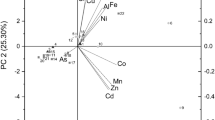
Abstract
Extremities in marine environmental conditions led the marine macroalga-associated bacteria to adapt and biosynthesize potential bioactive agents. The myriad of marine macroalgae and the bacterial flora they are associated with constitute a potential source of bioactive components with significant biotechnological and pharmacological applications. Heterotrophic bacteria associated with the intertidal macroalgae were isolated and assessed for their pharmacological properties. Subsequently, Firmicutes dominated more than half of the 152 cultivable isolates from macroalgae-associated bacteria collected from the Gulf of Mannar (9°17′0′′ N, 79°7′0′′ E), on Peninsular India’s southern coast. A total of 43 of those demonstrated steady antibacterial activities against a wide range of nosocomial pathogens. Among the bacteria isolated from marine macroalgae, Bacillus atrophaeus SHB2097 (MW821482) exhibited significant antimicrobial activities against clinically important pathogens. Organic extract of B. atrophaeus SHB2097 showed potential antimicrobial activities against test pathogens (minimum inhibitory concentration 6.25 µg/mL). Organic extract of B. atrophaeus SHB2097 revealed promising inhibition potential against cyclooxygenase-2 (IC90 53.26 µg/mL) and 5-lipoxygenase (IC90 9.74 µg/mL). The carbolytic enzyme α-glucosidase inhibition potential of the organic extract of the studied heterotrophic bacterium was significantly greater than (IC90 118 µg/mL) than that displayed by acarbose (IC90 645 µg/mL, p < 0.05). The significance of nuclear magnetic resonance-centered analyses of distinguishing signals in the organic extract and correlating those with bioactive potential was accentuated. The utilities of nuclear magnetic resonance-based fingerprinting emphasized the assessment of the distinctive signals in the solvent extracts and their correlation with the pharmacological properties. Thus, the heterotrophic B. atrophaeus SHB2097 could be used to develop potential therapeutic and biomedical agents.
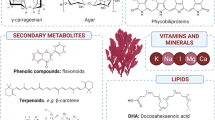
Graphical abstract





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abada E, Al-Fif Z, Osman M (2019) Bioethanol production with carboxymethylcellulase of Pseudomonas poae using castor bean (Ricinus communis L.) cake. Saudi J Biol Sci 26:866–871
Ademiluyi AO, Oboh G (2013) Soybean phenolic-rich extracts inhibit key-enzymes linked to type 2 diabetes (α-amylase and α-glucosidase) and hypertension (angiotensin I converting enzyme) in vitro. Exp Toxicol Pathol 65:305–309
Ali SG, Mulay S, Palekar A, Sejpal D, Joshi A, Gufran H (2012) Prevalence of and factors affecting post-obturation pain following single visit root canal treatment in Indian population: a prospective, randomized clinical trial. Contemp Clin Dent 3:459–463
Archer NK, Mazaitis MJ, Costerton JW, Leid JG, Powers ME, Shirtliff ME (2011) Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: properties, regulation, and roles in human disease. Virulence 2(5):445–459
Atkinson AB, Robertson JI (1979) Captopril in the treatment of clinical hypertension and cardiac failure. Lancet 2:836–839
Bauer AW, Kirby WM, Sherris JC, Turck M (1966) Antibiotic susceptibility testing by a standardized single disk method. Tech Bull Regist Med Technol 36:49–52
Baylac S, Racine P (2003) Inhibition of 5-lipoxygenase by essential oils and other natural fragrant extracts. Int J Aromather 13:138–142
Brand-Williams W, Cuvelier ME, Berset C (1995) Use of a free radical method to evaluate antioxidant activity. LWT-Food Sci Technol 28:25–30
Chakraborty K, Thilakan B, Raola VK (2014) Polyketide family of novel antibacterial 7-O-methyl-5′-hydroxy-3′-heptenoate–macrolactin from seaweed-associated Bacillus subtilis MTCC 10403. J Agric Food Chem 62:12194–12208
Chakraborty K, Thilakan B, Chakraborty RD, Raola VK, Joy M (2017) O-heterocyclic derivatives with antibacterial properties from marine bacterium Bacillus subtilis associated with seaweed. Sargassum myriocystum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 101:569–583
Chakraborty K, Kizhakkekalam VK, Joy M, Chakraborty RD (2020) Moving away from traditional antibiotic treatment: can macrocyclic lactones from marine macroalga-associated heterotrophy be the alternatives? Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 104:7117–7130
Chakraborty K, Kizhakkekalam VK, Joy M, Dhara S (2021) Difficidin class of polyketide antibiotics from marine macroalga-associated Bacillus as promising antibacterial agents. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 105:6395–6408
