Abstract
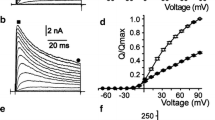
The effects of dapoxetine were examined on cloned Kv1.5 channels stably expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells using the whole-cell patch clamp technique. Dapoxetine decreased the peak amplitude of Kv1.5 currents and accelerated the decay rate of current inactivation in a concentration-dependent manner with an IC 50 of 11.6 μM. Kinetic analysis of the time-dependent effects of dapoxetine on Kv1.5 current decay yielded the apparent association (k +1 ) and dissociation (k −1 ) rate constants of 2.8 μM−1 s−1 and 34.2 s−1, respectively. The theoretical K D value, derived by k −1 /k +1 , yielded 12.3 μM, which was reasonably similar to the IC 50 value obtained from the concentration–response curve. Dapoxetine decreased the tail current amplitude and slowed the deactivation process of Kv1.5, which resulted in a tail crossover phenomenon. The block by dapoxetine is voltage-dependent and steeply increased at potentials between −10 and +10 mV, which correspond to the voltage range of channel activation. At more depolarized potentials, a weaker voltage dependence was observed (δ = 0.31). Dapoxetine had no effect on the steady-state activation of Kv1.5 but shifted the steady-state inactivation curves in a hyperpolarizing direction. Dapoxetine produced a use-dependent block of Kv1.5 at frequencies of 1 and 2 Hz and slowed the time course for recovery of inactivation. These effects were reversible after washout of the drug. Our results indicate that dapoxetine blocks Kv1.5 currents by interacting with the channel in both the open and inactivated states of the channel.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Archer SL, Wu XC, Thebaud B, Nsair A, Bonnet S, Tyrrell B, McMurtry MS, Hashimoto K, Harry G, Michelakis ED (2004) Preferential expression and function of voltage-gated, O2-sensitive K+ channels in resistance pulmonary arteries explains regional heterogeneity in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction: ionic diversity in smooth muscle cells. Circ Res 95:308–318
Belik J (2008) Fetal and neonatal effects of maternal drug treatment for depression. Semin Perinatol 32:350–354
Brendel J, Peukert S (2003) Blockers of the Kv1.5 channel for the treatment of atrial arrhythmias. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents 1:273–287
Brown J, PM OB, Marjoribanks J, Wyatt K (2009) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors for premenstrual syndrome. Cochrane Database Syst Rev: CD001396
Caballero R, Gomez R, Moreno I, Nunez L, Gonzalez T, Arias C, Guizy M, Valenzuela C, Tamargo J, Delpon E (2004) Interaction of angiotensin II with the angiotensin type 2 receptor inhibits the cardiac transient outward potassium current. Cardiovasc Res 62:86–95
Choi JS, Hahn SJ, Rhie DJ, Yoon SH, Jo YH, Kim MS (1999) Mechanism of fluoxetine block of cloned voltage-activated potassium channel Kv1.3. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 291:1–6
Choi BH, Choi JS, Jeong SW, Hahn SJ, Yoon SH, Jo YH, Kim MS (2000) Direct block by bisindolylmaleimide of rat Kv1.5 expressed in Chinese hamster ovary cells. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 293:634–640
Choi BH, Choi JS, Yoon SH, Rhie DJ, Min DS, Jo YH, Kim MS, Hahn SJ (2001) Effects of norfluoxetine, the major metabolite of fluoxetine, on the cloned neuronal potassium channel Kv3.1. Neuropharmacology 41:443–453
Choi BH, Choi JS, Ahn HS, Kim MJ, Rhie DJ, Yoon SH, Min DS, Jo YH, Kim MS, Hahn SJ (2003) Fluoxetine blocks cloned neuronal A-type K+ channels Kv1.4. Neuroreport 14:2451–2455
Claassen V, Davies JE, Hertting G, Placheta P (1977) Fluvoxamine, a specific 5-hydroxytryptamine uptake inhibitor. Br J Pharmacol 60:505–516
