Abstract
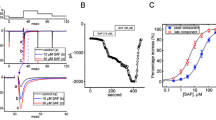
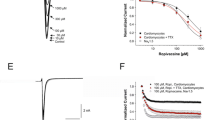
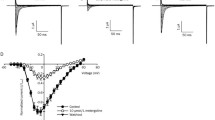
Tricyclic antidepressants (TCAs) and duloxetine are used to treat neuropathic pain. However, the mechanisms underlying their analgesic effects remain unclear. Although many investigators have shown inhibitory effects of antidepressants on voltage-gated sodium channels (Nav) as a possible mechanism of analgesia, to our knowledge, no one has compared effects on the diverse variety of sodium channel α subunits. We investigated the effects of antidepressants on sodium currents in Xenopus oocytes expressing Nav1.2, Nav1.3, Nav1.6, Nav1.7, and Nav1.8 with a β1 subunit by using whole-cell, two-electrode, voltage clamp techniques. We also studied the role of the β3 subunit on the effect of antidepressants on Nav1.3. All antidepressants inhibited sodium currents in an inactivated state induced by all five α subunits with β1. The inhibitory effects were more potent for Nav1.3, Nav1.7, and Nav1.8, which are distributed in dorsal root ganglia, than Nav1.2 and Nav1.6, which are distributed primarily in the central nervous system. The effect of amitriptyline on Nav1.7 with β1 was most potent with a half-maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) 4.6 μmol/L. IC50 for amitriptyline on Nav1.3 coexpressed with β1 was lowered from 8.4 to 4.5 μmol/L by coexpression with β3. Antidepressants predominantly inhibited the sodium channels expressed in dorsal root ganglia, and amitriptyline has the most potent inhibitory effect. This is the first evidence, to our knowledge, showing the diverse effects of antidepressants on various α subunits. Moreover, the β3 subunit appears important for inhibition of Nav1.3. These findings may aid better understanding of the mechanisms underlying the pain relieving effects of antidepressants.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akk G, Li P, Bracamontes J, Reichert DE, Covey DF, Steinbach JH (2008) Mutations of the GABA-A receptor alpha1 subunit M1 domain reveal unexpected complexity for modulation by neuroactive steroids. Mol Pharmacol 74:614–627
Akopian AN, Souslova V, England S, Okuse K, Ogata N, Ure J, Smith A, Kerr BJ, McMahon SB, Boyce S, Hill R, Stanfa LC, Dickenson AH, Wood JN (1999) The tetrodotoxin-resistant sodium channel SNS has a specialized function in pain pathways. Nat Neurosci 2:541–548
Arita M, Wada A, Takara H, Izumi F (1987) Inhibition of 22Na influx by tricyclic and tetracyclic antidepressants and binding of [3H]imipramine in bovine adrenal medullary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 243:342–348
Attal N, Cruccu G, BaronR HM, Hansson P, Jensen TS, Nurmikko T, European Federation of Neurological Societies (2010) EFNS guidelines on the pharmacological treatment of neuropathic pain: 2010 revision. Eur J Neurol 17:1113–1e88
Barber MJ, Starmer CF, Grant AO (1991) Blockade of cardiac sodium channels by amitriptyline and diphenylhydantoin. Evidence for two use-dependent binding sites. Circ Res 69:677–696
Baron R, Binder A, Wasner G (2010) Neuropathic pain: diagnosis, pathophysiological mechanisms, and treatment. Lancet Neurol 9:807–819
Baron R, Binder A, Attal N, Casale R, Dickenson AH, Treede RD (2016) Neuropathic low back pain in clinical practice. Eur J Pain 20:861–873
Bladessarini RJ (2001) Drugs and the treatment of psychiatric disorders: depression and anxiety disorders, The Pharmacological Basis of Therapeutics. In: Hardman JG, Limbird LE, Gilman AG (eds) , 10th edn. The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc., New York, pp 447–484
Bräu ME, Dreimann M, Olschewski A, Vogel W, Hempelmann G (2001) Effect of drugs used for neuropathic pain management on tetrodotoxin-resistant Na+ currents in rat sensory neurons. Anesthesiology 94:137–144
Catterall WA (2000) From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: the structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron 26:13–25
Catterall WA, Goldin AL, Waxman SG (2005) International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels. Pharmacol Rev 57:397–409
