Abstract
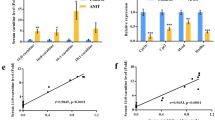
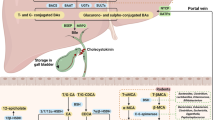
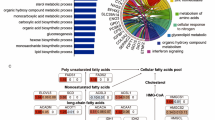
Consumption of herbal products containing pyrrolizidine alkaloids (PAs) is one of the major causes for hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (HSOS), a deadly liver disease. However, the crucial metabolic variation and biomarkers which can reflect these changes remain amphibious and thus to result in a lack of effective prevention, diagnosis and treatments against this disease. The aim of the study was to determine the impact of HSOS caused by PA exposure, and to translate metabolomics-derived biomarkers to the mechanism. In present study, cholic acid species (namely, cholic acid, taurine conjugated-cholic acid, and glycine conjugated-cholic acid) were identified as the candidate biomarkers (area under the ROC curve 0.968 [95% CI 0.908–0.994], sensitivity 83.87%, specificity 96.55%) for PA-HSOS using two independent cohorts of patients with PA-HSOS. The increased primary bile acid biosynthesis and decreased liver expression of farnesoid X receptor (FXR, which is known to inhibit bile acid biosynthesis in hepatocytes) were highlighted in PA-HSOS patients. Furtherly, a murine PA-HSOS model induced by senecionine (50 mg/kg, p.o.), a hepatotoxic PA, showed increased biosynthesis of cholic acid species via inhibition of hepatic FXR-SHP singling and treatment with the FXR agonist obeticholic acid restored the cholic acid species to the normal levels and protected mice from senecionine-induced HSOS. This work elucidates that increased levels of cholic acid species can serve as diagnostic biomarkers in PA-HSOS and targeting FXR may represent a therapeutic strategy for treating PA-HSOS in clinics.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The authors declare that the data supporting the findings of this study are available within the paper. All other data are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Cholic acid
- CYP7A1:
-
Cholesterol 7-alpha-hydroxylase
- CYP8B1:
-
Sterol 12-alpha-hydroxylase
- FXR:
-
Farnesoid X receptor
- GCA:
-
Glycocholic acid
- HSOS:
-
Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome
- HBV:
-
Hepatitis B virus infections
- PBC:
-
Primary biliary cirrhosis
- PA:
-
Pyrrolizidine alkaloid
- PPAs:
-
Pyrrole-protein adducts
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- SHP:
-
Small heterodimer partner
- TCA:
-
Taurocholic acid
- OCA:
-
Obeticholic acid
References
Aubrecht J, Schomaker SJ, Amacher DE (2013) Emerging hepatotoxicity biomarkers and their potential to improve understanding and management of drug-induced liver injury. Genome Med 5(9):85
Beger RD, Dunn WB, Bandukwala A, Bethan B, Broadhurst D, Clish CB, Dasari S, Derr L, Evans A, Fischer S, Flynn T, Hartung T, Herrington D, Higashi R, Hsu PC, Jones C, Kachman M, Karuso H, Kruppa G, Lippa K, Maruvada P, Mosley J, Ntai I, O’Donovan C, Playdon M, Raftery D, Shaughnessy D, Souza A, Spaeder T, Spalholz B, Tayyari F, Ubhi B, Verma M, Walk T, Wilson I, Witkin K, Bearden DW, Zanetti KA (2019) Towards quality assurance and quality control in untargeted metabolomics studies. Metabolomics 15(1):4
Chalasani NP, Maddur H, Russo MW, Wong RJ, Reddy KR (2021) Practice parameters committee of the american college of gastroenterology. ACG clinical guideline: diagnosis and management of idiosyncratic drug-induced liver injury. Am J Gastroenterol 116(5):878–898
