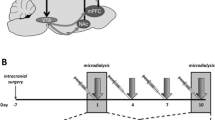
Abstract
Several lines of evidence implicate the neuropeptide substance P (SP) in the modulation of emotional behavior. Interaction between SP and noradrenergic systems has been proposed to be important in the regulation of stress, depression, and anxiety mechanisms; however, most evidence so far is based on studies in unchallenged and/or anesthetized animals. Thus, by using a dual-probe microdialysis approach in freely moving animals, the aim of the present study was to investigate whether a relevant stressor can trigger the release of SP in the locus coeruleus (LC) and whether and how this response modulates noradrenaline (NA) transmission both in the LC and in the medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), an important LC terminal region involved in emotional processing. While confirming previous reports that neurokinin 1 receptor (NK1R) antagonists activate cortical noradrenergic transmission under resting conditions, we present evidence that this interaction is opposite during stress challenge. Our results show that exposure to forced swimming considerably enhanced the release of SP and NA in the LC. Administration of a selective NK1R antagonist into the LC potentiated this NA response within the LC but abolished the stress-induced increase in NA release within the mPFC. These findings demonstrate stress-induced increase in endogenous extracellular SP levels within the LC exerting a facilitatory effect on the noradrenergic pathway to the mPFC. The attenuation of stress-induced hyperactivation of this pathway by NK1R antagonists, presumably via enhancing NA and autoinhibition in the LC, may contribute to the therapeutic efficacy of these drugs known to ameliorate symptoms of stress-related disorders.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LC:
-
locus coeruleus
- NA:
-
noradrenaline
- NK1R:
-
neurokinin 1 receptor
- SP:
-
substance P
- mPFC:
-
medial prefrontal cortex
References
Adell A (2004) Antidepressant properties of substance P antagonists: relationship to monoaminergic mechanisms? Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord 3:113–121
Aghajanian GK, Cedarbaum JM, Wang RY (1977) Evidence for norepinephrine-mediated collateral inhibition of locus coeruleus neurons. Brain Res 136:570–577
Berridge CW, Abercrombie ED (1999) Relationship between locus coeruleus discharge rates and rates of norepinephrine release within neocortex as assessed by in vivo microdialysis. Neuroscience 93:1263–1270
Bert L, Rodier D, Bougault I, Allouard N, Le-Fur G, Soubrie P, Steinberg R (2002) Permissive role of neurokinin NK(3) receptors in NK(1) receptor-mediated activation of the locus coeruleus revealed by SR 142801. Synapse 43:62–69
Blier P, Gobbi G, Haddjeri N, Santarelli L, Mathew G, Hen R (2004) Impact of substance P receptor antagonism on the serotonin and norepinephrine systems: relevance to the antidepressant/anxiolytic response. J Psychiatry Neurosci 29:208–218
Bremner JD, Krystal JH, Southwick SM, Charney DS (1996) Noradrenergic mechanisms in stress and anxiety: I. Preclinical studies. Synapse 23:28–38
Charney DS, Redmond DE Jr (1983) Neurobiological mechanisms in human anxiety. Evidence supporting central noradrenergic hyperactivity. Neuropharmacology 22:1531–1536
Cheeseman HJ, Pinnock RD, Henderson G (1983) Substance P excitation of rat locus coeruleus neurones. Eur J Pharmacol 94:93–99
Chen LW, Wei LC, Liu HL, Rao ZR (2000) Noradrenergic neurons expressing substance P receptor (NK1) in the locus coeruleus complex: a double immunofluorescence study in the rat. Brain Res 873:155–159
Dalley JW, Mason K, Stanford SC (1996) Increased levels of extracellular noradrenaline in the frontal cortex of rats exposed to naturalistic environmental stimuli: modulation by acute systemic administration of diazepam or buspirone. Psychopharmacology 127:47–54
Dazzi L, Vignone V, Seu E, Ladu S, Vacca G, Biggio G (2002) Inhibition by venlafaxine of the increase in norepinephrine output in rat prefrontal cortex elicited by acute stress or by the anxiogenic drug FG 7142. J Psychopharmacol 16:125–131
Devoto P, Flore G, Saba P, Fa M, Gessa GL (2005) Stimulation of the locus coeruleus elicits noradrenaline and dopamine release in the medial prefrontal and parietal cortex. J Neurochem 92:368–374