Chen YW, Huang KL, Liu SY, Tzeng JI, Chu KS, Lin MT, Wang JJ (2004) Intrathecal tri-cyclic antidepressants produce spinal anesthesia. Pain 112:106–112
Cheng KI, Wang HC, Chang LL, Wang FY, Lai CS, Chou CW, Tsai HP, Kwan AL (2012) Pretreatment with intrathecal amitriptyline potentiates anti-hyperalgesic effects of pos-injury intra-peritoneal amitriptyline following spinal nerve ligation. BMC Neurol 12:44
Cummins TR, Sheets PL, Waxman SG (2007) The roles of sodium channels in nociception: implications for mechanisms of pain. Pain 131:243–257
Delpón E, Valenzuela C, Carrón R, Pérez-Vizcaino F, Tamargo J (1991a) Tonic and frequency-dependent Vmax block induced by (S)-nafenodone, a new antidepressant drug, in guinea-pig papillary muscles. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 343:638–644
Delpón E, Tamargo J, Sánchez-Chapula J (1991b) Further characterization of the effects of imipramine on plateau membrane currents in guinea-pig ventricular myocytes. Naunyn Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 344:645–652
Dick IE, Brochu RM, Purohit Y, Kaczorowski GJ, Martin WJ, Priest BT (2007) Sodium channel blockade may contribute to the analgesic efficacy of antidepressants. J Pain 8:315–324
Dworkin RH, O’Connor AB, Audette J, Baron R, Gourlay GK, Haanpää ML, Kent JL, Krane EJ, Lebel AA, Levy RM, Mackey SC, Mayer SC, Mayer J, Miaskowski C, Raja SN, Rice AS, Schmader KE, Stacey B, Stanos S, Treede RD, Turk D, Walco GA, Wells CD (2010) Recommendations for the pharmacological management of neuropathic pain: an overview and literature update. Mayo Clin Proc 85(3 Suppl):S3–14
Finnerup NB, Otto M, McQuay HJ, Jensen TS, Sindrup SH (2005) Algorithm for neuropathic pain treatment: an evidence based proposal. Pain 118:289–305
Fukuoka T, Kobayashi K, Yamanaka H, Obata K, Dai Y, Noguchi K (2008) Comparative study of the distribution of the alpha-subunits of voltage-gated sodium channels in normal and axotomized rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. J Comp Neurol 510:188–206
Gerner P, Kao G, Srinivasa V, Narang S, Wang GK (2003) Topical amitriptyline in healthy volunteers. Reg Anesth Pain Med 28:289–293
Goldstein DJ, Lu Y, Detke MJ, Lee TC, Iyengar S (2005) Duloxetine vs. placebo in patients with painful diabetic neuropathy. Pain 116:109–118
Hains BC, Klein JP, Saab CY, Craner MJ, Black JA, Waxman SG (2003) Upregulation of sodium channel Nav1.3 and functional involvement in neuronal hyperexcitability associated with central neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. J Neurosci 23:8881–8892
Horishita T, Yanagihara N, Ueno S, Sudo Y, Uezono Y, Okura D, Minami T, Kawasaki T, Sata T (2014) Neurosteroids allopregnanolone sulfate and pregnanolone sulfate have diverse effect on the α subunit of the neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels Nav1.2, Nav1.6, Nav1.7, and Nav1.8 expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Anesthesiology 121:620–631
Ishii Y, Sumi T (1992) Amitriptyline inhibits striatal efflux of neurotransmitters via blockade of voltage-dependent Na+ channels. Eur J Pharmacol 221:377–380
Joshi SK, Mikusa JP, Hemandez G, Baker S, Shieh CC, Neelands T, Zhang XF, Niforatos W, Kage K, Han P, Krafte D, Faltynek C, Sullivan JP, Jarvis MF, Honore P (2006) Involvement of the TTX-resistant sodium channel Nav1.8 in inflammatory and neuropathic, but not post-operative, pain states. Pain 123:75–82
Karson CN, Newton JE, Livingston R, Jolly JB, Cooper TB, Sprigg J, Komoroski RA (1993) Human brain fluoxetine concentrations. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 5:322–329
Khan MA, Gerner P, Kuo Wang G (2002) Amitriptyline for prolonged cutaneous analgesia in the rat. Anesthesiology 96:109–116
Kopsky DJ, Hesselink JM (2012) High doses of topical amitriptyline in neuropathic pain: two cases and literature review. Pain Pract 12:148–153
Lambert JJ, Belelli D, Harney SC, Peters JA, Frenguelli BG (2001) Modulation of native and recombinant GABAA receptors by endogenous and synthetic neuroactive steroids. Brain Res Rev 37:68–80
Lance JW, Curran DA (1964) Treatment of chronic tension headache. Lancet 1:1236–1239