Chen WH, Wei YR, Xiong AZ, Li YM, Guan H, Wang Q, Miao Q, Bian Z, Xiao X, Lian M, Zhang J, Li B, Cao Q, Fan Z, Zhang W, Qiu D, Fang J, Gershwin ME, Yang L, Tang RQ, Ma X (2020a) Comprehensive analysis of serum and fecal bile acid profiles and interaction with gut microbiota in Primary Biliary Cholangitis. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 58(1):25–38
Chen Y, Xiong F, Wang WQ, Jiang KY, Ye XL, Deng G, Wang CH, Yang L, Xiong AZ, Wang ZT (2020b) The long persistence of pyrrolizidine alkaloid-derived pyrrole-protein adducts in vivo: kinetic study following multiple exposures of a pyrrolizidine alkaloid containing extract of Gynura japonica. Toxicol Lett 323:41–47
Chiang JY (2003) Bile acid regulation of hepatic physiology: III. Bile acids and nuclear receptors. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284(3):G349–G356
Danan G, Bénichou C (1993) Causality assessment of adverse reactions to drugs–I. A novel method based on the conclusions of international consensus meetings: Application to drug-induced liver injuries. J Clin Epidemiol 46:1323–1330
DeLeve LD, McCuskey RS, Wang X, Hu L, McCuskey MK, Epstein RB, Kanel GC (1999) Characterization of a reproducible rat model of hepatic veno-occlusive disease. Hepatology 29:1779–1791
DeLeve LD, Ito Y, Bethea NW, McCuskey MK, Wang X, McCuskey RS (2003) Embolization by sinusoidal lining cells obstructs the microcirculation in rat sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 284:G1045–G1052
Ding LL, Zhang EY, Yang Q, Jin L, Sousa KM, Dong B, Wang Y, Tu J, Ma X, Tian J, Zhang H, Fang Z, Guan A, Zhang Y, Wang ZT, Moore DD, Yang L, Huang WD (2021) Vertical sleeve gastrectomy confers metabolic improvements by reducing intestinal bile acids and lipid absorption in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 118:e2019388118
Gao H, Ruan JQ, Chen J, Li N, Ke CQ, Ye Y, Lin G, Wang JY (2015) Blood pyrrole-protein adducts as a diagnostic and prognostic index in pyrrolizidine alkaloid-hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Drug Des Devel Ther 9:4861–4868
Ghallab A, Hassan R, Hofmann U, Friebel A, Hobloss Z, Brackhagen L, Begher-Tibbe B, Myllys M, Reinders J, Overbeck N, Sezgin S, Zühlke S, Seddek AL, Murad W, Brecklinghaus T, Kappenberg F, Rahnenführer J, González D, Goldring C, Copple IM, Marchan R, Longerich T, Vucur M, Luedde T, Urban S, Canbay A, Schreiter T, Trauner M, Akakpo JY, Olyaee M, Curry SC, Sowa JP, Jaeschke H, Hoehme S, Hengstler JG (2022) Interruption of bile acid uptake by hepatocytes after acetaminophen overdose ameliorates hepatotoxicity. J Hepatol 77(1):71–83
Goodwin B, Jones SA, Price RR, Watson MA, McKee DD, Moore LB, Galardi C, Wilson JG, Lewis MC, Roth ME, Maloney PR, Willson TM, Kliewei SA (2000) A regulatory cascade of the nuclear receptors FXR, SHP-1, and LRH-1 represses bile acid biosynthesis. Mol Cell 6:517–526
He Y, Ma J, Fan X, Ding L, Ding X, Zhang QY, Lin G (2021) The key role of gut-liver axis in pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced hepatotoxicity and enterotoxicity. Acta Pharm Sin B 11(12):3820–3835
