Abstract
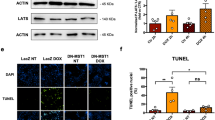
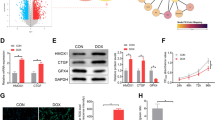
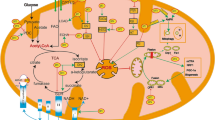
Administration of CHK1-targeted anticancer therapies is associated with an increased cumulative risk of cardiac complications, which is further amplified when combined with gemcitabine. However, the underlying mechanisms remain elusive. In this study, we generated hiPSC-CMs and murine models to elucidate the mechanisms underlying CHK1 inhibition combined with gemcitabine-induced cardiotoxicity and identify potential targets for cardioprotection. Mice were intraperitoneally injected with 25 mg/kg CHK1 inhibitor AZD7762 and 20 mg/kg gemcitabine for 3 weeks. hiPSC-CMs and NMCMs were incubated with 0.5 uM AZD7762 and 0.1 uM gemcitabine for 24 h. Both pharmacological inhibition or genetic deletion of CHK1 and administration of gemcitabine induced mtROS overproduction and pyroptosis in cardiomyocytes by disrupting mitochondrial respiration, ultimately causing heart atrophy and cardiac dysfunction in mice. These toxic effects were further exacerbated with combination administration. Using mitochondria-targeting sequence-directed vectors to overexpress CHK1 in cardiomyocyte (CM) mitochondria, we identified the localization of CHK1 in CM mitochondria and its crucial role in maintaining mitochondrial redox homeostasis for the first time. Mitochondrial CHK1 function loss mediated the cardiotoxicity induced by AZD7762 and CHK1-knockout. Mechanistically, mitochondrial CHK1 directly phosphorylates SIRT3 and promotes its expression within mitochondria. On the contrary, both AZD7762 or CHK1-knockout and gemcitabine decreased mitochondrial SIRT3 abundance, thus resulting in respiration dysfunction. Further hiPSC-CMs and mice experiments demonstrated that SIRT3 overexpression maintained mitochondrial function while alleviating CM pyroptosis, and thereby improving mice cardiac function. In summary, our results suggest that targeting SIRT3 could represent a novel therapeutic approach for clinical prevention and treatment of cardiotoxicity induced by CHK1 inhibition and gemcitabine.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request for purposes of reproducing the results or replicating the procedure.
References
Bartek J, Lukas J (2003) Chk1 and Chk2 kinases in checkpoint control and cancer. Cancer Cell 3(5):421–429. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1535-6108(03)00110-7
Benegiamo G, Bou Sleiman M, Wohlwend M et al (2022) COX7A2L genetic variants determine cardiorespiratory fitness in mice and human. Nat Metab 4(10):1336–1351. https://doi.org/10.1038/s42255-022-00655-0
Bruchard M, Mignot G, Derangère V et al (2013) Chemotherapy-triggered cathepsin B release in myeloid-derived suppressor cells activates the Nlrp3 inflammasome and promotes tumor growth. Nat Med 19(1):57–64. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2999
Cheng B, Pan W, Xing Y, Xiao Y, Chen J, Xu Z (2022) Recent advances in DDR (DNA damage response) inhibitors for cancer therapy. Eur J Med Chem 230:114109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmech.2022.114109
da Costa A, Chowdhury D, Shapiro GI, D’Andrea AD, Konstantinopoulos PA (2023) Targeting replication stress in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 22(1):38–58. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41573-022-00558-5
Deng Y, Xie M, Li Q et al (2021) Targeting mitochondria-inflammation circuit by beta-hydroxybutyrate mitigates HFpEF. Circ Res 128(2):232–245. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.317933
Dent P (2019) Investigational CHK1 inhibitors in early phase clinical trials for the treatment of cancer. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 28(12):1095–1100. https://doi.org/10.1080/13543784.2019.1694661
Fan Y, Cheng Y, Li Y et al (2020) Phosphoproteomic analysis of neonatal regenerative myocardium revealed important roles of checkpoint kinase 1 via activating mammalian target of rapamycin C1/ribosomal protein S6 kinase b-1 pathway. Circulation 141(19):1554–1569. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.119.040747
Guo Y, Wang J, Benedict B et al (2021) Targeting CDC7 potentiates ATR-CHK1 signaling inhibition through induction of DNA replication stress in liver cancer. Genome Med 13(1):166. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-021-00981-0
Hilmi M, Ederhy S, Waintraub X et al (2020) Cardiotoxicity associated with gemcitabine: literature review and a pharmacovigilance study. Pharmaceuticals (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/ph13100325
Isono M, Hoffmann MJ, Pinkerneil M et al (2017) Checkpoint kinase inhibitor AZD7762 strongly sensitises urothelial carcinoma cells to gemcitabine. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 36(1):1. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-016-0473-1
Jin L, Geng L, Ying L et al (2022) FGF21-sirtuin 3 axis confers the protective effects of exercise against diabetic cardiomyopathy by governing mitochondrial integrity. Circulation 146(20):1537–1557. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.122.059631
Ju HQ, Gocho T, Aguilar M et al (2015) Mechanisms of overcoming intrinsic resistance to gemcitabine in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma through the redox modulation. Mol Cancer Ther 14(3):788–798. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-14-0420
Koh SB, Courtin A, Boyce RJ, Boyle RG, Richards FM, Jodrell DI (2015) CHK1 inhibition synergizes with gemcitabine initially by destabilizing the DNA replication apparatus. Cancer Res 75(17):3583–3595. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-14-3347
Lee DE, Kang HW, Kim SY et al (2022) Ivermectin and gemcitabine combination treatment induces apoptosis of pancreatic cancer cells via mitochondrial dysfunction. Front Pharmacol 13:934746. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2022.934746
