Abstract
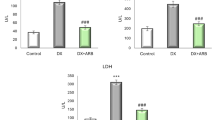
Cisplatin (cis-diammine dichloroplatinum (II), CDDP) is a widely used drug for treatment of various types of cancers. However, CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity remains the main dose-limiting side effect. Retinoids are a group of vitamin A-related compounds that exert their effects through retinoid receptors activation. In this study, we investigated the effect of CDDP treatment on retinoic acid receptor-α (RAR-α) and retinoid X receptor-α (RXR-α) expression. In addition, we investigated the possible modulatory effects of RAR agonist, all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA), on CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity. Rats were treated with saline, DMSO, CDDP, ATRA, or CDDP/ATRA. Twenty-four hours after the last ATRA injection, rats were killed; blood samples were collected; kidneys were dissected; and biochemical, immunohistochemical, and histological examinations were performed. Our results revealed that CDDP treatment significantly increased serum levels of creatinine and urea, with concomitant decrease in serum albumin. Moreover, reduced glutathione (GSH) content as well as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase (CAT) activities were significantly reduced with concurrent increase in kidney malondialdehyde (MDA) content following CDDP treatment. Furthermore, CDDP markedly upregulated tubular RAR-α, RXR-α, fibrin, and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) protein expression. Although administration of ATRA to control rats did not produce marked alterations in kidney function parameters, administration of ATRA to CDDP-treated rats significantly exacerbated CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity. In addition, CDDP/ATRA co-treatment significantly increased RAR-α, RXR-α, fibrin, and iNOS protein expression compared to CDDP alone. In conclusion, we report, for the first time, the crucial role of retinoid receptors in CDDP-induced nephrotoxicity. Moreover, our findings indicate that co-administration of ATRA with CDDP, although beneficial on the therapeutic effects, their deleterious effects on the kidney may limit their clinical use.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Bakky MS, Hammad MA, Walker LA, Ashfaq MK (2011a) Silencing of tissue factor by antisense deoxyoligonucleotide prevents monocrotaline/LPS renal injury in mice. Arch Toxicol 85:1245–1256
Abdel-Bakky MS, Hammad MA, Walker LA, Ashfaq MK (2011b) Tissue factor dependent liver injury causes release of retinoid receptors (RXR-α and RAR-α) as lipid droplets. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 410:146–151
Aburto A, Barría A, Cárdenas A, Carpio D, Figueroa CD, Burgos ME, Ardiles L (2014) Pre-stimulation of the kallikrein system in cisplatin-induced acute renal injury: an approach to renoprotection. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 280:216–223
Aebi S, Kröning R, Cenni B, Sharma A, Fink D, Los G, Weisman R, Howell SB, Christen RD (1997) All-trans retinoic acid enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in human ovarian adenocarcinoma and in squamous head and neck cancer cells. Clin Cancer Res 3:2033–2038
Arany I, Safirstein RL (2003) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Semin Nephrol 23:460–464
Arrieta O, González-De la Rosa CH, Aréchaga-Ocampo E, Villanueva-Rodríguez G, Cerón-Lizárraga TL, Martínez-Barrera L, De la Garza J (2010) Randomized phase II trial of all-trans-retinoic acid with chemotherapy based on paclitaxel and cisplatin as first-line treatment in patients with advanced non–small-cell lung cancer. J Clin Oncol 28:3463–3471
Atasayar S, Gürer-Orhan H, Orhan H, Gürel B, Girgin G, Ozgüneş H (2009) Preventive effect of aminoguanidine compared to vitamin E and C on cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats. Exp Toxicol Pathol 61:23–32