Hessel-Pras S, Braeuning A, Guenther G, Adawy A, Enge AM, Ebmeyer J, Henderson CJ, Hengstler JG, Lampen A, Reif R (2020) The pyrrolizidine alkaloid senecionine induces CYP-dependent destruction of sinusoidal endothelial cells and cholestasis in mice. Arch Toxicol 94:219–229
Hoofnagle JH, Björnsson ES (2019) Drug-induced liver injury—types and phenotypes. N Engl J Med 381:264–273
Huang ZL, Jing X, Sheng Y, Zhang J, Hao Z, Wang ZT, Ji LL (2019) (-)-Epicatechin attenuates hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome by inhibiting liver oxidative and inflammatory injury. Redox Biol 22:101117
Inagaki T, Choi M, Moschetta A, Peng L, Cummins CL, McDonald JG, Luo G, Jones SA, Goodwin B, Richardson JA, Gerard RD, Repa JJ, Mangelsdorf DJ, Kliewer SA (2005) Fibroblast growth factor 15 functions as an enterohepatic signal to regulate bile acid homeostasis. Cell Metab 2:217–225
IPCS; International Programme on Chemical Safety (1988) Environmental health criteria 80: pyrrolizidine alkaloids. World Health Organization, Geneva
Jones RJ, Lee KS, Beschorner WE, Vogel VG, Grochow LB, Braine HG, Vogelsang GB, Sensenbrenner LL, Santos GW, Saral R (1987) Venoocclusive disease of the liver following bone marrow transplantation. Transplantation 44:778–783
Lee FY, de Aguiar Vallim TQ, Chong HK, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Jones SA, Osborne TF, Edwards PA (2010) Activation of the farnesoid X receptor provides protection against acetaminophen-induced hepatic toxicity. Mol Endocrinol 24:1626–1636
Li-Hawkins J, Gåfvels M, Olin M, Lund EG, Andersson U, Schuster G, Björkhem I, Russell DW, Eggertsen G (2002) Cholic acid mediates negative feedback regulation of bile acid synthesis in mice. J Clin Invest 110:1191–1200
Lin G, Wang JY, Li N, Li M, Gao H, Ji Y, Zhang F, Wang H, Zhou Y, Ye Y, Xu HX, Zheng J (2011) Hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome associated with consumption of Gynura segetum. J Hepatology 54(4):666–673
Makishima M, Okamoto AY, Repa JJ, Tu H, Learned RM, Luk A, Hull MV, Lustig KD, Mangelsdorf DJ, Shan B (1999) Identification of a nuclear receptor for bile acids. Science 284:1362–1365
McDonald GB, Sharma P, Matthews DE, Shulman HM, Thomas ED (1984) Venocclusive disease of the liver after bone marrow transplantation: diagnosis, incidence, and predisposing factors. Hepatology 4:116–122
Mendel VE, Witt MR, Gitchell BS, Gribble DN, Rogers QR, Segall HJ, Knight HD (1988) Pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced liver disease in horses: an early diagnosis. Am J Vet Res 49:572–578
Mohty M, Malard F, Abecassis M, Aerts E, Alaskar AS, Aljurf M, Arat M, Bader P, Baron F, Bazarbachi A, Blaise D, Ciceri F, Corbacioglu S, Dalle JH, Dignan F, Fukuda T, Huynh A, Masszi T, Michallet M, Nagler A, NiChonghaile M, Okamoto S, Pagliuca A, Peters C, Petersen FB, Richardson PG, Ruutu T, Savani BN, Wallhult E, Yakoub-Agha I, Duarte RF, Carreras E (2016) Revised diagnosis and severity criteria for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease in adult patients: a new classification from the European Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 51:906–912
Myant NB, Mitropoulos KA (1977) Cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase. J Lipid Res 18(2):135–153