Charlier C, Michaux C (2003) Dual inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) and 5-lipoxygenase (5-LOX) as a new strategy to provide safer non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Eur J Med Chem 38:645–659
Cherian T, Yalla S, R M, (2019) Antimicrobial potential of methanolic extract of Bacillus aquimaris isolated from the marine waters of Burmanallah coast. South Andaman 8:2806–2813
Davidson Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Davidson BS (1995) New dimensions in natural products research: cultured marine microorganisms. Curr Opin Biotechnol 6:284–291
Debbab A, Aly AH, Lin WH, Proksch P (2010) Bioactive compounds from marine bacteria and fungi. Microb Biotechnol 5:544–563
Dostal DE, Baker KM (1999) The cardiac renin-angiotensin system: conceptual, or a regulator of cardiac function? Circ Res 85:643–650
Elahi MM, Matata BM (2006) Free radicals in blood: evolving concepts in the mechanism of ischemic heart disease. Arch Biochem Biophys 450:78–88
Holmquist B, Bunning P, Riordan JF (1979) A continuous spectrophotometric assay for angiotensin converting enzyme. Anal Biochem 95:540–548
Jamal MT, Morris PC, Hansen R, Jamieson DJ, Burgess JG, Austin B (2006) Recovery and characterization of a 30.7-kDa protein from Bacillus licheniformis associated with inhibitory activity against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus, vancomycin-resistant enterococci, and Listeria monocytogenes. Mar Biotechnol (NY) 8(6):587–592
Jones DT, Taylor WR, Thornton JM (1992) The rapid generation of mutation data matrices from protein sequences. Comput Appl Biosci 8:275–282
Kizhakkekalam VK, Chakraborty K (2020) Marine macroalgae associated heterotrophic Firmicutes and Gamma-proteobacteria: prospective anti-infective agents against multidrug resistant pathogens. Arch Microbiol 202:905–920
Kizhakkekalam VK, Chakraborty K (2021) Seaweed-associated heterotrophic bacteria: new paradigm of prospective anti-infective and anticancer agents. Arch Microbiol 203:1241–1250
Kizhakkekalam VK, Chakraborty K, Joy M (2020) Oxygenated elansolid type of polyketide spanned macrolides from a marine heterotrophic Bacillus as prospective antimicrobial agents against multidrug resistant pathogens. Int J Antimicrob Agents 55:105892
Krieg NR, Holt JG (1984) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, 1st edn. Williams and Wilkins Co, Baltimore, pp 161–172
Kubanek J, Jensen PR, Keifer PA, Sullards MC, Collins DO, Fenical W (2003) Seaweed resistance to microbial attack a targeted chemical defense against marine fungi. Proc Natl Acad Sci. USA 100:6916–6921
Lachnit T, Meske D, Wahl M, Harder T, Schmitz R (2011) Epi-bacterial community patterns on marine macroalgae are host-specific but temporally variable. Environ Microbiol 13:655–665
Larsen LN, Dahl E, Bremer J (1996) Peroxidative oxidation of leucodichlorofluorescein by prostaglandin H synthase in prostaglandin biosynthesis from polyunsaturated fatty acids. Biochim Biophys Acta 1299:47–53
Li JW, Vederas JC (2009) Drug discovery and natural products: end of an era or an endless frontier? Science 325:161–165
Maciejak A, Leszczynska A, Warchol I, Gora M, Kaminska J, Plochocka D, Kapcinska MW, Tulacz D, Siedlecka J, Swiezewska E, Sojka M, Danikiewicz W, Odolczyk N, Szkopinska A, Sygitowicz G, Burzyn ska (2013) The effects of statins on the mevalonic acid pathway in recombinant yeast strains expressing human HMG-CoA reductase. BMC Biotechnol 13:68
Maisuthisakul P (2008) Phenolic antioxidants from betel leaf (Piper betel Linn) extract obtained with different solvents and extraction time. UTCC J 28:52–64
Manthey A, Reuter G (1989) Microbial synthesis of metabolites with anti-hypertensive activity: aspects of fermentation derived inhibitors of angiotensin-converting enzyme ACE. J Basic Microbiol 29:623–639
Nandakumar R, Rush MC, Correa F (2007) Association of Burkholderia glumae and B. gladioli with panicle blight symptoms on rice in Panama. Plant Dis 91:767
National Research Council (1999) From monsoons to microbes: understanding the ocean’s role in human health. The National Academics Press, Washington, DC
Okamura M, Shimazaki K, Nakata T, Chida N, Miyatake T, Maemoku H, Tsutsumi H, Nakamura T, Yamaguchi C, Ogawa M (1993) Submarine active faults in the northwestern part of Beppu Bay Japan-on a new technique for submarine active fault survey. Mem Geol Soc Jpn 40:65–74
Ota A, Ulrih NP (2017) An overview of herbal products and secondary metabolites used for management of type two diabetes. Front Pharmacol 8:436
Penesyan A, Marshall-Jones Z, Holmstrom C, Kjelleberg S, Egan S (2009) Antimicrobial activity. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 69:113–124
