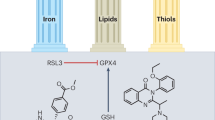
Abstract
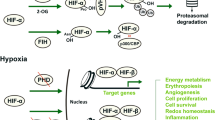
Renal I/R injury is a severe medical condition contributing to acute kidney injury (AKI), leading to rapid kidney dysfunction and high mortality rates. It is generally observed during renal transplantation, shock, trauma, and urologic and cardiovascular surgery, for which there is no effective treatment. Cell death and damage are commonly linked to I/R. Cell death triggered by iron-dependent lipid peroxidation, such as ferroptosis, has been demonstrated to have a significant detrimental effect in renal IRI models, making it a new type of cell death currently being researched. Ferroptosis is a nonapoptotic type of cell death that occurs when free iron enters the cell and is a critical component of many biological processes. In ferroptosis-induced renal I/R injury, iron chelators such as Deferasirox, Deferiprone, and lipophilic antioxidants are currently suppressed lipid peroxidation Liproxstatin-1 (Lip-1), Ferrostatin-1 along with antioxidants like vitamin and quercetin. Ferroptosis has been considered a potential target for pharmaceutical intervention to alleviate renal IRI-associated cell damage. Thus, this review emphasized the role of ferroptosis and its inhibition in renal IRI. Also, Pharmacological modulation of ferroptosis mechanism in renal I/R injury has been conferred.

Graphical abstract


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
References
Adam AC, Bornhövd C, Prokisch H, Neupert W (2006) Hell K The Nfs1 interacting protein Isd11 has an essential role in Fe/S cluster biogenesis in mitochondria. EMBO Rep 25(1):174–183. https://doi.org/10.1038/2Fsj.emboj.7600905
Adedoyin O, Boddu R, Traylor A et al (2018) Heme oxygenase-1 mitigates ferroptosis in renal proximal tubule cells. Am J Physiol 314(5):F702–F714. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00044.2017
Angeli JPF, Proneth B, Hammond VJ et al (2014) Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in a therapeutically relevant mechanism. Free Radic Biol Med 76:S77–S78. https://doi.org/10.1016/2Fj.freeradbiomed.2014.10.276
Aoyama K, Watabe M, Nakaki T (2008) Regulation of neuronal glutathione synthesis. J Pharmacol Sci 0811120169-. https://doi.org/10.1254/jphs.08R01CR.
Bagayoko S, Meunier E (2021) Emerging roles of ferroptosis in infectious diseases. FEBS Lett. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.16244
Barayuga SM, Pang X, Andres MA, Panee J (2013) Bellinger FP (2013) Methamphetamine decreases levels of glutathione peroxidases 1 and 4 in SH-SY5Y neuronal cells: protective effects of selenium. Neurotoxicology 37:240–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2013.05.009
Bersuker K, Hendricks JM, Li Z et al (2019) The CoQ oxidoreductase FSP1 acts parallel to GPX4 to inhibit ferroptosis. Nature 575(7784):688–692. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1705-2
Bertrand RL (2017) Iron accumulation, glutathione depletion, and lipid peroxidation must occur simultaneously during ferroptosis and are mutually amplifying events. Med Hypotheses 101:69–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mehy.2017.02.017
Brigelius-Flohé R, Maiorino M (2013) Glutathione peroxidases. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj 1830(5):3289–3303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbagen.2012.11.020
Capelletti MM, Manceau H, Puy H, Peoc’h K (2020) Ferroptosis in liver diseases: an overview. Int J Mol Sci 21(14):4908. https://www.mdpi.com/1422-0067/21/14/4908.
Cardoso BR, Hare DJ, Bush AI, Roberts BR (2017) Glutathione peroxidase 4: a new player in neurodegeneration? Mol Psychiatry 22(3):328–335. https://doi.org/10.1038/mp.2016.196
Carvalho EBTD, Melo ILPD, Mancini-Filho J (2010) Chemical and physiological aspects of isomers of conjugated fatty acids. Food Sci Tech 30:295–307. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0101-20612010000200002
Casañas-Sánchez V, Pérez JA, Fabelo N, Quinto-Alemany D, Diaz ML (2015) Docosahexaenoic (DHA) modulates phospholipid-hydroperoxide glutathione peroxidase (Gpx4) gene expression to ensure self-protection from oxidative damage in hippocampal cells. Front Physiol 6:203. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2015.00203
Casserly LF, Dember LM (2003) Thrombosis in end-stage renal disease. In Semin Dial (Vol. 16, No. 3, pp. 245–256). Malden, USA: Blackwell Science Inc. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1525-139X.2003.16048.x.