Nevens F, Andreone P, Mazzella G, Strasser SI, Bowlus C, Invernizzi P, Drenth JP, Pockros PJ, Regula J, Beuers U, Trauner M, Jones DE, Floreani A, Hohenester S, Luketic V, Shiffman M, van Erpecum KJ, Vargas V, Vincent C, Hirschfield GM, Shah H, Hansen B, Lindor KD, Marschall HU, Kowdley KV, Hooshmand-Rad R, Marmon T, Sheeron S, Pencek R, MacConell L, Pruzanski M, Shapiro D, POISE Study Group (2016) A placebo-controlled trial of obeticholic acid in primary biliary cholangitis. N Engl J Med 375:631–643
Pang X, Tang C, Cao P, Zhou L, Chen X (2021) Metabolic activation of retrorsine may disrupt bile acid homeostasis in mice through the Nrf2 pathway. Curr Drug Metab 22(11):870–881
Parks DJ, Blanchard SG, Bledsoe RK, Chandra G, Consler TG, Kliewer SA, Stimmel JB, Willson TM, Zavacki AM, Moore DD, Lehmann JM (1999) Bile acids: Natural ligands for an orphan nuclear receptor. Science 284:1365–1368
Pellicciari R, Fiorucci S, Camaioni E, Clerici C, Costantino G, Maloney PR, Morelli A, Parks DJ, Willson TM (2002) 6α-Ethyl-chenodeoxycholic acid (6-ECDCA), a potent and selective FXR agonist endowed with anticholestatic activity. J Med Chem 45:3569–3572
Russell DW (2003) The enzymes, regulation, and genetics of bile acid synthesis. Annu Rev Biochem 72:137–174
Sang C, Wang X, Zhou K, Sun T, Bian H, Gao X, Wang Y, Zhang H, Jia W, Liu P, Xie G, Chen T (2021) Bile acid profiles are distinct among patients with different etiologies of chronic liver disease. J Proteome Res 20(5):2340–2351
Schadt HS, Wolf A, Pognan F, Chibout SD, Merz M, Kullak-Ublick GA (2016) Bile acids in drug induced liver injury: Key players and surrogate markers. Clin Res Hepatol Gastroenterol 40(3):257–266
Schwabl P, Hambruch E, Seeland BA, Hayden H, Wagner M, Garnys L, Strobel B, Schubert TL, Riedl F, Mitteregger D, Burnet M, Starlinger P, Oberhuber G, Deuschle U, Rohr-Udilova N, Podesser BK, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Reiberger T, Kremoser C, Trauner M (2017) The FXR agonist PX20606 ameliorates portal hypertension by targeting vascular remodeling and sinusoidal dysfunction. J Hepatol 66(4):724–733
Shang H, Bai T, Zhu S, Yang X, Liu C, Xu D, Zhuge Y, Song Y, Hou X (2021) Prognostic factors for pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome: a multicenter study in China. Ann Transl Med 9:11
Song KH, Li T, Owsley E, Strom S, Chiang JY (2009) Bile acids activate fibroblast growth factor 19 signaling in human hepatocytes to inhibit cholesterol 7 alpha-hydroxylase gene expression. Hepatology 49:297–305
Sutherland RJ, Deol HS, Hood PJ (1992) Changes in plasma bile acids, plasma amino acids, and hepatic enzyme pools as indices of functional impairment in liver-damaged sheep. Vet Clin Pathol 21:51–56
Tian Q, Yang R, Wang Y, Liu J, Wee A, Saxena R, Wang L, Li M, Liu L, Shan S, Kong Y, Ma H, Ou X, You H, Zhao X, Jia J (2021) A high serum level of taurocholic acid is correlated with the severity and resolution of drug-induced liver injury. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 19(5):1009–1019
Verbeke L, Farre R, Trebicka J, Komuta M, Roskams T, Klein S, Elst IV, Windmolders P, Vanuytsel T, Nevens F, Laleman W (2014) Obeticholic acid, a farnesoid X receptor agonist, improves portal hypertension by two distinct pathways in cirrhotic rats. Hepatology 59:2286–2298
Waizenegger J, Glück J, Henricsson M, Luckert C, Braeuning A, Hessel-Pras S (2021) Pyrrolizidine alkaloids disturb bile acid homeostasis in the human hepatoma cell line HepaRG. Foods 10(1):161