Atessahin A, Yilmaz S, Karahan I, Ceribasi AO, Karaoglu A (2005) Effects of lycopene against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity and oxidative stress in rats. Toxicology 212:116–123
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1963) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Bilbija D, Haugen F, Sagave J, Baysa A, Bastani N, Levy FO, Sirsjö A, Blomhoff R, Valen G (2012) Retinoic acid signalling is activated in the postischemic heart and may influence remodelling. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0044740
Bushue N, Wan YJY (2010) Retinoid pathway and cancer therapeutics. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 62:1285–1298
Chabner BA, Bertino J, Cleary J, Ortiz T, Lane A, Supko JG, Ryan D (2012) Cytotoxic agents. In: Brunton LL, Chabner BA, Knollman BC (eds) Goodman and Gilman’s: the pharmacological basis of therapeutics. Mc Graw Hill Companies, New York, pp. 167–1730
Caliaro MJ, Vitaux P, Lafon C, Lochon I, Nehme A, Valette A, Canal P, Bugat R, Jozan S (1997) Multifactorial mechanism for the potentiation of cisplatin (CDDP) cytotoxicity by all-trans retinoic acid (ATRA) in human ovarian carcinoma cell lines. Br J Cancer 75:333–340
Claiborne A (1985) Catalase activity. In: Robert AG (ed) CRC handbook of methods for oxygen radical research. CRC Press in Boca Raton, Fla, pp. 283–284
Doumas BT, Watson WA, Biggs HG (1971) Albumin standards and the measurement of serum albumin with bromcresol green. Clin Chim Acta 31:87–96
El-Naga RN (2014) Pre-treatment with cardamonin protects against cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity in rats: impact on NOX-1, inflammation and apoptosis. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 274:87–95
Ewees MG, Abdelghany TM, Abdel-Aziz AA, Abdel-Bakky MS (2015) All-trans retinoic acid mitigates methotrexate-induced liver injury in rats; relevance of retinoic acid signaling pathway. Naunyn Schmiedeberg’s Arch Pharmacol. doi:10.1007/s00210-015-1130-5
Fawcett JK, Scott JE (1960) A rapid and precise method for the determination of urea. J Clin Pathol 13:156–159
Förstermann U, Sessa WC (2012) Nitric oxide synthases: regulation and function. Eur. Heart J. (33):829–837a-d
Gronemeyer H, Miturski R (2001) Molecular mechanisms of retinoid action. Cell Mol Biol Lett 6:3–52
Gudas LJ (2012) Emerging roles for retinoids in regeneration and differentiation in normal and disease states. Biochim Biophys Acta 1821:213–221
He JC, Lu TC, Fleet M, Sunamoto M, Husain M, Fang W, Neves S, Chen Y, Shankland S, Iyengar R, Klotman PE (2007) Retinoic acid inhibits HIV-1-induced podocyte proliferation through the cAMP pathway. J Am Soc Nephrol 18:93–102
Hertig A, Rondeau E (2004) Role of the coagulation/fibrinolysis system in fibrin-associated glomerular injury. J Am Soc Nephrol 15:844–853
Husdan H, Rapoport A (1968) Estimation of creatinine by the jaffe reaction. A Comparison of Three Methods Clin Chem 14:222–238
Jalal DI, Chonchol M, Targher G (2010) Disorders of hemostasis associated with chronic kidney disease. Semin Thromb Hemost 36:34–40
Kavukcu S, Turkmen MA, Soylu A (2001) Could the effective mechanisms of retinoids on nephrogenesis be also operative on the amelioration of injury in acquired renal lesions? Pediatr Nephrol 16:689–690
Kim CS, Choi JS, Park JW, Bae EH, Ma SK, Lee J, Kim SW (2012) Altered regulation of nitric oxide and natriuretic peptide system in cisplatin-induced nephropathy. Regul Pept 174:65–70
Kuhad A, Tirkey N, Pilkhwal S, Chopra K (2006) Renoprotective effect of spirulina fusiformis on cisplatin-induced oxidative stress and renal dysfunction in rats. Ren Fai 28:247–254
Lelievre-Pegorier M, Vilar J, Ferrier ML, Moreau E, Freund N, Gilbert T, Merlet-Bénichou C (1998) Mild vitamin A deficiency leads to inborn nephron deficit in the rat. Kidney Int 54:1455–1462