Chen X, Li J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Tang D (2002) Ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Autophagy 17(9):2054–2081. https://doi.org/10.1080/15548627.2020.1810918
Chen X, Yu C, Kang R, Tang D (2020) Iron metabolism in ferroptosis. Front Cell Dev Biol 2020:1089. https://doi.org/10.3389/2Ffcell.2020.590226
Chen J, Yang L, Geng L et al (2021) Inhibition of Acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 4 facilitates neurological recovery after stroke by regulation ferroptosis. Front Cell Neurosci 15:93. https://doi.org/10.3389/fncel.2021.632354
Chen Y, Liu S, Li J,et al (2020b)The latest view on the mechanism of ferroptosis and its research progress in spinal cord injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2020b. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/6375938
Choi N, Whitlock R, Klassen J et al (2019) Early intraoperative iron-binding proteins are associated with acute kidney injury after cardiac surgery. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 157(1):287–297. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtcvs.2018.06.091
Cicenas J, Tamosaitis L, Kvederaviciute K et al (2017) KRAS, NRAS and BRAF mutations in colorectal cancer and melanoma. Med Oncol 34(2):1–1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-016-0879-9
Conrad M, Sato H (2012) The oxidative stress-inducible cystine/glutamate antiporter, system xc−: cystine supplier and beyond. Amino Acids 42(1):231–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00726-011-0867-5
Diallo I, Ho J, Laffont B, Laugier J et al (2021) Altered microRNA transcriptome in cultured human liver cells upon infection with ebola virus. Int J Mol Sci 22(7):3792. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051137
Dixon SJ, Stockwell BR (2019) The hallmarks of ferroptosis. Annu Rev Cancer Biol 3:35–54. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-cancerbio-030518-055844
Dixon SJ, Lemberg KM, Lamprecht MR et al (2012) Ferroptosis: an iron-dependent form of nonapoptotic cell death. Cell J 149(5):1060–1072. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.03.042
Doll S, Proneth B, Tyurina YY et al (2017) ACSL4 dictates ferroptosis sensitivity by shaping cellular lipid composition. Nat Chem Biol 13(1):91–98. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2239
Doll S, Freitas FP, Shah R et al (2019) FSP1 is a glutathione-independent ferroptosis suppressor. Nature 575(7784):693–698. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-1707-0
Drobna M, Szarzyńska B, Jaksik R, Sędek Ł, Kuchmiy A, Taghon T, Van Vlierberghe P, Szczepański T, Witt M, Dawidowska M (2020) hsa-miR-20b-5p and hsa-miR-363-3p affect expression of PTEN and BIM tumor suppressor genes and modulate survival of T-ALL cells in vitro. Cells 9(5):1137. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells9051137
Fang X, Cai Z, Wang H et al (2020) Loss of cardiac ferritin H facilitates cardiomyopathy via Slc7a11-mediated ferroptosis. Circ Res 127(4):486–501. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.120.316509
Finazzi D, Arosio P (2014) Biology of ferritin in mammals: an update on iron storage, oxidative damage and neurodegeneration. Arch Toxicol 88(10):1787–1802. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-014-1329-0
Franklin CC, Backos DS, Mohar I et al (2009) Structure, function, and post-translational regulation of the catalytic and modifier subunits of glutamate cysteine ligase. Mol Asp Med 30(1–2):86–98. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2008.08.009
Frei B, Kim MC, Ames BN (1990) Ubiquinol-10 is an effective lipid-soluble antioxidant at physiological concentrations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87(12):4879–4883. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.87.12.4879
Friedmann Angeli JP, Schneider M, Proneth B et al (2014) Inactivation of the ferroptosis regulator Gpx4 triggers acute renal failure in mice. Nat Cell Biol 16(12):1180–1191. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncb3064
Fujii J, Homma T, Kobayashi S (2020) Ferroptosis caused by cysteine insufficiency and oxidative insult. Free Radic Res 54(11–12):969–980. https://doi.org/10.1080/10715762.2019.1666983
Ghini F, Rubolino C, Climent M, Simeone I, Marzi MJ, Nicassio F (2018) Endogenous transcripts control miRNA levels and activity in mammalian cells by target-directed miRNA degradation. Nat Commun 9(1):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-05182-9