Wang YD, Chen WD, Moore DD, Huang WD (2008) FXR: a metabolic regulator and cell protector. Cell Res 18:1087–1095
Wang Y, Qiao D, Li Y, Xu F (2018) Risk factors for hepatic veno-occlusive disease caused by Gynura segetum: A retrospective study. BMC Gastroenterol 18:156
Wang WQ, Chen Y, Yin Y, Wang XJ, Ye XL, Jiang KY, Zhang Y, Zhang JW, Zhang W, Zhuge YZ, Chen L, Peng C, Xiong AZ, Yang L, Wang ZT (2022a) A TMT-based shotgun proteomics uncovers overexpression of thrombospondin 1 as a contributor in pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Arch Toxicol 96(7):2003–2019
Wang Z, Ma J, He Y, Miu KK, Yao S, Tang C, Ye Y, Lin G (2022b) Nrf2-mediated liver protection by 18β-glycyrrhetinic acid against pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced toxicity through PI3K/Akt/GSK3β pathway. Phytomedicine 102:154162
Wei J, Chen T, Liu YM, Sun S, Yuan Z, Zhang Y, Xiong AZ, Li LN, Wang ZT, Yang L (2023) Targeted bile acids metabolomics in cholesterol gallbladder polyps and gallstones: From analytical method development towards application to clinical samples. J Pharm Anal 13(9):1080–1087
Willmot FC, Robertson GW (1920) Senecio disease, or cirrhosis of the liver due to Senecio poisoning. Lancet 196:848–849
Woolbright BL, McGill MR, Staggs VS, Winefield RD, Gholami P, Olyaee M, Sharpe MR, Curry SC, Lee WM, Jaeschke H, Acute Liver Failure Study Group (2014) Glycodeoxycholic acid levels as prognostic biomarker in acetaminophen-induced acute liver failure patients. Toxicol Sci 142:436–444
Xiong AZ, Yang F, Fang L, Yang L, He Y, Wan YJ, Xu Y, Qi M, Wang X, Yu K, Tsim KW, Wang ZT (2014) Metabolomic and genomic evidence for compromised bile acid homeostasis by senecionine, a hepatotoxic pyrrolizidine alkaloid. Chem Res Toxicol 27:775–786
Xiong AZ, Shao YL, Fang L, Yang X, Zhang S, Zheng J, Ding W, Yang L, Wang ZT (2019) Comparative analysis of toxic components in different medicinal parts of Gynura japonica and its toxicity assessment on mice. Phytomedicine 54:77–88
Xiong H, Zhang C, Han L, Xu T, Saeed K, Han J, Liu J, Klaassen CD, Gonzalez FJ, Lu Y, Zhang Y (2022) Suppressed farnesoid X receptor by iron overload in mice and humans potentiates iron-induced hepatotoxicity. Hepatology 76(2):387–403
Yamazaki M, Miyake M, Sato H, Masutomi N, Tsutsui N, Adam KP, Alexander DC, Lawton KA, Milburn MV, Ryals JA, Wulff JE, Guo L (2013) Perturbation of bile acid homeostasis is an early pathogenesis event of drug induced liver injury in rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 268:79–89
Yan T, Yan N, Wang H, Yagai T, Luo Y, Takahashi S, Zhao M, Krausz KW, Wang G, Hao H, Gonzalez FJ (2021) FXR-deoxycholic acid-TNF-α axis modulates acetaminophen-induced hepatotoxicity. Toxicol Sci 181(2):273–284
Yang F, Huang X, Yi T, Yen Y, Moore DD, Huang WD (2007) Spontaneous development of liver tumors in the absence of the bile acid receptor farnesoid X receptor. Cancer Res 67:863–867
Yang L, Xiong AZ, He YQ, Wang ZY, Wang CH, Wang ZT, Li W, Yang L, Hu ZB (2008) Bile acids metabonomic study on the CCl4- and alpha-naphthylisothiocyanate-induced animal models: Quantitative analysis of 22 bile acids by ultraperformance liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Chem Res Toxicol 21:2280–2288