Davies AR, Kozlowski RZ (2001) Kv channel subunit expression in rat pulmonary arteries. Lung 179:147–161
Deak F, Lasztoczi B, Pacher P, Petheo GL, Valeria K, Spat A (2000) Inhibition of voltage-gated calcium channels by fluoxetine in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. Neuropharmacology 39:1029–1036
Fedida D, Wible B, Wang Z, Fermini B, Faust F, Nattel S, Brown AM (1993) Identity of a novel delayed rectifier current from human heart with a cloned K+ channel current. Circ Res 73:210–216
Fedida D, Eldstrom J, Hesketh JC, Lamorgese M, Castel L, Steele DF, Van Wagoner DR (2003) Kv1.5 is an important component of repolarizing K+ current in canine atrial myocytes. Circ Res 93:744–751
Fuller RW, Wong DT (1990) Serotonin uptake and serotonin uptake inhibition. Ann N Y Acad Sci 600:68–78, discussion 79–80
Gerlach U (2003) Blockers of the slowly delayed rectifier potassium IKs channel: potential antiarrhythmic agents. Curr Med Chem Cardiovasc Hematol Agents 1:243–252
Gomez R, Nunez L, Caballero R, Vaquero M, Tamargo J, Delpon E (2005) Spironolactone and its main metabolite canrenoic acid block hKv1.5, Kv4.3 and Kv7.1 + minK channels. Br J Pharmacol 146:146–161
Gonzalez T, David M, Moreno C, Macias A, Valenzuela C (2010) Kv1.5-Kvβ interactions: molecular determinants and pharmacological consequences. Mini Rev Med Chem 10:635–642
Guignabert C, Raffestin B, Benferhat R, Raoul W, Zadigue P, Rideau D, Hamon M, Adnot S, Eddahibi S (2005) Serotonin transporter inhibition prevents and reverses monocrotaline-induced pulmonary hypertension in rats. Circulation 111:2812–2819
Hellstrom WJ (2009) Emerging treatments for premature ejaculation: focus on dapoxetine. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 5:37–46
Jeong I, Kim SW, Yoon SH, Hahn SJ (2012) Block of cloned Kv4.3 potassium channels by dapoxetine. Neuropharmacology 62:2260–2265
Kallen B, Olausson PO (2008) Maternal use of selective serotonin re-uptake inhibitors and persistent pulmonary hypertension of the newborn. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 17:801–806
Kawut SM, Horn EM, Berekashvili KK, Lederer DJ, Widlitz AC, Rosenzweig EB, Barst RJ (2006) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor use and outcomes in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Pulm Pharmacol Ther 19:370–374
Keller MB (2000) Citalopram therapy for depression: a review of 10 years of European experience and data from U.S. clinical trials. J Clin Psychiatry 61:896–908
Kendirci M, Salem E, Hellstrom WJ (2007) Dapoxetine, a novel selective serotonin transport inhibitor for the treatment of premature ejaculation. Ther Clin Risk Manag 3:277–289
Kowey PR, Mudumbi RV, Aquilina JW, Dibattiste PM (2011) Cardiovascular safety profile of dapoxetine during the premarketing evaluation. Drugs R D 11:1–11
Lee HM, Hahn SJ, Choi BH (2010a) Inhibitory action of fluvoxamine on Kv1.5 currents. Biol Pharm Bull 33:977–982
Lee HM, Hahn SJ, Choi BH (2010b) Open channel block of Kv1.5 currents by citalopram. Acta Pharmacol Sin 31:429–435
Max MB, Lynch SA, Muir J, Shoaf SE, Smoller B, Dubner R (1992) Effects of desipramine, amitriptyline, and fluoxetine on pain in diabetic neuropathy. N Engl J Med 326:1250–1256
Modi NB, Nath R, Staehr P, Gupta SK, Aquilina JW, Rivas D (2009) Pharmacokinetic, pharmacodynamic, and electrocardiographic effects of dapoxetine and moxifloxacin compared with placebo in healthy adult male subjects. J Clin Pharmacol 49:634–642
Moreno I, Caballero R, Gonzalez T, Arias C, Valenzuela C, Iriepa I, Galvez E, Tamargo J, Delpon E (2003) Effects of irbesartan on cloned potassium channels involved in human cardiac repolarization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 304:862–873