Gryzik M, Asperti M, Denardo A, Arosio P, Poli M (2021) NCOA4-mediated ferritinophagy promotes ferroptosis induced by erastin, but not by RSL3 in HeLa cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1868(2):118913. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118913
Gupta A, Khan H, Kaur A, Singh TG (2021) Novel targets explored in the treatment of alcohol withdrawal syndrome. CNS Neurol Disord - Drug Targets 20(2):158–173. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871527319999201118155721
Haase M, Bellomo R, Haase-Fielitz A (2010) Novel biomarkers, oxidative stress, and the role of labile iron toxicity in cardiopulmonary bypass-associated acute kidney injury. J Am Coll Cardiol 55(19):2024–2033. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2009.12.046
Han C, Liu Y, Dai R, Ismail N, Su W, Li B (2020) Ferroptosis and its potential role in human diseases. Front Pharmacol 11:239. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00239
Hatcher HC, Singh RN, Torti FM, Torti SV (2009) Synthetic and natural iron chelators: therapeutic potential and clinical use. Future Med Chem 1(9):1643–1670. https://doi.org/10.4155/fmc.09.121
Hayashima K, Kimura I, Katoh H (2021) Role of ferritinophagy in cystine deprivation-induced cell death in glioblastoma cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 539:56–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2020.12.075
He L, Liu YY, Wang K et al (2021) Tanshinone IIA protects human coronary artery endothelial cells from ferroptosis by activating the NRF2 pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 575:1–7. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2020.586578
Hinman A, Holst CR, Latham JC et al (2018) Vitamin E hydroquinone is an endogenous regulator of ferroptosis via redox control of 15-lipoxygenase. PLoS One 13(8):e0201369. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0201369
Hirschhorn T, Stockwell BR (2019) The development of the concept of ferroptosis. Free Radic Biol Med 133:130–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/2Fj.freeradbiomed.2018.09.043
Ho J, Reslerova M, Gali B et al (2011) Urinary hepcidin-25 and risk of acute kidney injury following cardiopulmonary bypass. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 6(10):2340–2346. https://doi.org/10.2215/cjn.01000211
Hou W, Xie Y, Song X, et al (2016) Autophagy promotes ferroptosis by degradation of ferritin. Autophagy 12(8):1425–8. https://doi.org/10.1080/2F15548627.2016.1187366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-013-1110-9
Hu Z, Zhang H, Yang SK, Wu X, He D, Cao K, Zhang W (2019) Emerging role of ferroptosis in acute kidney injury. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1155/2F2019%2F8010614
Ighodaro OM, Akinloye OA (2018) First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alexandria J Med 54(4):287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajme.2017.09.001
Ingold I, Berndt C, Schmitt S et al (2018) Selenium utilization by GPX4 is required to prevent hydroperoxide-induced ferroptosis. Cell J 172(3):409–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.11.048
Jiang X, Stockwell BR, Conrad M (2021) Ferroptosis: mechanisms, biology and role in disease. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 22(4):266–282. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-020-00324-8
Jomova K, Valko M (2011) Importance of iron chelation in free radical-induced oxidative stress and human disease. Curr Pharm Des 17(31):3460–3473. https://doi.org/10.2174/138161211798072463
Kajarabille N, Latunde-Dada GO (2019) Programmed cell-death by ferroptosis: antioxidants as mitigators. Int J Mol Sci 20(19):4968. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20194968
Kalra P, Khan H, Kaur A, Singh TG (2022) Mechanistic insight on autophagy modulated molecular pathways in cerebral ischemic injury: from preclinical to clinical perspective. Neurochem Res 7:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03500-0
Karatas H, Erdener SE, Gursoy-Ozdemir Y et al (2013) Spreading depression triggers headache by activating neuronal Panx1 channels. J Sci 339(6123):1092–1095. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1231897