Liang J, Liu X, Pan M, Dai M, Dong Z, Wang X, Liu R, Zheng J, Yu S (2014) Blockade of Nav1.8 currents in nociceptive trigeminal neurons contributes to anti-trigeminovascular nocciceptive effect of amitriptyline. NeuroMolecular Med 16:308–321
Lindia JA, Köhler MG, Martin WJ, Abbadie C (2005) Relationship between sodium channel Nav1.3 expression and neuropathic pain behavior in rats. Pain 117:145–153
Lynch ME, Clark AJ, Sawynok J, Sullivan MJ (2005a) Topical amitriptyline and ketamine in neuropathic pain syndromes: an open-label study. J Pain 6:644–649
Lynch ME, Clark AJ, Sawynok J, Sullivan MJ (2005b) Topical 2% amitriptyline and 1% ketamine in neuropathic pain syndromes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Anesthesiology 103:140–146
Micó JA, Ardid D, Berrocoso E, Eschalier A (2006) Antidepressants and pain. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:348–354
Nicholson GM, Blanche T, Mansfield K, Tran Y (2002) Differential blockade of neuronal voltage-gated Na(+) and K(+) channels by antidepressant drugs. Eur J Pharmacol 452:35–48
Ogata N, Narahashi T (1989) Block of sodium channels by psychotropic drugs in single guinea-pig cardiac myocytes. Br J Pharmacol 97:905–913
Saarto T, Wiffen PJ (2005) Antidepressants for neuropathic pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD005454
Shah BS, Stevens EB, Gonzalez MI, Bramwell S, Pinnock RD, Lee K, Dixon AK (2000) Beta3, a novel auxiliary subunit for the voltage-gated sodium channel, is expressed preferentially in sensory neurons and is upregulated in the chronic constriction injury model of neuropathic pain. Eur J Neurosci 12:3985–3990
Song JH, Ham SS, Shin YK, Lee CS (2000) Amitriptyline modulation of Na+ channels in rat dorsal root ganglion neurons. Eur J Pharmacol 401:297–305
Sun YH, Li HS, Zhu C, Hu W, Yang J, Zhao GL, Lu GJ, Wu SX, Dong YL (2014) The analgesia effect of duloxetine on post-operative pain via intrathecal or intraperitoneal administration. Neurosci Lett 568:6–11
Takahashi N, Kikuchi S, Dai Y, Kobayashi K, Fukuoka T, Noguchi K (2003) Expression of auxiliary beta subunits of sodium channels in primary afferent neurons and the effect of nerve injury. Neuroscience 121:441–450
Wang GK, Rusell C, Wang SY (2004) State-dependent block of voltage-gated Na+ channels by amitriptyline via the local anesthetic receptor and its implication for neuropathic pain. Pain 110:166–174
Wang W, Gu J, Li YQ, Tao YX (2011) Are voltage-gated sodium channels on the dorsal root ganglion involved in the development of neuropathic pain? Mol Pain 7:16
Wang SY, Calderon J, Kuo Wang G (2010) Block of neuronal Na+ channels by antidepressant duloxetine in a state-dependent manner. Anesthesiology 113:655–665
Watson CP (1994) Antidepressant drugs as adjuvant analgesics. J Pain Sympton Manage 9:392–405
Wood JN, Boorman JP, Okuse K, Baker MD (2004) Voltage-gated sodium channels and pain pathways. J Neurobiol 61:55–71
Yang YC, Huang CS, Kuo CC (2010) Lidocaine, carbamazepine, and imipramine have partially overlapping binding sites and additive inhibitory effect on neuronal Na+ channels. Anesthesiology 113:160–174
Yeomans DC, Levinson SR, Peters MC, Koszowski AG, Tzabazis AZ, Gilly WF, Wilson SP (2005) Decrease in inflammatory hyperalgesia by herpes vector-mediated knockdown of Nav1.7 sodium channels in primary afferents. Hum Gene Ther 16:271–277
Acknowledgements
Funding
This study was supported by a Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research from Japan Society for the Promotion of Science, 25462462 (to Takeyoshi Sata).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Animal Research Committee of the University of Occupational and Environmental Health, Kitakyushu, Japan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horishita, T., Yanagihara, N., Ueno, S. et al. Antidepressants inhibit Nav1.3, Nav1.7, and Nav1.8 neuronal voltage-gated sodium channels more potently than Nav1.2 and Nav1.6 channels expressed in Xenopus oocytes. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 390, 1255–1270 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1424-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-017-1424-x