Penesyan A, Kjelleberg S, Egan S (2010) Development of novel drugs from marine surface associated microorganisms. Mar Drugs 8:438–459
Quevrain E, Roue M, Bourguet-Kondracki IM (2014) Assessing the potential bacterial origin of the chemical diversity in calcareous sponges. J Mar Sci Tech 22:36–49
Pandey S, Sree A, Dash SS, Sethi DP, Chowdhury L (2013) Diversity of marine bacteria producing beta-glucosidase inhibitors. Microb Cell Fact 12:35
Rajan L, Chakraborty K, Chakraborty RD (2021) Pharmacological properties of some mangrove sediment-associated Bacillus isolates. Arch Microbiol 203:67–76
Re R, Pellegrini N, Proteggente A, Pannala A, Yang M, Rice-Evans C (1999) Antioxidant activity applying an improved ABTS radical cation decolorization assay. Free Radic Biol Med 26(9–10):1231–1237
Scott J (2004) Pathophysiology and biochemistry of cardiovascular disease. Curr Opin Genet Dev 14:271–279
Shimaa RH, Mohamed SS, Selim MS, Al-Wasify RS, El SOH (2015) Assessment of secondary metabolites as antioxidants from terrestrial fungi and bacteria. J Chem Pharm Res 7:173–179
Suganthi C, Mageswari A, Karthikeyan S, Anbalagan M, Sivakumar A, Gothanda KM (2013) Screening and optimization of protease production from a halotolerant Bacillus licheniformis isolated from saltern sediments. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 11:47–52
Tabatabaei-Malazy O, Larijani B, Abdollahi M (2015) Targeting metabolic disorders by natural products. J Diabetes Metab Disord 14:57
Tamura K, Nei M (1993) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions in the control region of mitochondrial DNA in humans and chimpanzees. Mol Biol Evol 10:512–526
Tang JS, Zhao F, Gao H, Dai Y, Yao ZH, Hong K, Li J, Ye WC, Yao XS (2010) Characterization and online detection of surfactin isomers based on HPLC-MS analyses and their inhibitory effects on the overproduction of nitric oxide and the release of TNF-α and IL-6 in LPS induced macrophages. Mar Drugs 8:2605–2618
Thilakan B, Chakraboty K, Chakraborty RD (2016) Antimicrobial properties of cultivable bacteria associated with seaweeds in Gulf of Mannar of South East Coast of India. Can J Microbiol 62:668–681
Vairappan CS, Suzuki M (2000) Dynamics of total surface bacteria and bacterial species counts during desiccation in the Malaysian sea lettuce, Ulva reticulata (Ulvales, Chlorophyta). Phycol Res 48(2):55–61
Wiese J, Thiel V, Gartner A, Schmaljohann R, Imhoff JF (2009) Kiloniella laminariae gen. nov., sp. nov., an alpha-proteobacterium from the marine macroalga Laminaria saccharina. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59:350–356
Wright E Jr, Scism-Bacon JL, Glass LC (2006) Oxidative stress in type 2 diabetes: the role of fasting and postprandial glycemia. Int J Clin Pract 60:308–314
Zeng L, Han X, Chen HM, Lin W, Yan XJ (2005) Marine bacteria associated with marine macro-organisms: the potential antimicrobial resources. Ann Microbiol 55:119–124
Zhao K, Tung CW, Eizenga GC, Wright MH, Ali ML, Price AH, Norton GJ, Islam MR, Reynolds A, Mezey J, McClung AM, Bustamante CD, McCouch SR (2011) Genome-wide association mapping reveals a rich genetic architecture of complex traits in Oryza sativa. Nat Commun 2:467
Acknowledgements
This work was funded by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR) (grant number MBT/HM/SUB/23). The authors thank the Director, Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute and Head, Marine Biotechnology Fish Nutrition and Health Division, Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, for facilitating the research activities. The authors thank the Dean, School of Biotechnology, Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham for supporting CV.
Funding
This study was funded by the Indian Council of Agricultural Research (ICAR), New Delhi (grant number MBT/HM/SUB/23).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
CV conducted experiments and analyzed data. KC conceived and designed research, acquired funds and conducted experiments. SA analyzed data. The authors have drafted and approved the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the authors. This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Communicated by R. El-Sayed.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Varghese, C., Chakraborty, K. & Asharaf, S. Pharmacological potential of seaweed-associated heterotrophic bacterium Bacillus atrophaeus. Arch Microbiol 205, 6 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03338-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-022-03338-2