Khan H, Kashyap A, Kaur A, Singh TG (2020) Pharmacological postconditioning: a molecular aspect in ischemic injury. J Pharm Pharmacol 72(11):1513–1527. https://doi.org/10.1111/jphp.13336
Khan H, Bangar A, Grewal AK, Bansal P, Singh TG (2022) Caspase-mediated regulation of the distinct signaling pathways and mechanisms in neuronal survival. Int Immunopharmacol 110:108951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2022.108951
Khan H, Garg N, Singh TG, Kaur A, Thapa K (2022b) Calpain inhibitors as potential therapeutic modulators in neurodegenerative diseases. Neurochem Res 1-25. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11064-021-03521-9
Khan H, Sharma K, Kumar A, Kaur A, Singh TG (2022c) Therapeutic implications of cyclooxygenase (COX) inhibitors in ischemic injury. Inflamm Res 1-6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-022-01546-6
Kihara A (2012) Very long-chain fatty acids: elongation, physiology and related disorders. J Biochem 152(5):387–395. https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvs105
Kim S, Kang SW, Joo J, Han SH et al (2021) Correction: characterization of ferroptosis in kidney tubular cell death under diabetic conditions. Cell Death Dis 12(4):1–1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-021-03667-y
Lewerenz J, Hewett SJ, Huang Y et al (2013) The cystine/glutamate antiporter system xc− in health and disease: from molecular mechanisms to novel therapeutic opportunities. Antioxid Redox Signal 18(5):522–55. https://doi.org/10.1089/2Fars.2011.4391
Li J, Cao F, Yin HL,et al (2020) Ferroptosis: past, present and future. Cell Death Dis 11(2). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-2298-2
Li D, Li Y (2020) The interaction between ferroptosis and lipid metabolism in cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 5(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-020-00216-5
Liang C, Zhang X, Yang M et al (2019) Recent progress in ferroptosis inducers for cancer therapy. J Adv Mater 31(51):1904197. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201904197
Lin Z, Liu J, Kang R, Yang M, Tang D (2021) Lipid metabolism in ferroptosis. Front Biol (beijing) 5(8):2100396. https://doi.org/10.1002/adbi.202100396
Linkermann A, Chen G, Dong G, Kunzendorf U, Krautwald S, Dong Z (2014) Regulated cell death in AKI. J Am Soc Nephrol 25(12):2689–2701
Linkermann A, Skouta R, Himmerkus N et al (2014) Synchronized renal tubular cell death involves ferroptosis. PNAS USA 111(47):16836–16841. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1415518111
Liu J, Kuang F, Kroemer G, Klionsky DJ, Kang R, Tang D (2020) Autophagy-dependent ferroptosis: machinery and regulation. Cell Chem Biol 27(4):420–435. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chembiol.2020.02.005
Liu J, Zhang C, Wang J, Hu W, Feng Z (2020) The regulation of ferroptosis by tumor suppressor p53 and its pathway. Int J Mol Sci 21(21):8387. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21218387
Malek M, Nematbakhsh M (2015) Renal ischemia/reperfusion injury; from pathophysiology to treatment. J renal inj prev 4(2):20. https://doi.org/10.12861/jrip.2015.06
Mao XY, Jin MZ, Li Q et al (2019) Lysyl oxidase promotes neuronal ferroptosis exacerbating seizure-induced hippocampal damage. BioRxiv 1:839852. https://doi.org/10.1101/839852
Matzanke BF, Winkelmann G, Carrano C (1997) Iron storage in microorganisms. Transition metals in microbial metabolism. Harwood Acad Publishers GmbH Amst Neth 23:117–158
Mohammad G, Matakidou A, Robbins PA, Lakhal-Littleton S (2021) The kidney hepcidin/ferroportin axis controls iron reabsorption and determines the magnitude of kidney and systemic iron overload. Kidney Int 100(3):559–569. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2021.04.034
Mullen PJ, Yu R, Longo J, Archer MC, Penn LZ (2016) The interplay between cell signalling and the mevalonate pathway in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 16(11):718–731. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.76
Müller T, Dewitz C, Schmitz J et al (2017) Necroptosis and ferroptosis are alternative cell death pathways that operate in acute kidney failure. Cell Mol Life Sci 74(19):3631–3645. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-017-2547-4
Nath KA (2014) Heme oxygenase-1 and acute kidney injury. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 23(1):17. https://doi.org/10.1097/2F01.mnh.0000437613.88158.d3