Yang F, Tang X, Ding L, Zhou Y, Yang Q, Gong J, Wang G, Wang Z, Yang L (2016) Curcumin protects ANIT-induced cholestasis through signaling pathway of FXR-regulated bile acid and inflammation. Sci Rep 6:33052
Yang X, Wang H, Ni HM, Xiong AZ, Wang ZT, Sesaki H, Ding WX, Yang L (2017) Inhibition of Drp1 protects against senecionine-induced mitochondria-mediated apoptosis in primary hepatocytes and in mice. Redox Biol 12:264–273
Zhang L, Wei TT, Li Y, Li J, Fan Y, Huang FQ, Cai YY, Ma G, Liu JF, Chen QQ, Wang SL, Li H, Alolga RN, Liu B, Zhao DS, Shen JH, Wang XM, Zhu W, Li P, Qi LW (2018) Functional metabolomics characterizes a key role for N-acetylneuraminic acid in coronary artery diseases. Circulation 137:1374–1390
Zhang W, Liu L, Zhang M, Zhang F, Peng C, Zhang B, Chen J, Li L, He J, Xiao J, Feng Y, Wang X, Xiong A, Yang L, Zou X, Yu Y, Zhuge YZ (2021) Validation of the Nanjing Criteria for diagnosing pyrrolizidine alkaloids-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. J Clin Transl Hepatol 9:345–352
Zhu L, Zhang CY, Li DP, Chen HB, Ma J, Gao H, Ye Y, Wang JY, Fu PP, Lin G (2021) Tu-San-Qi (Gynura japonica): the culprit behind pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced liver injury in China. Acta Pharmacol Sin 42(8):1212–1222
Zhuge YZ, Wang Y, Zhang F, Zhu CK, Zhang W, Zhang M, He Q, Yang J, He J, Chen J, Zou XP (2018) Clinical characteristics and treatment of pyrrolizidine alkaloid-related hepatic vein occlusive disease. Liver Int 38:1867–1874
Zhuge YZ, Liu Y, Xie W, Zou X, Xu J, Wang J (2019) Chinese society of gastroenterology committee of hepatobiliary disease. Expert consensus on the clinical management of pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 34:634–642
Funding
This work was funded by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81603384 and 82122074), the Nature Science Foundation of Shanghai (No. 20ZR1473300, 23ZR1463200), Changjiang Scholars Programme of China (No. T2022255), the Shanghai Rising-Star Program (No. 17QA1403600), and the Shanghai Talents Development Foundation (No. 2020099).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Aizhen Xiong, Lili Ding, Zhengtao Wang, and Li Yang for study conception and design; Aizhen Xiong, Longhui Lu, Kaiyuan Jiang, Xiaoning Wang, Yan Chen, Wei Zhang, Qi Liao, Fan Yang, Yuzheng Zhuge, and Ping Liu participant screening and collection; Aizhen Xiong, Xiaoning Wang, and Lujin Li for statistical analysis and interpretation of data; Aizhen Xiong and Lili Ding for drafting of the manuscript; Wendong Huang, Fan Yang, Li Yang, and Zhengtao Wang for manuscript review and critical revision; Aizhen Xiong, Lili Ding, Zhengtao Wang, and Li Yang for obtaining funding.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no completing interests.
Ethical approval
Approved by Shanghai University of Traditional Chinese Medicine and Drum Tower Hospital of Nanjing.
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed to publish this manuscript.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, A., Lu, L., Jiang, K. et al. Functional metabolomics characterizes the contribution of farnesoid X receptor in pyrrolizidine alkaloid-induced hepatic sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Arch Toxicol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-024-03762-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-024-03762-x