Abstract
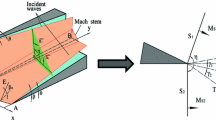
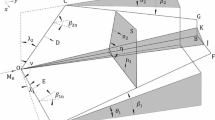
The three-dimensional (3D) shock wave reflections over two perpendicularly intersecting wedges are numerically studied in this paper, using the finite volume method which is based on the MUSCL-Hancock interpolation technique and self-adaptive unstructured mesh. Two kinds of 3D Mach stem structures are demonstrated by the numerical simulations for different shock Mach numbers and wedge angles. A four-shock or three-shock wave configuration appears in the vicinity of the corner of the wedges.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mach E.: Über den Verlauf von Funkenwellen in der Ebene undim Raume. Sitzungsbr Akad Wien 78, 819–838 (1878)
von Neumann J.: Oblique reflection of shocks, Explos Res Rept 12. Navy Dept Bureau of ordinance, Washington, DC (1943)
von Neumann J.: Refraction, interaction and reflection of shock waves, NAVORD Rep 203-45. Navy Dept Bureau of ordinance, Washington, DC (1943)
Hornung H.G.: Regular and Mach reflection of shock waves. Ann. Rev. Fluid Mech. 18, 33–58 (1986)
Ben-Dor G.: Shock Wave Reflection phenomena, 38–170. Springer, New York (1992)
Li H., Ben-Dor G.: Reconsideration of pseudo-steady shock wave reflections and the transition criteria between them. Shock waves 5, 59–73 (1995)
Hornung H.G., Oertel H., Sandeman R.J.: Transition to Mach reflexion of shock waves in steady and pseudosteady flow with and without relaxation. J. Fluid Mech. 90, 541–560 (1979)
Chpoun A., Passerel D., Li H., Ben-Dor G.: Reconsideration of oblique shock wave reflections in steady flows, Part 1. Experimental investigation. J. Fluid Mech. 301, 19–35 (1995)
Ivanov M., Gimelshein S., Beylich A.: Hysteresis effect in stationary reflection of shock waves. Phys. Fluids 7, 685–687 (1995)
Hu Z.M., Myong R.S., Kim M.S., Cho T.H.: Downstream flow condition effects on the RR MR transition of asymmetric shock waves in steady flows. J. Fluid Mech. 620, 43–62 (2009)
Takayama K.: Application of holographic interferometry to shock wave research. Proc. SPIE 398, 174–180 (1983)
Meguro T., Takayama K., Onodera K.: Three-dimensional shock wave reflection over a corner of two intersecting wedges. Shock Wave 7, 107–121 (1997)
Li, H.H.:Experimental and numerical study on unsteady complex flow and wave interaction. PhD Thesis, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei (2005)
Mirels H.: Mach reflection flow fields associated with strong waves. AIAA J. 23, 522–529 (1985)
Li H., Ben-Dor G.: Analysis of double-Mach-reflection wave configurations with convexly curved Mach stems. Shock Waves 9(5), 319–326 (1999)
Gao, Y.L.: Study on hypervelocity flow generation techniques and essential hypersonic phenomena. PhD Thesis, Institute of Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Science, Beijing (2008)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by B.W. Skews.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, Y., Teng, H., Jiang, Z. et al. Numerical investigation on three-dimensional shock wave reflection over two perpendicularly intersecting wedges. Shock Waves 22, 151–159 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-011-0350-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00193-011-0350-y