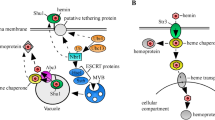
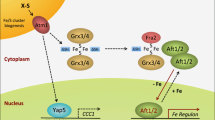
Abstract
Iron is an essential trace metal ion required for all living organisms, and is taken up by iron transporters. Here, we identified and characterized three-candidate high-affinity (Fio1, Frp1 and Frp2) and two-candidate low-affinity iron transporters (Fet4 and Pdt1) from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Protein sequence analyses revealed that Fio1 is a multicopper oxidase that contains three cupredoxin domains with eleven candidate iron-binding ligands, whereas Frp1 harbors a ferric reductase domain with three-candidate heme-binding ligands. Protein sequence analyses also revealed that Fet4 and Pdt1 are integral membrane proteins with 10 and 11 transmembrane regions, respectively. Deletion of fio1 and, to a lesser extent, frp1 impaired growth under iron-depleted conditions, whereas deletion of frp1 and, to a lesser extent, frp2 inhibited growth under iron-replete conditions. Deletion of fet4 and pdt1 did not affect the growth of cells under iron-depleted and iron-replete conditions. Deletion of fio1 or frp1 also increased the sensitivity of cells to other transition metals. The copper sensitivity of Δfio1 cells could be rescued by iron, suggesting that the addition of iron might decrease the uptake of potentially toxic copper in Δfio1 cells. The copper sensitivity of Δfio1 cells could also be rescued by deletion of frp1, suggesting that Fio1 and Frp1 may function together in iron and copper uptakes in S. pombe. Our results revealed that iron and copper uptake systems may be partially overlapped in S. pombe.





Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data sets generated and analyzed during the current study are available on the request from the corresponding author.
References
Askwith C, Eide D, Van Ho A, Bernard PS, Li L, Davis-Kaplan S, Sipe DM, Kaplan J (1994) The FET3 gene of S. cerevisiae encodes a multicopper oxidase required for ferrous iron uptake. Cell 76(2):403–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/0092-8674(94)90346-8
Bähler J, Wu JQ, Longtine MS, Shah NG, McKenzie A 3rd, Steever AB, Wach A, Philippsen P, Pringle JR (1998) Heterologous modules for efficient and versatile PCR-based gene targeting in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 14(10):943–951. https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1097-0061(199807)14:10%3C943::aid-yea292%3E3.0.co;2-y
Bairwa G, Hee Jung W, Kronstad JW (2017) Iron acquisition in fungal pathogens of humans. Metallomics 9(3):215–227. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6mt00301j
Bozzi AT, Gaudet R (2021) Molecular mechanism of Nramp-family transition metal transport. J Mol Biol 433(16):166991. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmb.2021.166991
Bradley JM, Svistunenko DA, Wilson MT, Hemmings AM, Moore GR, Le Brun NE (2020) Bacterial iron detoxification at the molecular level. J Biol Chem 295(51):17602–17623. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.rev120.007746
Chen XZ, Peng JB, Cohen A, Nelson H, Nelson N, Hediger MA (1999) Yeast SMF1 mediates H(+)-coupled iron uptake with concomitant uncoupled cation currents. J Biol Chem 274(49):35089–35094. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.274.49.35089
Dix DR, Bridgham JT, Broderius MA, Byersdorfer CA, Eide DJ (1994) The FET4 gene encodes the low affinity Fe(II) transport protein of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 269(42):26092–26099
Encinar del Dedo J, Gabrielli N, Carmona M, Ayté J, Hidalgo E (2015) A cascade of iron-containing proteins governs the genetic iron starvation response to promote iron uptake and inhibit iron storage in fission yeast. PLoS Genet 11(3):e1005106. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005106
Fleischhacker AS, Sarkar A, Liu L, Ragsdale SW (2021) Regulation of protein function and degradation by heme, heme responsive motifs, and CO. Crit Rev Biochem Mol Biol. https://doi.org/10.1080/10409238.2021.1961674
Forsburg SL, Rhind N (2006) Basic methods for fission yeast. Yeast 23(3):173–183. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1347
Hentges P, Van Driessche B, Tafforeau L, Vandenhaute J, Carr AM (2005) Three novel antibiotic marker cassettes for gene disruption and marker switching in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 22(13):1013–1019. https://doi.org/10.1002/yea.1291
Kennedy PJ, Vashisht AA, Hoe KL, Kim DU, Park HO, Hayles J, Russell P (2008) A genome-wide screen of genes involved in cadmium tolerance in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Toxicol Sci 106(1):124–139. https://doi.org/10.1093/toxsci/kfn153
Kobayashi T, Nozoye T, Nishizawa NK (2019) Iron transport and its regulation in plants. Free Radic Biol Med 133:11–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2018.10.439
Kwok EY, Severance S, Kosman DJ (2006) Evidence for iron channeling in the Fet3p–Ftr1p high-affinity iron uptake complex in the yeast plasma membrane. Biochemistry 45(20):6317–6327. https://doi.org/10.1021/bi052173c
Lesuisse E, Labbe P (1989) Reductive and non-reductive mechanisms of iron assimilation by the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Gen Microbiol 135(2):257–263. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-135-2-257
Letunic I, Khedkar S, Bork P (2021) SMART: recent updates, new developments and status in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res 49(D1):D458–D460. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkaa937
Li L, Kaplan J (1998) Defects in the yeast high affinity iron transport system result in increased metal sensitivity because of the increased expression of transporters with a broad transition metal specificity. J Biol Chem 273(35):22181–22187. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.273.35.22181