Li Y, Chen B, Yang X et al (2019) S100a8/a9 signaling causes mitochondrial dysfunction and cardiomyocyte death in response to ischemic/reperfusion injury. Circulation 140(9):751–764. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.039262
Liu R, Fan M, Candas D et al (2015) CDK1-mediated SIRT3 activation enhances mitochondrial function and tumor radioresistance. Mol Cancer Ther 14(9):2090–2102. https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.Mct-15-0017
Liu Y, Li Y, Wang X et al (2017) Gemcitabine and Chk1 inhibitor AZD7762 synergistically suppress the growth of Lkb1-deficient lung adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 77(18):5068–5076. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-17-0567
Montastruc G, Favreliere S, Sommet A et al (2010) Drugs and dilated cardiomyopathies: a case/noncase study in the French PharmacoVigilance Database. Br J Clin Pharmacol 69(3):287–294. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2125.2009.03596.x
Park W, Chawla A, O’Reilly EM (2021) Pancreatic cancer: a review. JAMA 326(9):851–862. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2021.13027
Peoples JN, Saraf A, Ghazal N, Pham TT, Kwong JQ (2019) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in heart disease. Exp Mol Med 51(12):1–13. https://doi.org/10.1038/s12276-019-0355-7
Rogers RF, Walton MI, Cherry DL et al (2020) CHK1 inhibition is synthetically lethal with loss of B-family DNA polymerase function in human lung and colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Res 80(8):1735–1747. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.Can-19-1372
Santini D, Tonini G, Abbate A et al (2000) Gemcitabine-induced atrial fibrillation: a hitherto unreported manifestation of drug toxicity. Ann Oncol 11(4):479–481. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1008380208045
Sausville E, Lorusso P, Carducci M et al (2014) Phase I dose-escalation study of AZD7762, a checkpoint kinase inhibitor, in combination with gemcitabine in US patients with advanced solid tumors. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 73(3):539–549. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-014-2380-5
Sen T, Della Corte CM, Milutinovic S et al (2019) Combination treatment of the oral CHK1 inhibitor, SRA737, and low-dose gemcitabine enhances the effect of programmed death ligand 1 blockade by modulating the immune microenvironment in SCLC. J Thorac Oncol 14(12):2152–2163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtho.2019.08.009
Seto T, Esaki T, Hirai F et al (2013) Phase I, dose-escalation study of AZD7762 alone and in combination with gemcitabine in Japanese patients with advanced solid tumours. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 72(3):619–627. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00280-013-2234-6
Stroud DA, Surgenor EE, Formosa LE et al (2016) Accessory subunits are integral for assembly and function of human mitochondrial complex I. Nature 538(7623):123–126. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature19754
Tang X, Zhao S, Liu J et al (2023) Mitochondrial GSNOR alleviates cardiac dysfunction via ANT1 denitrosylation. Circ Res 133(3):220–236. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.123.322654
Wang M, Ding Y, Hu Y et al (2023) SIRT3 improved peroxisomes-mitochondria interplay and prevented cardiac hypertrophy via preserving PEX5 expression. Redox Biol 62:102652. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.redox.2023.102652
Wang T, Cao Y, Zheng Q et al (2019) SENP1-Sirt3 signaling controls mitochondrial protein acetylation and metabolism. Mol Cell 75(4):823-834.e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2019.06.008
Wu QJ, Zhang TN, Chen HH et al (2022) The sirtuin family in health and disease. Signal Transduct Target Ther 7(1):402. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41392-022-01257-8
Xiao J, Liu H, Cretoiu D et al (2017) miR-31a-5p promotes postnatal cardiomyocyte proliferation by targeting RhoBTB1. Exp Mol Med 49(10):e386. https://doi.org/10.1038/emm.2017.150
Yang T, Gu J, Du C et al (2021) Adverse cerebral cardiovascular events associated with checkpoint kinase 1 inhibitors: a systemic review. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol 77(5):549–556. https://doi.org/10.1097/fjc.0000000000000997
Zhang J, Simpson CM, Berner J et al (2023) Systematic identification of anticancer drug targets reveals a nucleus-to-mitochondria ROS-sensing pathway. Cell 186(11):2361-2379.e25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2023.04.026
Acknowledgements
We thank for the technical assistance support from Jiangsu Province Collaborative Innovation Center for Cardiovascular Disease Translational Medicine.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Key Clinical Frontier Technology Project of Department of Science and Technology of Jiangsu Provincial (No. BE2022806), the National Natural Science Foundation of China Innovative Research Group Project (No. 82121001), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82003094), the Jiangsu Province Hospital (the First Affiliated Hospital with Nanjing Medical University) Clinical Capacity Enhancement Project (NO. JSPH-MA-2021-2), and a Project Funded by the Scientific Research Innovation Projects of Graduate Students in Jiangsu Province (NO. KYCX22_1838).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, JW., Shan, TK., Wei, TW. et al. SIRT3-dependent mitochondrial redox homeostasis mitigates CHK1 inhibition combined with gemcitabine treatment induced cardiotoxicity in hiPSC-CMs and mice. Arch Toxicol 97, 3209–3226 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03611-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-023-03611-3