Ebner K, Singewald N (2006) The role of substance P in stress and anxiety responses. Amino Acids 31:251–272
Ebner K, Rupniak NM, Saria A, Singewald N (2004) Substance P in the medial amygdala: emotional stress-sensitive release and modulation of anxiety-related behavior in rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:4280–4285
Egan TM, Henderson G, North RA, Williams JT (1983) Noradrenaline-mediated synaptic inhibition in rat locus coeruleus neurones. J Physiol 345:477–488
Fernandez-Pastor B, Mateo Y, Gomez-Urquijo S, Javier Meana J (2005) Characterization of noradrenaline release in the locus coeruleus of freely moving awake rats by in vivo microdialysis. Psychopharmacology 180:570–579
Finlay JM, Zigmond MJ, Abercrombie ED (1995) Increased dopamine and norepinephrine release in medial prefrontal cortex induced by acute and chronic stress: effects of diazepam. Neuroscience 64:619–628
Florin-Lechner SM, Druhan JP, Aston-Jones G, Valentino RJ (1996) Enhanced norepinephrine release in prefrontal cortex with burst stimulation of the locus coeruleus. Brain Res 742:89–97
Gobbi G, Blier P (2005) Effect of neurokinin-1 receptor antagonists on serotoninergic, noradrenergic and hippocampal neurons: comparison with antidepressant drugs. Peptides 26:1383–1393
Guyenet PG, Aghajanian GK (1977) Excitation of neurons in the nucleus locus coeruleus by substance P and related peptides. Brain Res 136:178–184
Haddjeri N, Blier P (2000) Effect of neurokinin-I receptor antagonists on the function of 5-HT and noradrenaline neurons. NeuroReport 11:1323–1327
Hahn MK, Bannon MJ (1998) Tachykinin NK1 receptor antagonists enhance stress-induced c-fos in rat locus coeruleus. Eur J Pharmacol 348:155–160
Hahn MK, Bannon MJ (1999) Stress-induced C-fos expression in the rat locus coeruleus is dependent on neurokinin 1 receptor activation. Neuroscience 94:1183–1188
Harro J, Oreland L (2001) Depression as a spreading adjustment disorder of monoaminergic neurons: a case for primary implication of the locus coeruleus. Brain Res Brain Res Rev 38:79–128
Heidbreder CA, Groenewegen HJ (2003) The medial prefrontal cortex in the rat: evidence for a dorso-ventral distinction based upon functional and anatomical characteristics. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 27:555–579
Herpfer I, Lieb K (2005) Substance P receptor antagonists in psychiatry: rationale for development and therapeutic potential. CNS Drugs 19:275–293
Herpfer I, Hunt SP, Stanford SC (2005) A comparison of neurokinin 1 receptor knock-out (NK1−/−) and wildtype mice: exploratory behaviour and extracellular noradrenaline concentration in the cerebral cortex of anaesthetised subjects. Neuropharmacology 48:706–719
Hökfelt T, Broberger C, Xu ZQ, Sergeyev V, Ubink R, Diez M (2000) Neuropeptides—an overview. Neuropharmacology 39:1337–1356
Iijima K, Ohtomo K (1988) Immunocytochemical study using a GABA antiserum for the demonstration of inhibitory neurons in the rat locus ceruleus. Am J Anat 181:43–52
Jorm CM, Stamford JA (1993) Actions of the hypnotic anaesthetic, dexmedetomidine, on noradrenaline release and cell firing in rat locus coeruleus slices. Br J Anaesth 71:447–449
Kawahara Y, Kawahara H, Westerink BH (1999) Tonic regulation of the activity of noradrenergic neurons in the locus coeruleus of the conscious rat studied by dual-probe microdialysis. Brain Res 823:42–48
Kawahara H, Kawahara Y, Westerink BH (2000) The role of afferents to the locus coeruleus in the handling stress-induced increase in the release of noradrenaline in the medial prefrontal cortex: a dual-probe microdialysis study in the rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 387:279–286
Keller M, Montgomery S, Ball W, Morrison M, Snavely D, Liu G, Hargreaves R, Hietala J, Lines C, Beebe K, Reines S (2006) Lack of efficacy of the substance P (Neurokinin(1) Receptor) antagonist aprepitant in the treatment of major depressive disorder. Biol Psychiatry 59:216–23
Kramer MS, Cutler N, Feighner J, Shrivastava R, Carman J, Sramek JJ, Reines SA, Liu G, Snavely D, Wyatt-Knowles E, Hale JJ, Mills SG, MacCoss M, Swain CJ, Harrison T, Hill RG, Hefti F, Scolnick EM, Cascieri MA, Chicchi GG, Sadowski S, Williams AR, Hewson L, Smith D, Carlson EJ, Hargreaves RJ, Rupniak NM (1998) Distinct mechanism for antidepressant activity by blockade of central substance P receptors. Science 281:1640–1645
