Abstract
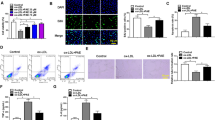
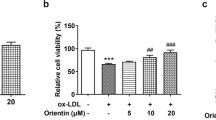
As a cardiovascular disease, coronary heart disease (CHD) is characterized by poor prognosis and increasing morbidity and mortality rates. Echinacoside (ECH) can protect against multiple cardiovascular diseases due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. However, the role of ECH in CHD remains unclear. In ECH-treated human coronary artery endothelial cells (HCAECs), cell viability, NO production, endothelial nitric oxide synthase (eNOS) expression, and angiogenesis ability were detected using cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) assay, diaminofluorescein-FM diacetate (DAF-FM DA) staining, western blot, and tube formation assay, respectively. The activities of oxidative stress markers were detected using dichloro-dihydro-fluorescein diacetate (DCFH-DA) assay and corresponding assay kits. Cell apoptosis was detected utilizing flow cytometry and caspase3 assay. Western blot was used to detect the expressions of Nrf2/PPARγ signaling pathway- and mitochondrial dynamics-related proteins. Mitochondrial membrane potential and mitochondrial fusion and fission were detected using JC-1 staining and immunofluorescence (IF) assay. In this study, ECH was found to revive the viability, ameliorate the endothelial dysfunction, suppress oxidative stress, and inhibit the apoptosis in ox-LDL-induced HCAECs via activating Nrf2/PPARγ signaling pathway, which were all abolished following the treatment of Nrf2 inhibitor ML385. It was also identified that ECH regulated mitochondrial fusion-fission balance in ox-LDL-induced HCAECs through the activation of Nrf2/PPARγ signaling pathway. In summary, ECH activated Nrf2/PPARγ signaling pathway to regulate mitochondrial fusion-fission balance, thereby improving ox-LDL-induced dysfunction of HCAECs.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The analyzed data sets generated during the present study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Albarrati AM et al (2018) Effectiveness of low to moderate physical exercise training on the level of low-density lipoproteins: a systematic review. Biomed Res Int 2018:5982980
Archer SL (2013) Mitochondrial dynamics–mitochondrial fission and fusion in human diseases. N Engl J Med 369(23):2236–2251
Chandran R et al (2018) A combination antioxidant therapy to inhibit NOX2 and activate Nrf2 decreases secondary brain damage and improves functional recovery after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 38(10):1818–1827
Cheng Z (2022) FoxO transcription factors in mitochondrial homeostasis. Biochem J 479(4):525–536
Chuang HW et al (2022) Echinacoside exhibits antidepressant-like effects through AMPAR-Akt/ERK-mTOR pathway stimulation and BDNF expression in mice. Chin Med 17(1):9
De Hert M, Detraux J, Vancampfort D (2018) The intriguing relationship between coronary heart disease and mental disorders. Dialogues Clin Neurosci 20(1):31–40
Forte M et al (2021) The role of mitochondrial dynamics in cardiovascular diseases. Br J Pharmacol 178(10):2060–2076
Gao S et al (2017) Association between circulating oxidized LDL and atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Can J Cardiol 33(12):1624–1632
Garcia-Rios A, Ordovas JM (2022) Chronodisruption and cardiovascular disease. Clin Investig Arterioscler 34(Suppl 1):S32-s37
Gu C et al (2021) Regulation of mitochondrial dynamics by aerobic exercise in cardiovascular diseases. Front Cardiovasc Med 8:788505
He X, Liu J, Zang WJ (2022) Mitochondrial homeostasis and redox status in cardiovascular diseases: protective role of the vagal system. Free Radic Biol Med 178:369–379
Hu Y et al (2020) Downregulation of microRNA-106a-5p alleviates ox-LDL-mediated endothelial cell injury by targeting STAT3. Mol Med Rep 22(2):783–791
Hu Q et al (2022) β-Caryophyllene suppresses ferroptosis induced by cerebral ischemia reperfusion via activation of the NRF2/HO-1 signaling pathway in MCAO/R rats. Phytomedicine 102:154112
Huang X et al (2022) Antioxidation function of EGCG by activating Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in mice with coronary heart disease. Contrast Media Mol Imaging 2022:8639139
Jain KK (2017) Personalized management of cardiovascular disorders. Med Princ Pract 26(5):399–414
Kratzer A, Giral H, Landmesser U (2014) High-density lipoproteins as modulators of endothelial cell functions: alterations in patients with coronary artery disease. Cardiovasc Res 103(3):350–361
Li J et al (2022) Therapeutic potential and molecular mechanisms of echinacoside in neurodegenerative diseases. Front Pharmacol 13:841110
Li F et al (2022) KLF9 aggravates streptozotocin-induced diabetic cardiomyopathy by inhibiting PPARγ/NRF2 signalling. Cells 11(21):3393