Moudgil R, Michelakis ED, Archer SL (2006) The role of K+ channels in determining pulmonary vascular tone, oxygen sensing, cell proliferation, and apoptosis: implications in hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction and pulmonary arterial hypertension. Microcirculation 13:615–632
Overturf KE, Russell SN, Carl A, Vogalis F, Hart PJ, Hume JR, Sanders KM, Horowitz B (1994) Cloning and characterization of a Kv1.5 delayed rectifier K+ channel from vascular and visceral smooth muscles. Am J Physiol 267:C1231–C1238
Pancrazio JJ, Kamatchi GL, Roscoe AK, Lynch C 3rd (1998) Inhibition of neuronal Na+ channels by antidepressant drugs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 284:208–214
Perchenet L, Hilfiger L, Mizrahi J, Clement-Chomienne O (2001) Effects of anorexinogen agents on cloned voltage-gated K+ channel hKv1.5. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 298:1108–1119
Shah SJ, Gomberg-Maitland M, Thenappan T, Rich S (2009) Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors and the incidence and outcome of pulmonary hypertension. Chest 136:694–700
Snyders DJ (1999) Structure and function of cardiac potassium channels. Cardiovasc Res 42:377–390
Snyders DJ, Yeola SW (1995) Determinants of antiarrhythmic drug action. Electrostatic and hydrophobic components of block of the human cardiac hKv1.5 channel. Circ Res 77:575–583
Snyders DJ, Tamkun MM, Bennett PB (1993) A rapidly activating and slowly inactivating potassium channel cloned from human heart. Functional analysis after stable mammalian cell culture expression. J Gen Physiol 101:513–543
Standen NB, Quayle JM (1998) K+ channel modulation in arterial smooth muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 164:549–557
Thomas D, Gut B, Wendt-Nordahl G, Kiehn J (2002) The antidepressant drug fluoxetine is an inhibitor of human ether-a-go-go-related gene (HERG) potassium channels. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 300:543–548
Tytgat J, Maertens C, Daenens P (1997) Effect of fluoxetine on a neuronal, voltage-dependent potassium channel (Kv1.1). Br J Pharmacol 122:1417–1424
Wang Z, Fermini B, Nattel S (1993) Sustained depolarization-induced outward current in human atrial myocytes. Evidence for a novel delayed rectifier K+ current similar to Kv1.5 cloned channel currents. Circ Res 73:1061–1076
Weir EK, Olschewski A (2006) Role of ion channels in acute and chronic responses of the pulmonary vasculature to hypoxia. Cardiovasc Res 71:630–641
Weir EK, Lopez-Barneo J, Buckler KJ, Archer SL (2005) Acute oxygen-sensing mechanisms. N Engl J Med 353:2042–2055
Wong DT, Bymaster FP, Engleman EA (1995) Prozac (fluoxetine, Lilly 110140), the first selective serotonin uptake inhibitor and an antidepressant drug: twenty years since its first publication. Life Sci 57:411–441
Woodhull AM (1973) Ionic blockage of sodium channels in nerve. J Gen Physiol 61:687–708
Yeung SY, Millar JA, Mathie A (1999) Inhibition of neuronal KV potassium currents by the antidepressant drug, fluoxetine. Br J Pharmacol 128:1609–1615
Yuan XJ, Wang J, Juhaszova M, Gaine SP, Rubin LJ (1998) Attenuated K+ channel gene transcription in primary pulmonary hypertension. Lancet 351:726–727
Acknowledgment
We thank Dr. Kaczmarek (Yale University School of Medicine, USA) for the Kv1.5-transfected CHO cells. This work was supported by a grant from the Medical Research Center, Korea Science and Engineering Foundation, Republic of Korea (R13-2002-005-01002-0).
Disclosures
No conflicts of interest, financial or otherwise, are declared by the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, I., Yoon, S.H. & Hahn, S.J. Effects of dapoxetine on cloned Kv1.5 channels expressed in CHO cells. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 385, 707–716 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0754-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-012-0754-y