Li Y, Wongsiriroj N, Blaner WS (2014) The multifaceted nature of retinoid transport and metabolism. Hepatobiliary Surg Nutr 3:126–139
Lieberthal W, Triaca V, Levine J (1996) Mechanisms of death induced by cisplatin in proximal tubular epithelial cells: apoptosis vs. necrosis. Am. J. Physiol. 270:F700–F708
Liebler S, Uberschär B, Kübert H, Brems S, Schnitger A, Tsukada M, Zouboulis CC, Ritz E, Wagner J (2004) The renal retinoid system: time-dependent activation in experimental glomerulonephritis. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 286:F458–F465
Macnaul KL, Hutchinson NI (1993) Differential expression of iNOS and cNOS mRNA in human vascular smooth muscle cells and endothelial cells under normal and inflammatory conditions. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 196:1330–1334
Mangelsdorf DJ, Evans RM (1995) The RXR heterodimers and orphan receptors. Cell 83:841–850
Manzano VM, Muñoz JC, Jiménez JR, Puyol MR, Puyol DR, Kitamura M, Cazaña FJ (2000) Human renal mesangial cells are a target for the anti-inflammatory action of 9-cis retinoic acid. Br J Pharmacol 131:1673–1683
Mendelsohn C, Batourina E, Fung S, Gilbert T, Dodd J (1999) Stromal cells mediate retinoid-dependent functions essential for renal development. Development 126:1139–1148
Mendelsohn C, Lohnes D, Décimo D, Lufkin T, LeMeur M, Chambon P, Mark M (1994) Function of the retinoic acid receptors (RARs) during development. Development 120:2749–2771
Mezaki Y, Yamaguchi N, Yoshikawa K, Miura M, Imai K, Itoh H, Senoo H (2009) Insoluble, speckled cytosolic distribution of retinoic acid receptor alpha protein as a marker of hepatic stellate cell activation in vitro. J Histochem Cytochem 57:687–699
Mezaki Y, Yoshikawa K, Yamaguchi N, Miura M, Imai K, Kato S, Senoo H (2007) Rat hepatic stellate cells acquire retinoid responsiveness after activation in vitro by post-transcriptional regulation of retinoic acid receptor alpha gene expression. Arch Biochem Biophys 465:370–379
Miller RP, Tadagavadi RK, Ramesh G, Reeves WB (2010) Mechanisms of cisplatin nephrotoxicity. Toxins 2:2490–2518
Moulder JE, Fish BL, Regner KR, Cohen EP, Raife TJ (2002) Retinoic acid exacerbates experimental radiation nephropathy. Radiat Res 157:199–203
Nathan CF, Hibbs JB (1999) Role of nitric oxide synthesis in macrophage antimicrobial activity. Curr Opin Immunol 3:65–70
Nishikimi M, Appaji N, Yagi K (1972) The occurrence of superoxide anion in the reaction of reduced phenazine methosulfate and molecular oxygen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 46:849–854
Núñez V, Alameda D, Rico D, Mota R, Gonzalo P, Cedenilla M, Fischer T, Boscá L, Glass CK, Arroyo AG, Ricote M (2010) Retinoid X receptor alpha controls innate inflammatory responses through the up-regulation of chemokine expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:10626–10631
Ohata M, Lin M, Satre M, Tsukamoto H (1997) Diminished retinoic acid signaling in hepatic stellate cells in cholestatic liver fibrosis. Am J Physiol 272:G589–G596
Okamura M, Takano Y, Saito Y, Yao J, Kitamura M (2009) Induction of nephrin gene expression by selective cooperation of the retinoic acid receptor and the vitamin D receptor. Nephrology Dialysis Transplantation:gfp243.2009. Nephrol Dial Transplant 24:3006–3012
Osterholm C, Veress B, Simanaitis M, Hedner U, Ekberg H (2005) Differential expression of tissue factor (TF) in calcineurin inhibitor-induced nephrotoxicity and rejection–implications for development of a possible diagnostic marker. Transpl Immunol 15:165–172
Pabla N, Dong Z (2008) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: mechanisms and renoprotective strategies. Kidney Int 73:994–1007
Palipoch S, Punsawad C (2013) Biochemical and histological study of rat liver and kidney injury induced by cisplatin. J Toxicol Pathol 26:293–299