Lill R, Freibert SA (2020) Mechanisms of mitochondrial iron-sulfur protein biogenesis. Annu Rev Biochem. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-biochem-013118-111540
Liu G, Sil D, Maio N, Tong WH, Bollinger JM Jr, Krebs C, Rouault TA (2020) Heme biosynthesis depends on previously unrecognized acquisition of iron-sulfur cofactors in human amino-levulinic acid dehydratase. Nat Commun 11(1):6310. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-020-20145-9
Lu S, Wang J, Chitsaz F, Derbyshire MK, Geer RC, Gonzales NR, Gwadz M, Hurwitz DI, Marchler GH, Song JS, Thanki N, Yamashita RA, Yang M, Zhang D, Zheng C, Lanczycki CJ, Marchler-Bauer A (2020) CDD/SPARCLE: the conserved domain database in 2020. Nucleic Acids Res 48(D1):D265–D268. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz991
Matsuyama A, Arai R, Yashiroda Y, Shirai A, Kamata A, Sekido S, Kobayashi Y, Hashimoto A, Hamamoto M, Hiraoka Y, Horinouchi S, Yoshida M (2006) ORFeome cloning and global analysis of protein localization in the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Nat Biotechnol 24(7):841–847. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1222
Mercier A, Labbé S (2010) Iron-dependent remodeling of fungal metabolic pathways associated with ferrichrome biosynthesis. Appl Environ Microbiol 76(12):3806–3817. https://doi.org/10.1128/aem.00659-10
Misslinger M, Hortschansky P, Brakhage AA, Haas H (2021) Fungal iron homeostasis with a focus on Aspergillus fumigatus. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res 1868(1):118885. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2020.118885
Mourer T, Jacques JF, Brault A, Bisaillon M, Labbé S (2015) Shu1 is a cell-surface protein involved in iron acquisition from heme in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem 290(16):10176–10190. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m115.642058
Mourer T, Normant V, Labbé S (2017) Heme assimilation in Schizosaccharomyces pombe requires cell-surface-anchored protein Shu1 and vacuolar transporter Abc3. J Biol Chem 292(12):4898–4912. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m117.776807
Mourer T, Brault A, Labbé S (2019) Heme acquisition by Shu1 requires Nbr1 and proteins of the ESCRT complex in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mol Microbiol 112(5):1499–1518. https://doi.org/10.1111/mmi.14374
Normant V, Mourer T, Labbé S (2018) The major facilitator transporter Str3 is required for low-affinity heme acquisition in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. J Biol Chem 293(17):6349–6362. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.ra118.002132
Pelletier B, Beaudoin J, Philpott CC, Labbé S (2003) Fep1 represses expression of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe siderophore-iron transport system. Nucleic Acids Res 31(15):4332–4344. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkg647
Rouault TA, Maio N (2017) Biogenesis and functions of mammalian iron-sulfur proteins in the regulation of iron homeostasis and pivotal metabolic pathways. J Biol Chem 292(31):12744–12753. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.r117.789537
Schrettl M, Winkelmann G, Haas H (2004) Ferrichrome in Schizosaccharomyces pombe—An iron transport and iron storage compound. Biometals 17(6):647–654. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10534-004-1230-z
Sedlák E, Ziegler L, Kosman DJ, Wittung-Stafshede P (2008) In vitro unfolding of yeast multicopper oxidase Fet3p variants reveals unique role of each metal site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(49):19258–19263. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0806431105
Shi X, Stoj C, Romeo A, Kosman DJ, Zhu Z (2003) Fre1p Cu2+ reduction and Fet3p Cu1+ oxidation modulate copper toxicity in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 278(50):50309–50315. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m307019200
Su Y, Yang Y, Huang Y (2017) Loss of ppr3, ppr4, ppr6, or ppr10 perturbs iron homeostasis and leads to apoptotic cell death in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. FEBS J 284(2):324–337. https://doi.org/10.1111/febs.13978
Tamura K, Stecher G, Kumar S (2021) MEGA11: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 11. Mol Biol Evol 38(7):3022–3027. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msab120
Wang Y, Yan J, Zhang Q, Ma X, Zhang J, Su M, Wang X, Huang Y (2017) The Schizosaccharomyces pombe PPR protein Ppr10 associates with a novel protein Mpa1 and acts as a mitochondrial translational activator. Nucleic Acids Res 45(6):3323–3340. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx127
Zhang X, Krause KH, Xenarios I, Soldati T, Boeckmann B (2013) Evolution of the ferric reductase domain (FRD) superfamily: modularity, functional diversification, and signature motifs. PLoS One 8(3):e58126. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0058126
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Siddiq Akbar for his critical reading of the manuscript and valuable comments.
Funding
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31770810 to YH).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HY and YZ designed and performed the experiments. FA and YL conducted bioinformatics analyses. YH, FA, HY and YZ analyzed the data. YH, FA and YL prepared the manuscript. All authors read, reviewed and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Consent for publication
All authors read and approved the final version of the manuscript for publication.
Additional information
Communicated by Erko Stackebrandt.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ahmad, F., Luo, Y., Yin, H. et al. Identification and analysis of iron transporters from the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Arch Microbiol 204, 152 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02683-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-021-02683-y