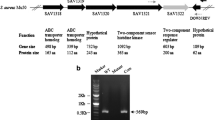
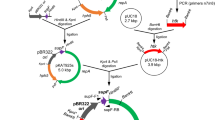
Abstract
In Streptococcus thermophilus, the locus rggC contains a frameshift mutation and thus consists of two open reading frames (ORFs), rggC 1 and rggC 2, which encode proteins exhibiting similarity with the Rgg transcriptional regulator family. In this work, mutants showing a partial deletion of rggC 1 and rggC 2 were constructed and their response to menadione, a superoxide-generating compound, was analysed. These mutants exhibited different behaviour to this oxidative stress compared with the wild-type strain. Analysis of this locus among 21 strains of S. thermophilus showed a polythymine tract length variability and a strain-dependant adenine residue could be found upstream of this repeat. This interstrain polymorphism supports evidence for the hypothesis that the rggC locus is phase variable.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baranov PV, Hammer AW, Zhou J, Gesteland RF, Atkins JF (2005) Transcriptional slippage in bacteria: distribution in sequenced genomes and utilization in IS element gene expression. Genome Biol 6:R25
Biswas I, Gruss A, Ehrlich SD, Maguin E (1993) High-efficiency gene inactivation and replacement system for gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 175:3628–3635
Bolotin A et al (2004) Complete sequence and comparative genome analysis of the dairy bacterium Streptococcus thermophilus. Nat Biotechnol 22:1554–1558
Bracquart P (1981) An agar medium for the differential enumeration of Streptococcus thermophilus and Lactobacillus bulgaricus in yoghurt. J Appl Bacteriol 51:303–305
Chaussee MS, Ajdic D, Ferretti JJ (1999) The rgg gene of Streptococcus pyogenes NZ131 positively influences extracellular SPE B production. Infect Immun 67:1715–1722
Chaussee MS, Watson RO, Smoot JC, Musser JM (2001) Identification of Rgg-regulated exoproteins of Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun 69:822–831
Chaussee MS et al (2002) Rgg influences the expression of multiple regulatory loci to coregulate virulence factor expression in Streptococcus pyogenes. Infect Immun 70:762–770
Chaussee MS, Somerville GA, Reitzer L, Musser JM (2003) Rgg coordinates virulence factor synthesis and metabolism in Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol 185:6016–6024
Chaussee MA, Callegari EA, Chaussee MS (2004) Rgg regulates growth phase-dependent expression of proteins associated with secondary metabolism and stress in Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol 186:7091–7099
Demple B (1996) Redox signaling and gene control in the Escherichia coli soxRS oxidative stress regulon––a review. Gene 179:53–57
Echenique JR, Trombe MC (2001) Competence modulation by the NADH oxidase of Streptococcus pneumoniae involves signal transduction. J Bacteriol 183:768–772
Echenique JR, Chapuy-Regaud S, Trombe MC (2000) Competence regulation by oxygen in Streptococcus pneumoniae: involvement of ciaRH and comCDE. Mol Microbiol 36:688–696
Fernandez A, Thibessard A, Borges F, Gintz B, Decaris B, Leblond-Bourget N (2004) Characterization of oxidative stress-resistant mutants of Streptococcus thermophilus CNRZ368. Arch Microbiol 182:364–372
Hallet B (2001) Playing Dr Jekyll and Mr Hyde: combined mechanisms of phase variation in bacteria. Curr Opin Microbiol 4:570–581
Hecker M, Volker U (1998) Non-specific, general and multiple stress resistance of growth-restricted Bacillus subtilis cells by the expression of the sigmaB regulon. Mol Microbiol 29:1129–1136
Higuchi M (1992) Reduced nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide oxidase involvement in defense against oxygen toxicity of Streptococcus mutans. Oral Microbiol Immunol 7:309–314
Higuchi M et al (1999) Functions of two types of NADH oxidases in energy metabolism and oxidative stress of Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol 181:5940–5947
Hols P et al (2005) New insights in the molecular biology and physiology of Streptococcus thermophilus revealed by comparative genomics. FEMS Microbiol Rev 29:435–463
Larsen B, Wills NM, Nelson C, Atkins JF, Gesteland RF (2000) Nonlinearity in genetic decoding: homologous DNA replicase genes use alternatives of transcriptional slippage or translational frameshifting. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:1683–1688
Leenhouts K (1995) Integration strategies and vectors. Dev Biol Stand 85:523–530
Lukomski S et al (2001) Identification and characterization of a second extracellular collagen-like protein made by group A Streptococcus: control of production at the level of translation. Infect Immun 69:1729–1738