Kramer MS, Winokur A, Kelsey J, Preskorn SH, Rothschild AJ, Snavely D, Ghosh K, Ball WA, Reines SA, Munjack D, Apter JT, Cunningham L, Kling M, Bari M, Getson A, Lee Y (2004) Demonstration of the efficacy and safety of a novel substance P (NK1) receptor antagonist in major depression. Neuropsychopharmacology 29:385–392
Kubota T, Hirota K, Yoshida H, Takahashi S, Anzawa N, Ohkawa H, Kushikata T, Matsuki A (1999) Effects of sedatives on noradrenaline release from the medial prefrontal cortex in rats. Psychopharmacology 146:335–338
Landgraf R, Neumann ID (2004) Vasopressin and oxytocin release within the brain: a dynamic concept of multiple and variable modes of neuropeptide communication. Front Neuroendocrinol 25:150–176
Ljungdahl A, Hökfelt T, Nilsson G (1978) Distribution of substance P-like immunoreactivity in the central nervous system of the rat–I. Cell bodies and nerve terminals. Neuroscience 3:861–943
Ludwig M, Pittman QJ (2003) Talking back: dendritic neurotransmitter release. Trends Neurosci 26:255–261
Ma QP, Bleasdale C (2002) Modulation of brain stem monoamines and gamma-aminobutyric acid by NK1 receptors in rats. NeuroReport 13:1809–1812
Mateo Y, Pineda J, Meana JJ (1998) Somatodendritic alpha2-adrenoceptors in the locus coeruleus are involved in the in vivo modulation of cortical noradrenaline release by the antidepressant desipramine. J Neurochem 71:790–798
Maubach KA, Martin K, Chicchi G, Harrison T, Wheeldon A, Swain CJ, Cumberbatch MJ, Rupniak NM, Seabrook GR (2002) Chronic substance P (NK1) receptor antagonist and conventional antidepressant treatment increases burst firing of monoamine neurones in the locus coeruleus. Neuroscience 109:609–617
McLean S (1996) Nonpeptide antagonists of the NK1 tachykinin receptor. Med Res Rev 16:297–317
McLean S, Ganong A, Seymour PA, Snider RM, Desai MC, Rosen T, Bryce DK, Longo KP, Reynolds LS, Robinson G, Schmidt AW, Siok C, Heym J (1993) Pharmacology of CP-99,994; a nonpeptide antagonist of the tachykinin neurokinin-1 receptor. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 267:472–479
Millan MJ, Lejeune F, De Nanteuil G, Gobert A (2001) Selective blockade of neurokinin (NK)(1) receptors facilitates the activity of adrenergic pathways projecting to frontal cortex and dorsal hippocampus in rats. J Neurochem 76:1949–1954
Morilak DA, Barrera G, Echevarria DJ, Garcia AS, Hernandez A, Ma S, Petre CO (2005) Role of brain norepinephrine in the behavioral response to stress. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 29:1214–24
Morrison JH, Molliver ME, Grzanna R, Coyle JT (1979) Noradrenergic innervation patterns in three regions of medial cortex: an immunofluorescence characterization. Brain Res Bull 4:849–857
Muigg P, Sartori SB, Sparber T, Landgraf R, Singewald N (2006) Reduced depression-like behavior in HAB rats after NK1-receptor antagonist treatment is associated with an altered neuronal activation pattern in specific brain areas. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 372(Suppl. 1):79
Nakane H, Shimizu N, Hori T (1994) Stress-induced norepinephrine release in the rat prefrontal cortex measured by microdialysis. Am J Physiol 267:R1559–R1566
Nakaya Y, Kaneko T, Shigemoto R, Nakanishi S, Mizuno N (1994) Immunohistochemical localization of substance P receptor in the central nervous system of the adult rat. J Comp Neurol 347:249–274
Page ME, Lucki I (2002) Effects of acute and chronic reboxetine treatment on stress-induced monoamine efflux in the rat frontal cortex. Neuropsychopharmacology 27:237–247
Pan WH, Lai YJ (1995) Anesthetics decreased the microdialysis extraction fraction of norepinephrine but not dopamine in the medial prefrontal cortex. Synapse 21:85–92
Paxinos G, Watson C (1998) The rat brain in stereotaxic coordinates. Academic, San Diego
Pickel VM, Joh TH, Reis DJ, Leeman SE, Miller RJ (1979) Electron microscopic localization of substance P and enkephalin in axon terminals related to dendrites of catecholaminergic neurons. Brain Res 160:387–400
Pudovkina OL, Westerink BH (2005) Release of noradrenaline in the locus coeruleus. In: Ludwig M (ed) Dendritic neurotransmitter release. Springer, Berlin, pp 145–153
Redmond DE Jr, Huang YH (1979) Current concepts. II. New evidence for a locus coeruleus–norepinephrine connection with anxiety. Life Sci 25:2149–2162