Pan H, Mukhopadhyay P, Rajesh M, Patel V, Mukhopadhyay B, Gao B, Haskó G, Pacher P (2009) Cannabidiol attenuates cisplatin-induced nephrotoxicity by decreasing oxidative/nitrosative stress, inflammation, and cell death. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 328:708–714
Patatanian E, Thompson DF (2008) Retinoic acid syndrome: a review. J Clin Pharm Ther 33:331–338
Penniston KL, Tanumihardjo SA (2006) The acute and chronic toxic effects of vitamin A. Am J Clin Nutr 83:191–201
Rao J, Zhang C, Wang P, Lu L, Zhang F (2010) All-trans retinoic acid alleviates hepatic ischemia/reperfusion injury by enhancing manganese superoxide dismutase in rats. Biol Pharm Bull 33:869–875
Saleh IG, Ali Z, Hamada FM, Abd-Ellah MF, Walker LA, Khan IA, Ashfaq MK (2013) Effect of green tea on hepatic cells under the influence of inflammatory conditions: in vitro study. Am J Pharmacol Toxicol 8:209–2013
Satoh K (1978) Serum lipid peroxide in cerebrovascular disorders determined by a new colorimetric method. Clin Chim Acta 90:37–43
Sindhu G, Nishanthi E, Sharmila R (2015) Nephroprotective effect of vanillic acid against cisplatin induced nephrotoxicity in wistar rats: a biochemical and molecular study. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 39:392–404
Smith GF (1980) Fibrinogen-fibrin conversion. The mechanism of fibrin-polymer formation in solution. Biochem J 185:1–11
Sugawara A, Sanno N, Takahashi N, Osamura RY, Abe K (1997) Retinoid X receptors in the kidney: their protein expression and functional significance. Endocrinology 138:3175–3180
Taguchi T, Nazneen A, Abid MR, Razzaque MS (2005) Cisplatin-associated nephrotoxicity and pathological events. Contrib Nephrol 148:107–121
Wong YF, Wilson PD, Unwin RJ, Norman JT, Arno M, Hendry BM, Xu Q (2012) Retinoic acid receptor-dependent, cell-autonomous, endogenous retinoic acid signaling and its target genes in mouse collecting duct cells. PLoS One. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0045725
Xiao JH, Durand B, Chambon P, Voorhees JJ (1995) Endogenous retinoic acid receptor (RAR)-retinoid X receptor (RXR) heterodimers are the major functional forms regulating retinoid-responsive elements in adult human keratinocytes. Binding of ligands to RAR only is sufficient for RAR-RXR heterodimers to confer ligand-dependent activation of hRAR beta 2/RARE (DR5). J Biol Chem 270:3001–3011
Xu Q, Lucio-Cazana J, Kitamura M, Ruan X, Fine LG, Norman T (2004) Retinoids in nephrology: promises and pitfalls. Kidney Int 66:2119–2131
Yang T, Michele DE, Park J, Smart AM, Lin Z, Brosius FC, Schnermann JB, Briggs JP (1999) Expression of peroxisomal proliferator-activated receptors and retinoid X receptors in the kidney. Am J Physiol 277:F966–F973
Yao X, Panichpisal K, Kurtzman N, Nugent K (2007) Cisplatin nephrotoxicity: a review. Am J Med Sci 334:115–124
Zhelyaznik N, Mey J (2006) Regulation of retinoic acid receptors alpha, beta and retinoid X receptor alpha after sciatic nerve injury. Neuroscience 141:1761–1774
Zhou TB, Drummen GP, Qin YH (2012) The controversial role of retinoic acid in fibrotic diseases: analysis of involved signaling pathways. Int J Mol Sci 14:226–243
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
All animal procedures were carried out according to the international guide for the care and use of laboratory animals and were conducted in compliance with the guidelines of our institutional research ethical committee.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elsayed, A.M., Abdelghany, T.M., Akool, ES. et al. All-trans retinoic acid potentiates cisplatin-induced kidney injury in rats: impact of retinoic acid signaling pathway. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 389, 327–337 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1193-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-015-1193-3