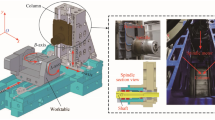
Abstract
As the demand for high speed and highly accurate machines has significantly increased, error motions from thermal change, which is up to 70 % of the total machining error, is found to be the main hurdles to overcome in improving the accuracy of CNC machine tools. In this research work, the authors installed four eddy current displacement sensors in the spindle structure near to the front bearing to monitor the spindle offset in the bearing level, which is mainly attributable to the thermal error motions of the spindle. In addition, another three capacitance sensors are mounted on the machine table level and aligned with the x-, y-, and z-axis of the machine to monitor the spindle shift in the table level to find out the correlation between temperature change and the thermal error motions of the spindle. To measure the temperature changes, we attached thermal sensors in the machine and cooling system. The estimation of the spindle thermal displacement based on temperature data from these thermal sensors can provide more information for the monitoring of thermal error motions of the spindle.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Postlethwaite SR, Ford DG, Morton D (1997) Dynamic calibration of CNC machine tools. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 37(3):287–294
Heisel U, Gringel M (1996) Machine tool design requirements for high-speed machining. Ann CIRP 45:389–392
Xu S, Wang Y, Zhao J, Le G (2008) A study of fault monitoring in CNC machining of free-form surfaces based on NN-wavelet analysis—technical communication. Mach Sci Technol V12(3):PP405–PP416
Sarhan AAD, El-Zahry RM (2011) Monitoring of tool wear and surface roughness in end-milling for intelligent machining. Int J Phys Sci 6(10):2380–2392
Lin Z-C, Chang J-S (2007) The building of spindle thermal displacement model of high speed machine center. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 34(5-6):556–566
Sarhan A, Sayed R, Nassr AA, EL-Zahry RM (2001) Interrelationships between cutting force variation and tool wear in end-milling. J Mater Process Technol 109(3):229–235
Kim S-M, Lee S-K (2005) Spindle housing design parameter optimization considering thermo-elastic behavior. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25(11-12):1061–1070
Bryan J (1990) International status of thermal error research (1990). CIRP Ann - Manuf Technol 39(2):645–656
Cao H, Holkup T, Altintas Y (2011) A comparative study on the dynamics of high speed spindles with respect to different preload mechanisms. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 57(9-12):871–883
Tseng P-C (1997) A real-time thermal inaccuracy compensation method on a machining centre. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 13(3):182–190
Weck M, McKeown P, Bonse R, Herbst U (1995) Reduction and compensation of thermal errors in machine tools. CIRP Annals 44(2):589–598
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sarhan, A.A.D. Investigate the spindle errors motions from thermal change for high-precision CNC machining capability. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 70, 957–963 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5339-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-013-5339-5