Renoldi G, Invernizzi RW (2006) Blockade of tachykinin NK1 receptors attenuates stress-induced rise of extracellular noradrenaline and dopamine in the rat and gerbil medial prefrontal cortex. J Neurosci Res 84:961–968
Rupniak NM (2002) New insights into the antidepressant actions of substance P (NK1 receptor) antagonists. Can J Physiol Pharmacol 80:489–494
Sacchetti G, Bonini I, Waeterloos GC, Samanin R (1993) Tianeptine raises dopamine and blocks stress-induced noradrenaline release in the rat frontal cortex. Eur J Pharmacol 236:171–175
Saffroy M, Beaujouan JC, Petitet F, Torrens Y, Glowinski J (1994) Differential localization of 3H-[Pro9]SP binding sites in the guinea pig and rat brain. Brain Res 633:317–325
Saria A (1999) The tachykinin NK1 receptor in the brain: pharmacology and putative functions. Eur J Pharmacol 375:51–60
Sarter M, Bruno JP, Parikh V (2007) Abnormal neurotransmitter release underlying behavioral and cognitive disorders: toward concepts of dynamic and function-specific dysregulation. Neuropsychopharmacology 32:1452–1461
Shimokawa A, Jin QH, Ishizuka Y, Kunitake T, Takasaki M, Kannan H (1998) Effects of anesthetics on norepinephrine release in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus region of awake rats. Neurosci Lett 244:21–24
Shults CW, Quirion R, Chronwall B, Chase TN, O’Donohue TL (1984) A comparison of the anatomical distribution of substance P and substance P receptors in the rat central nervous system. Peptides 5:1097–1128
Singewald N, Philippu A (1993) Catecholamine release in the locus coeruleus is modified by experimentally induced changes in haemodynamics. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 347:21–27
Singewald N, Philippu A (1998) Release of neurotransmitters in the locus coeruleus. Prog Neurobiol 56:237–267
Singewald N, Schneider C, Pfitscher A, Philippu A (1994) In vivo release of catecholamines in the locus coeruleus. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 350:339–345
Singewald N, Kaehler ST, Philippu A (1999) Noradrenaline release in the locus coeruleus of conscious rats is triggered by drugs, stress and blood pressure changes. NeuroReport 10:1583–1587
Stanford SC (1995) Central noradrenergic neurones and stress. Pharmacol Ther 68:297–242
Steinberg R, Alonso R, Rouquier L, Desvignes C, Michaud JC, Cudennec A, Jung M, Simiand J, Griebel G, Emonds-Alt X, Le Fur G, Soubrie P (2002) SSR240600 [(R)-2-(1-{2-[4-{2-[3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]acetyl}-2-(3,4-dichlorophenyl)-2-morpholinyl]ethyl}-4-piperidinyl)-2-methylpropanamide], a centrally active nonpeptide antagonist of the tachykinin neurokinin 1 receptor. II. Neurochemical and behavioral characterization. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 303:1180–1188
Tamiya R, Inoue K, Takagi H (1994) GABA-ergic and substance P-ergic double-innervation to noradrenergic neurons in the rat locus coeruleus. Osaka City Med J 40:1–11
van Bockstaele EJ (1998) Morphological substrates underlying opioid, epinephrine and gamma-aminobutyric acid inhibitory actions in the rat locus coeruleus. Brain Res Bull 47:1–15
van Praag HM (2005) Can stress cause depression? World J Biol Psychiatry 6(Suppl 2):5–22
Weiss GK, Ratner A, Voltura A, Savage D, Lucero K, Castillo N (1994) The effect of two different types of stress on locus coeruleus alpha-2 receptor binding. Brain Res Bull 33:219–221
Zocchi A, Varnier G, Arban R, Griffante C, Zanetti L, Bettelini L, Marchi M, Gerrard PA, Corsi M (2003) Effects of antidepressant drugs and GR 205171, an neurokinin-1 (NK1) receptor antagonist, on the response in the forced swim test and on monoamine extracellular levels in the frontal cortex of the mouse. Neurosci Lett 345:73–76
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a grant from the Österreichische Nationalbank (N.S.) and by the Austrian Academy of Sciences (K.E.). The authors would like to thank Peter Bauer for excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ebner, K., Singewald, N. Stress-induced release of substance P in the locus coeruleus modulates cortical noradrenaline release. Naunyn-Schmied Arch Pharmacol 376, 73–82 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0185-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00210-007-0185-3