Nehring H, Meierjohann S, Friedmann Angeli JP (2020) Emerging aspects in the regulation of ferroptosis. Biochem Soc Trans 48(5):2253–2259. https://doi.org/10.1042/BST20200523
Ng SW, Norwitz SG, Norwitz ER (2019) The impact of iron overload and ferroptosis on reproductive disorders in humans: implications for preeclampsia. Int J Mol Sci 20(13):3283. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20133283
Ni HM, Chao X, Kaseff J et al (2019) Receptor-interacting serine/threonine-protein kinase 3 (RIPK3)–mixed lineage kinase domain-like protein (MLKL)–mediated necroptosis contributes to ischemia-reperfusion injury of steatotic livers. Am J Clin Pathol 189(7):1363–1374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajpath.2019.03.010
Nie J, Lin B, Zhou M, Wu L, Zheng T (2018) Role of ferroptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 144(12):2329–2337. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-018-2740-3
Olzmann JA, Carvalho P (2019) Dynamics and functions of lipid droplets. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 20(3):137–155. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41580-018-0085-z
Paller MS, Hedlund BE (1994) Extracellular iron chelators protect kidney cells from hypoxia/reoxygenation. Free Radic Biol Med 17(6):597–603. https://doi.org/10.1016/0891-5849(94)90099-X
Paller MS, Hedlund BE, Sikora JJ, Faassen A, Waterfield R (1998) Role of iron in postischemic renal injury in the rat. Kidney Int 4(4):474–480. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.1988.205
Pefanis A, Ierino FL, Murphy JM, Cowan PJ (2019) Regulated necrosis in kidney ischemia-reperfusion injury. Kidney Int 96(2):291–301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2019.02.009
Penuela S, Gehi R, Laird DW (2013) The biochemistry and function of pannexin channels. Biochim Biophys Acta Biomembr 1828(1):15–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamem.2012.01.017
Pittock ST, Norby SM, Grande JP et al (2005) MCP-1 is up-regulated in unstressed and stressed HO-1 knockout mice: pathophysiologic correlates. Kidney Int 68:611–622. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1523-1755.2005.00439.x
Ran Q, Chen L, Hambright WS, Na R (2015) Ablation of GPX4 in neurons results in rapid motor neuron degeneration and paralysis. Free Radic Biol Med 1(87):S34. https://doi.org/10.1016/2Fj.freeradbiomed.2015.10.093
Rodríguez-Vargas JM, Oliver-Pozo FJ, Dantzer F (2019) PARP1 and poly (ADP-ribosyl) ation signaling during autophagy in response to nutrient deprivation. Oxid Med Cell Longev. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mam.2013.01.007
Saklani P, Khan H, Gupta S, Kaur A, Singh TG (2022) Neuropeptides: potential neuroprotective agents in ischemic injury. Life Sci 288:120186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2021.120186
Saklani P, Khan H, Singh TG, Gupta S, Grewal AK (2022) Demethyleneberberine, a potential therapeutic agent in neurodegenerative disorders: a proposed mechanistic insight. Mol Biol Rep 3:1–3. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-022-07594-9
Sarkar S, Chakraborty D, Bhowmik A, Ghosh MK (2019) Cerebral ischemic stroke: cellular fate and therapeutic opportunities. Front Biosci 24:435–450. https://doi.org/10.2741/4727
Schipper HM, Song W, Zukor H, Hascalovici JR, Zeligman D (2009) Heme oxygenase-1 and neurodegeneration: expanding frontiers of engagement. J Neurochem 110(2):469–485. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-4159.2009.06160.x
Scindia Y, Dey P, Thirunagari A et al (2015) Hepcidin mitigates renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating systemic iron homeostasis. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(11):2800–2814. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.2014101037
Sharma S, Leaf DE (2019) Iron chelation as a potential therapeutic strategy for AKI prevention. J Am Soc Nephrol 30(11):2060–2071. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2019060595
Sharma A, Khan H, Singh TG, Grewal AK, Najda A, Kawecka-Radomska M, Kamel M, Altyar AE, Del-Daim MM (2021) Pharmacological modulation of ubiquitin-proteasome pathways in oncogenic signaling. Int J Mol Sci 22(21):11971. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms222111971