Li Y et al (2023) Echinacoside ameliorates 5-fluorouracil-induced endothelial injury and senescence through SIRT1 activation. Int Immunopharmacol 120:110279
Liu J et al (2018) Echinacoside, an inestimable natural product in treatment of neurological and other disorders. Molecules 23(5):1213
Liu L et al (2022) Procyanidin B2 ameliorates endothelial dysfunction and impaired angiogenesis via the Nrf2/PPARγ/sFlt-1 axis in preeclampsia. Pharmacol Res 177:106127
Ni Y et al (2021) Echinacoside reverses myocardial remodeling and improves heart function via regulating SIRT1/FOXO3a/MnSOD axis in HF rats induced by isoproterenol. J Cell Mol Med 25(1):203–216
Ni Y et al (2022) Echinacoside inhibited cardiomyocyte pyroptosis and improved heart function of HF rats induced by isoproterenol via suppressing NADPH/ROS/ER stress. J Cell Mol Med 26(21):5414–5425
Ong SB, Hausenloy DJ (2010) Mitochondrial morphology and cardiovascular disease. Cardiovasc Res 88(1):16–29
Parra V et al (2011) The complex interplay between mitochondrial dynamics and cardiac metabolism. J Bioenerg Biomembr 43(1):47–51
Reglero-Real N et al (2016) Endothelial cell junctional adhesion molecules: role and regulation of expression in inflammation. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 36(10):2048–2057
Shao Y et al (2022) Echinacoside ameliorates cyclophosphamide-induced bladder damage in mice. J Med Food 25(7):722–731
Shi L et al (2021) MiR-339 is a potential biomarker of coronary heart disease to aggravate oxidative stress through Nrf2/FOXO3 targeting Sirt2. Ann Palliat Med 10(3):2596–2609
Sun Y et al (2021) Knockdown of lncRNA ENST00000609755.1 confers protection against early oxLDL-induced coronary heart disease. Front Cardiovasc Med 8:650212
Tang Y et al (2016) ox-LDL induces endothelial dysfunction by promoting Arp2/3 complex expression. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 475(2):182–188
Tang Z et al (2021) Mangiferin prevents the impairment of mitochondrial dynamics and an increase in oxidative stress caused by excessive fluoride in SH-SY5Y cells. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 35(4):e22705
Toda C, Diano S (2014) Mitochondrial UCP2 in the central regulation of metabolism. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 28(5):757–764
Trpkovic A et al (2015) Oxidized low-density lipoprotein as a biomarker of cardiovascular diseases. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 52(2):70–85
Vásquez-Trincado C et al (2016) Mitochondrial dynamics, mitophagy and cardiovascular disease. J Physiol 594(3):509–525
Wei W et al (2019) Echinacoside alleviates hypoxic-ischemic brain injury in neonatal rat by enhancing antioxidant capacity and inhibiting apoptosis. Neurochem Res 44(7):1582–1592
Wu L et al (2020) Therapeutic potential of phenylethanoid glycosides: a systematic review. Med Res Rev 40(6):2605–2649
Wu Y et al (2021) Effect of nicorandil combined with trimetazidine on miR-223-3p and NRF2 expression in patients with coronary heart disease. Am J Transl Res 13(5):4804–4811
Yang K, Song H, Yin D (2021) PDSS2 inhibits the ferroptosis of vascular endothelial cells in atherosclerosis by activating Nrf2. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 77(6):767–776
Yang Y et al (2022) Knockdown of lncRNA H19 alleviates ox-LDL-induced HCAECs inflammation and injury by mediating miR-20a-5p/HDAC4 axis. Inflamm Res 71(9):1109–1121
Zhang X, Hao Y (2020) Beneficial effects of echinacoside on diabetic cardiomyopathy in diabetic Db/Db mice. Drug Des Devel Ther 14:5575–5587
Zhang Z et al (2021) Pioglitazone inhibits diabetes-induced atrial mitochondrial oxidative stress and improves mitochondrial biogenesis, dynamics, and function through the PPAR-γ/PGC-1α signaling pathway. Front Pharmacol 12:658362
Zhou L et al (2020) Echinacoside attenuates inflammatory response in a rat model of cervical spondylotic myelopathy via inhibition of excessive mitochondrial fission. Free Radic Biol Med 152:697–714
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Xiandi Qiu and Yuxing Feng conceived the experiments. Xiandi Qiu performed the experiments. Xiandi Qiu analyzed the data. Xiandi Qiu and Yuxing Feng confirmed the authenticity of all the raw data. Both authors have read and approved the final manuscript. The authors declare that all data were generated in-house and that no paper mill was used.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Qiu, X., Feng, Y. Echinacoside activates Nrf2/PPARγ signaling pathway to modulate mitochondrial fusion-fission balance to ameliorate ox-LDL-induced dysfunction of coronary artery endothelial cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 397, 9767–9776 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-03233-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-024-03233-1