixed finite element methods to the wave equation. Math. Model. Numer. Anal. 22, 243–250 (1988)
Glowinski, R., Rossi, T.: A mixed formulation and exact controllability approach for the computation of the periodic solutions of the scalar wave equation. (i): controllability problem formulation and related iterative solution. Comptes Rendus Math. 343(7), 493–498 (2006)
Cowsar, L.C., Dupont, T.F., Wheeler, M.F.: A priori estimates for mixed finite element methods for the wave equation. Comput. Methods Appl. Mech. Eng. 82(1–3), 205–222 (1990)
Jenkins, E.W., Rivière, B., Wheeler, M.F.: A priori error estimates for mixed finite element approximations of the acoustic wave equation. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 40(5), 1698–1715 (2002)
Jenkins, E.W.: Numerical solution of the acoustic wave equation using Raviart–Thomas elements. J. Comput. Appl. Math. 206(1), 420–431 (2007)
Chung, E.T., Engquist, B.: Optimal discontinuous Galerkin methods for the acoustic wave equation in higher dimensions. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47, 3820–3848 (2009)
Boffi, D., Buffa, A., Gastaldi, L.: Convergence analysis for hyperbolic evolution problems in mixed form. Tech. Rep., IMATI Technical Report 17-PV, IMATI del CNR, Pavia, Italy (2005)
Arnold, D.N., Falk, R.S., Winther, R.: Finite element exterior calculus, homological techniques, and applications. Acta Numer. 15, 1–155 (2006)
Bochev, P., Hyman, M.: Principles of mimetic discretizations. In: Arnold, D., Bochev, P., Lehoucq, R., Nicolaides, R., Shashkov, M. (eds.) Compatible Spatial Discretizations, IMA, vol. 142, pp. 89–119. Springer, New York (2006)
Rieben, R., Rodrigue, G., White, D.: A high order mixed vector finite element method for solving the time dependent maxwell equations on unstructured grids. J. Comput. Phys. 204(2), 490–519 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.jcp.2004.10.030. http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0021999104004255
Rieben, R., White, D., Rodrigue, G.: High-order symplectic integration methods for finite element solutions to time dependent Maxwell equations. IEEE Trans. Antennas Propag. 52(8), 2190–2195 (2004)
Brenner, S.C., Scott, L.R.: The mathematical theory of finite element methods. In: Texts in Applications Mathematics, vol. 15, 3rd edn. Springer, New York (2008)
Nédélec, J.C.: Mixed finite elements in \({\bf R}^{3}\). Numer. Math. 35(3), 315–341 (1980)
Raviart, P.A., Thomas, J.M.: A mixed finite element method for 2nd order elliptic problems. In: Mathematical Aspects of Finite Element Methods [Proc. Conf., Consiglio Naz. delle Ricerche (C.N.R.), Rome, 1975]. Lecture Notes in Math., vol. 606, pp. 292–315. Springer, Berlin (1977)
Douglas, J. Jr, Roberts, J.E.: Global estimates for mixed methods for second order elliptic equations. Math. Comput 44(169), 39–52 (1985)
Arnold, D.N., Boffi, D., Falk, R.S.: Quadrilateral \(H({{\rm div}})\) finite elements. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 42(6), 2429–2451 (2005)
Bochev, P.B., Ridzal, D.: Rehabilitation of the lowest-order Raviart–Thomas element on quadrilateral grids. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 47(1), 487–507 (2008)
Brezzi, F., Fortin, M.: Mixed and Hybrid Finite Element Methods. Springer, New York (1991)
Hairer, E., Lubich, C., Wanner, G.: Geometric numerical integration: structure-preserving algorithms for ordinary differential equations. In: Springer Series in Computational Mathematics, vol. 31. Springer, New York (2006)
de Vogelaere, R.: Methods of integration which preserve the contact transformation property of the hamiltonian equations. Tech. Rep. 4, University of Notre Dame Department of Mathematics (1956)
Logg, A.: Multi-adaptive Galerkin methods for ODE I. SIAM J. Sci. Comput. 24, 1879–1902 (2003)
Budd, C.J., Piggott, M.D.: Geometric integration and its applications. Handb. Numer. Anal. 11, 35–139 (2003)
Logg, A., Mardal, K.A., Wells, G.N.: Automated Solution of Differential Equations by the Finite Element Method: The FEniCS Book, vol. 84. Springer, New York (2012)
Hientzsch, B.: Fast solvers and Schwarz preconditioners for spectral Nédélec elements for a model problem in \(H({{\rm curl}})\). In: Domain Decomposition Methods in Science and Engineering, pp. 427–433 (electronic). Natl. Auton. Univ. Mex., México (2003)
Hientzsch, B.: Domain decomposition preconditioners for spectral Nédélec elements in two and three dimensions. In: Domain Decomposition Methods in Science and Engineering. Lect. Notes Comput. Sci. Eng., vol. 40, pp. 597–604. Springer, Berlin (2005)
Weiser, A., Wheeler, M.F.: On convergence of block-centered finite differences for elliptic problems. SIAM J. Numer. Anal. 25(2), 351–375 (1988). http://www.jstor.org/stable/2157321
Wheeler, M.F., Yotov, I.: A cell-centered finite difference method on quadrilaterals. In: Arnold, D., Bochev, P., Lehoucq, R., Nicolaides, R., Shashkov, M. (eds.) Compatible Spatial Discretizations, IMA, vol. 142, pp. 189–207. Springer, New York (2006)
Acknowledgments
This was was supported by the National Science Foundation under Award Number 1117794, and the first author wishes to thank Prof. Roland Glowinski for valuable pointers to the relevant literature and Dr. Colin Cotter for helpful discussions regarding the Hamiltonian nature of the mixed form.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kirby, R.C., Kieu, T.T. Symplectic-mixed finite element approximation of linear acoustic wave equations. Numer. Math. 130, 257–291 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-014-0667-4
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00211-014-0667-4