Shimada K, Skouta R, Kaplan A et al (2016) Global survey of cell death mechanisms reveals metabolic regulation of ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol 12(7):497–503. https://doi.org/10.1038/nchembio.2079
Shiraishi F, Curtis LM, Truong L, Poss K, Visner GA, Madsen K, Nick HS, Agarwal A (2000) Heme oxygenase-1 gene ablation or expression modulates cisplatin-induced renal tubular apoptosis. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 278:F726–F736. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.2000.278.5.f726
Skouta R, Dixon SJ, Wang J et al (2014) Ferrostatins inhibit oxidative lipid damage and cell death in diverse disease models. J Am Chem Soc 136(12):4551–4556. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja411006a
Song E, Su C, Fu J et al (2014) Selenium supplementation shows protective effects against patulin-induced brain damage in mice via increases in GSH-related enzyme activity and expression. Life Sci 109(1):37–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2014.05.022
Su L, Jiang X, Yang C, Zhang J et al (2019) Pannexin 1 mediates ferroptosis that contributes to renal ischemia/reperfusion injury. Int J Biol Chem 294(50):19395–19404. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.ra119.010949
Swaminathan S (2018) Iron homeostasis pathways as therapeutic targets in acute kidney injury. Nephron 140(2):156–159. https://doi.org/10.1159/000490808
Tang D, Chen X, Kang R, Kroemer G (2021) Ferroptosis: molecular mechanisms and health implications. Cell Res 31(2):107–125. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41422-020-00441-1
Tao N, Li K, Liu J (2020) Molecular mechanisms of ferroptosis and its role in pulmonary disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2020. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/9547127
Tao W, Liu F, Zhang J, Fu S, Zhan H, Qian K (2021) miR-3587 Inhibitor attenuates ferroptosis following renal ischemia-reperfusion through HO-1. Front Mol Biosci 8. https://doi.org/10.3389/2Ffmolb.2021.789927
Thapa K, Khan H, Kanojia N, Singh TG, Kaur A, Kaur G (2022) Therapeutic insights on ferroptosis in Parkinson’s disease. Eur J Pharmacol 175133. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2022.175133
Thévenod F, Lee WK (2013) Cadmium and cellular signaling cascades: interactions between cell death and survival pathways. Arch Toxicol 87(10):1743–1786
Tosatto SC, Bosello V, Fogolari F et al (2008) The catalytic site of glutathione peroxidases. Antioxid Redox Signal 10(9):1515–1526. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2008.2055
Ursini F, Maiorino M (2020) Lipid peroxidation and ferroptosis: the role of GSH and GPx4. Free Radic Biol Med 152:175–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2020.02.027
Wang Y, Bellomo R (2017) Cardiac surgery-associated acute kidney injury: risk factors, pathophysiology and treatment. Nat Rev Nephrol 13(11):697–711. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneph.2017.119
Wang X, Zheng X, Zhang J, Zhao S, Wang Z, Wang F, Shang W, Barasch J, Qiu A (2018) Physiological functions of ferroportin in the regulation of renal iron recycling and ischemic acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 315(4):F1042–F1057. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.00072.2018
Wang C, Liu T, Tong Y, Cui R, Qu K, Liu C, Zhang J (2021) Ulinastatin protects against acetaminophen-induced liver injury by alleviating ferroptosis via the SIRT1/NRF2/HO-1 pathway. Am J Trans Res 13(6):6031
Wang H, Cheng Y, Mao C et al (2021) Emerging mechanisms and targeted therapy of ferroptosis in cancer. Mol Ther 29(7):2185–2208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ymthe.2021.03.022
Wang Q, Zhan S, Han F, Liu Y, Wu H, Huang Z (2021) The possible mechanism of physiological adaptation to the low-Se diet and its health risk in the traditional endemic areas of Keshan diseases. Biol Trace Elem Res 8:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m116.738930
Wang Y, Quan F, Cao Q et al (2021) Quercetin alleviates acute kidney injury by inhibiting ferroptosis. J Adv Res 28:231–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jare.2020.07.007
Wang J, Liu Y, Wang Y, Sun L (2021c) The cross-link between ferroptosis and kidney diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2021c https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/6654887
