Abstract
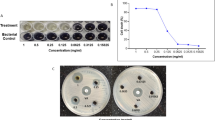
Effects of different flavonoids on various bacterial strains have been extensively reported; however, the mechanism(s) of their action on bacterial cells remain largely elusive. In this study, the antibacterial mechanism of soybean isoflavone (SI) on Staphylococcus aureus is systematically investigated using 4′6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) staining, pBR322DNA decatenation experiment mediated by topoisomerase and agarose gel electrophoresis for direct decatenation. The results of fluorescence microscopy and fluorescence spectrophotometer indicated that DAPI was integrated in Staphylococcus aureus. Additionally, the quantity of both DNA and RNA reduced to 66.47 and 60.18%, respectively, after treated with SI for 28 h. Effects of SI on topoisomerase I and II were also investigated. SI completely inhibited the pBR322DNA unwinding mediated by topoisomerase I and topoisomerase II at the concentration of 6.4 mg/ml and could denature the plasmid DNA at the concentration of 12.8 mg/ml. These results indicate that topoisomerase I and II are the most important targets by SI to restrain bacterial cell division.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
An J, Tzagarakis-foster C, Scharschmid TC (2001) Estrogen receptor beta-selective trans-criptional activity and recruitment of coregulators by phytoestrogens. J Biol Chem 276:17–808
Angulo F, Johnson K, Tauxe R, Cohen M (2000) Significance and source of antimicrobial-resistant nontyphoidal Salmonella infection in the United States. Microb Drug Resist 1:77–83
Boege F, Straub T, Kehr A, Boesenberg C, Christiansen K, Andersen A, Jakob F, Köhrle J (1996) Selected novel flavones inhibit the DNA binding or the DNA religation step of eukaryotic topoisomerase I. Biol Chem 271:2262–2270
Chang YC, Nair MG, Nitiss JL (1995) Metabolites of daidzein and genistein and their biological activities. J Nat Prod 58:1901–1905
Haraguchi H, OikeS MuroiH, Kubo I (1996) Mode of antibacterial action of totarol, diterpene from Podocarpus nagi. J Planta Med 62:122–125
Hraiky C, Raymond MA, Drolet M (2000) RNase H overproduction corrects a defect at the level of transcription elongation during rRNA synthesis in the absence of DNA topoisomerase I in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem 275:11257–11263
Hyunki H, Michael R, Landauer M, Foriska G, David L (2006) Antibacterial activity of the soy isoflavone genistein. Basic Microbiol 46:329–335
Kubo I, Taniguchi M (1988) Polygodial, an antifungal potentiator. J Nat Prod 51:22–29
Levy SB (2005) Antibiotic resistance—the problem intensifies. Adv Drug Del Rev 57:1443–1450
Li YZ, Lin QL, Xiao HQ (2005) Research of features progress about soy isoflavones. J Food Nutr China 10:21–22
Liu LM, Liu HG (2010) Anti-hepatoma activity of nitidine chloride and its effect on topoisomerase. Chin Pharmacol Bull 26:497–500
McClendon A, Osheroff N (2007) DNA Topoisomerase II, genotoxicity, and cancer. Mutat Res 623:83–97
Minkah N, Hwang Y, Perry K, Duyne GD, Hendrick RC, Lefkowitz EJ, Hannenhalli S, Bushman FD (2007) Variola virus topoisomerase: DNA cleavage specificity and distribution of sites in poxvirus genomes. Virology 365:60–69
Morrissey I, George J (1999) Activities of fluoroquinolones against Streptococcus pneumoniae Type II topoisomerases purified as recombinant proteins. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 43:2579–2585
Oppegard LM, Ougolkov AV, Luchini DN, Schoon RA, Goodell JR, Kaur H, Billadeau DD, Ferguson DM, Hiasa H (2009) Novel acridine-based compounds that exhibit an anti-pancreatic cancer activity are catalytic inhibitors of human topoisomerase II. Eur J Pharmacol 602:223–229
Pan XS, Ambler J, Mehtar S, Fisher LM (1996) Involvement of topoisomerase IV and DNA gyrase as ciprofloxacin targets in Streptococcus pneumoniae. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 40:2321–2326
Peterson LR (2005) Squeezing the antibiotic balloon: the impact of antimicrobial classes on emerging resistance. Clin Microb Infect 11:4–16
Raspaglio G, Ferlini C, Mozzetti S (2005) Thiocolchicine dimers: a novel class of topoisomerase-I inhibitors. Biochem Pharmacol 69:113–121
Rochman M, Blot N, Dyachenko M, Glaser G, Travers A, Muskhelishvili G (2004) Buffering of stable RNA promoter activity against DNA relaxation requires a far upstream sequence. Mol Microbiol 53:143–152
Sabanero M, Quijano L, Rios T, Trejo R (1995) Encelin: a fungal growth inhibitor. J Planta Med 61:185–186
Sarkar FH, Li Y (2002) Mechanisms of cancer chemoprevention by soy isoflavone genistein. Cancer Metastasis Rev 21:265–280
Snyder RD, Gillies PJ (2002) Evaluation of the clastogenic, DNA intercalative, and topoisomerase II-interactive properties of bioflavonoids in Chinese hamster V79 ells. Environ Mol Mutagen 40:266–276
Sulivan DM, Glisson BS, Hodges PK (1986) Proliferation dependence of topoisomerase II mediated drug action. J Biochem 5:2248–2256
Ulanowska K, Tkaczyk A, Konopa G, Wegrzyn G (2006) Differential antibacterial activity of genistein arising from global inhibition of DNA, RNA and protein synthesis in some bacterial strains. J Arch Microb 14:271–278
Wang JC (2002) Cellular roles of DNA topoisomerases: a molecular perspective. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:430–440
Wang HB (2008) The study of antioxidant activity of soyasaponin and isoflavone. J Food Res Devel 29:9–12
Wang LG, Liu XM, Ji XJ (1991) Determination of DNA topoisomerase II activity from L1210 cells-a target for screening antitumor agent. J Acta Pharmacol Sinica 12:108–114
Wang HT, Shi SS, Li YX, Li HQ, Xie MJ (2008) Study on anti-microbial activity of genistein and its mechanism. Acta Nutr Sinica 30: 403–406, 409
Zewdu E, Cornelius P (2008) Antimicrobial resistance pattern of Salmonella serotypes isolated from food items and personnel in addis ababa, Ethiopia. Trop Anim Health Prod 41:241–249
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Liaoning Province under grants 20072153 and the Liaoning Provincial Department of Education research project under grants L2010236.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Jose membrillo-Hernandez.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Wang, H. & Xie, M. Antibacterial mechanism of soybean isoflavone on Staphylococcus aureus . Arch Microbiol 192, 893–898 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-010-0617-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-010-0617-1