Lyon WR, Gibson CM, Caparon MG (1998) A role for trigger factor and an rgg-like regulator in the transcription, secretion and processing of the cysteine proteinase of Streptococcus pyogenes. Embo J 17:6263–6275
Maguin E, Prévost H, Ehrlich SD, Gruss A (1996) Efficient insertional mutagenesis in Lactococci and other Gram-positive bacteria. J Bacteriol 178:931–935
Mongkolsuk S, Helmann JD (2002) Regulation of inducible peroxide stress responses. Mol Microbiol 45:9–15
Neely MN, Lyon WR, Runft DL, Caparon M (2003) Role of RopB in growth phase expression of the SpeB cysteine protease of Streptococcus pyogenes. J Bacteriol 185:5166–5174
Niven DF, Ekins A (2001) Iron content of Streptococcus suis and evidence for a dpr homologue. Can J Microbiol 47:412–416
O’Sullivan TF, Fitzgerald GF (1999) Electrotransformation of industrial strains of Streptococcus thermophilus. J Appl Microbiol 86:275–283
Penno C, Sansonetti P, Parsot C (2005) Frameshifting by transcriptional slippage is involved in production of MxiE, the transcription activator regulated by the activity of the type III secretion apparatus in Shigella flexneri. Mol Microbiol 56:204–214
Pulliainen AT, Haataja S, Kahkonen S, Finne J (2003) Molecular basis of H2O2 resistance mediated by Streptococcal Dpr. demonstration of the functional involvement of the putative ferroxidase center by site-directed mutagenesis in Streptococcus suis. J Biol Chem 278:7996–8005
Pulliainen AT, Kauko A, Haataja S, Papageorgiou AC, Finne J (2005) Dps/Dpr ferritin-like protein: insights into the mechanism of iron incorporation and evidence for a central role in cellular iron homeostasis in Streptococcus suis. Mol Microbiol 57:1086–1100
Puopolo KM, Madoff LC (2003) Upstream short sequence repeats regulate expression of the alpha C protein of group B Streptococcus. Mol Microbiol 50:977–991
Qi F, Chen P, Caufield PW (1999) Purification of mutacin III from group III Streptococcus mutans UA787 and genetic analyses of mutacin III biosynthesis genes. Appl Environ Microbiol 65:3880–3887
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (eds) (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, New York
Sofia HJ, Chen G, Hetzler BG, Reyes-Spindola JF, Miller NE (2001) Radical SAM, a novel protein superfamily linking unresolved steps in familiar biosynthetic pathways with radical mechanisms: functional characterization using new analysis and information visualization methods. Nucleic Acids Res 29:1097–1106
Sulavik MC, Clewell DB (1996) Rgg is a positive transcriptional regulator of the Streptococcus gordonii gtfG gene. J Bacteriol 178:5826–5830
Terzaghy BE, Sandine WE (1975) Improved medium for lactic streptococci. Curr Microbiol 7:245–250
Thibessard A, Fernandez A, Gintz B, Leblond-Bourget N, Decaris B (2001) Hydrogen peroxide effects on Streptococcus thermophilus CNRZ368 cell viability. Res Microbiol 152:593–596
Thibessard A, Borges F, Fernandez A, Gintz B, Decaris B, Leblond-Bourget N (2004) Identification of Streptococcus thermophilus CNRZ368 genes involved in defense against superoxide stress. Appl Environ Microbiol 70:2220–2229
Voskuil MI, Chambliss GH (1998) The −16 region of Bacillus subtilis and other gram-positive bacterial promoters. Nucleic Acids Res 26:3584–3590
Wagner LA, Weiss RB, Driscoll R, Dunn DS, Gesteland RF (1990) Transcriptional slippage occurs during elongation at runs of adenine or thymine in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res 18:3529–3535
Wen ZT, Suntharaligham P, Cvitkovitch DG, Burne RA (2005) Trigger factor in Streptococcus mutans is involved in stress tolerance, competence development, and biofilm formation. Infect Immun 73:219–225
Yamamoto Y, Poole LB, Hantgan RR, Kamio Y (2002) An iron-binding protein, Dpr, from Streptococcus mutans prevents iron-dependent hydroxyl radical formation in vitro. J Bacteriol 184:2931–2939
Yamamoto Y, Fukui K, Koujin N, Ohya H, Kimura K, Kamio Y (2004) Regulation of the intracellular free iron pool by Dpr provides oxygen tolerance to Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol 186:5997–6002
Acknowledgments
Annabelle Fernandez was supported by grants from the Ministère de la recherche. Frédéric Borges was supported by a grant from the Institut National de la Recherche Agronomique. We are grateful to Arran Johnson for his advice regarding the English formulation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fernandez, A., Borges, F., Gintz, B. et al. The rggC locus, with a frameshift mutation, is involved in oxidative stress response by Streptococcus thermophilus . Arch Microbiol 186, 161–169 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0130-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00203-006-0130-8