Wu M, Xu LG, Li X, Zhai Z, Shu HB (2002) AMID, an apoptosis-inducing factor-homologous mitochondrion-associated protein, induces caspase-independent apoptosis. Int J Biol Chem 277(28):25617–25623. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m202285200
Wu JR, Tuo QZ, Lei P (2018) Ferroptosis, a recent defined form of critical cell death in neurological disorders. Mol Neurobiol 66(2):197–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-018-1155-6
Xia L, Zhang D, Du R et al (2008) miR-15b and miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer 123(2):372–379. https://doi.org/10.1002/ijc.23501
Xu J, Chen L, Li L (2018) Pannexin hemichannels: a novel promising therapy target for oxidative stress related diseases. J Cell Physiol 233(3):2075–2090. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.25906
Yan HF, Tuo QZ, Yin QZ, Lei P (2020) The pathological role of ferroptosis in ischemia/reperfusion-related injury. Zool Res 41(3):220. https://doi.org/10.24272/j.issn.2095-8137.2020.042
Yang WS, Stockwell BR (2016) Ferroptosis: death by lipid peroxidation. Trends Cell Biol 26(3):165–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2015.10.014
Yang WS, Kim KJ, Gaschler MM, Patel M, Shchepinov MS, Stockwell BR (2016) Peroxidation of polyunsaturated fatty acids by lipoxygenases drives ferroptosis. PNAS 113(34):E4966–E4975. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1603244113
Yarishkin O, Phuong TT, Bretz CA et al (2018) TREK-1 channels regulate pressure sensitivity and calcium signaling in trabecular meshwork cells. J Gen Physiol 150(12):1660–1675. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci44927
Yu L, Huang B, Po SS et al (2017) Low-level tragus stimulation for the treatment of ischemia and reperfusion injury in patients with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction: a proof-of-concept study. JACC Cardiovasc Interv 10(15):1511–1520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcin.2017.04.036
Zager RA, Johnson AC, Lund S (2009) Uremia impacts renal inflammatory cytokine gene expression in the setting of experimental acute kidney injury. Am J Physiol 297(4):F961–F970. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-03135-z
Zárate R, el Jaber-Vazdekis N, Tejera N, Pérez JA, Rodríguez C (2017) Significance of long chain polyunsaturated fatty acids in human health. Clin Transl Med 6(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40169-017-0153-6
Zarjou A, Bolisetty S, Joseph R et al (2013) Proximal tubule H-ferritin mediates iron trafficking in acute kidney injury. J Clin Investig 123(10):4423–4434. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI67867/
Zhao Z, Wu J, Xu H et al (2020) XJB-5-131 inhibited ferroptosis in tubular epithelial cells after ischemia− reperfusion injury. Cell Death Dis 11(8):1–5. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-020-02871-6
Zhou RP, Chen Y, Wei X et al (2020) Novel insights into ferroptosis: Implications for age-related diseases. Theranostics 10(26):11976. https://doi.org/10.7150/thno.50663
Zhou B, Liu J, Kang R, Klionsky DJ, Kroemer G, Tang D (2020a) Ferroptosis is a type of autophagy-dependent cell death. Annu Rev Cancer Biol (Vol. 66, pp. 89–100). Academic Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semcancer.2019.03.002.
Zou Y, Li H, Graham ET et al (2020) Cytochrome P450 oxidoreductase contributes to phospholipid peroxidation in ferroptosis. Nat Chem Biol 16(3):302–9. https://doi.org/10.1038/2Fs41589-020-0472-6
Acknowledgements
The authors extend their appreciation to the Chitkara University Punjab for support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization: conceived and designed the experiments: Thakur Gurjeet Singh. Analyzed the data: Amarjot Kaur. Wrote the manuscript: Komal Thapa. Visualization: Amarjot Kaur. Editing of the manuscript: Komal Thapa, Amarjot Kaur, and Thakur Gurjeet Singh. Critically reviewed the article: Thakur Gurjeet Singh. Supervision: Thakur Gurjeet Singh. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Compliance with ethical standards
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Thapa, K., Singh, T.G. & Kaur, A. Targeting ferroptosis in ischemia/reperfusion renal injury. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 395, 1331–1341 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-022-02277-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-022-02277-5