Abstract
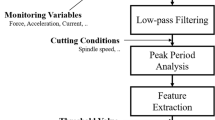
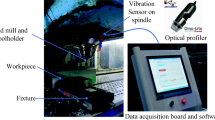
Machine condition plays an important role in machining performance. A machine condition monitoring system will provide significant economic benefits when applied to machine tools and machining processes. Development of such a system requires reliable machining data that can reflect machining processes. This study demonstrates a tool condition monitoring approach in an end-milling operation based on the vibration signal collected through a low-cost, microcontroller-based data acquisition system. A data acquisition system has been built through interfacing a microcontroller with a signal transducer for collecting cutting vibration. The examination tests of this developed system have been carried out on a CNC milling machine. Experimental studies and data analysis have been performed to validate the proposed system. The onsite tests show the developed system can perform properly as proposed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Habaibeh A, Gindy N (2000) A new approach for systematic design of condition monitoring systems for milling operations. J Mater Process Technol 107:243–251
Frankowiak M, Grosvenor R, Prickett P (2005) A review of the evolution of microcontroller-based machine and process monitoring. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 45:578–582
DeGarmo EP, Black JT, Kohser RA (1997) Materials and processes in manufacturing, 8th ed. Prentice Hall, Upper Saddle River, NJ
Chen S, Jen YW (2000) Data fusion neural network for tool condition monitoring in CNC milling machining. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 40(3):381–400
Al-Habaibeh A, Zorriasatine F, Gindy N (2002) Comprehensive experimental evaluation of a systematic approach for cost effective and rapid design of condition monitoring systems using Taguchi’s method. J Mater Process Technol 124:372–383
Milfelner M, Cus F, Balic J (2005) An overview of data acquisition systems for cutting force measuring and optimization in milling. J Mater Process Technol 164:1281–1288
Rehorm AG, Jiang J, Peter E (2005) State-of-the-art methods and results in tool condition monitoring: a review. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 26:693–710
Tzeng Y, Jean M (2005) Dimensional quality of optimization of high-speed CNC milling process with dynamic quality characteristic. Robot Comput-Integr Manuf 21:506–517
Ertekin YM, Kwon Y, Tseng T (2003) Identification of common sensory features for the control of CNC milling operations under varying cutting conditions. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 43(9):897–904
Jantunen E (2002) A summary of methods applied to condition monitoring in drilling. Int J Mach Tools Manuf 42:997–1010
Chung KT, Geddam A (2003) A multi-sensor approach to the monitoring of end milling operations. J Mater Process Technol 139:15–20
Zhang Z, Chen JC (in press) Development of an in-process surface roughness adaptive control in end milling operations. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 31:877–887
Shearman S (2003) Machine condition monitoring, part 1: vibration acquisition and analysis. Sensors. Retrieved August 29, 2007 from http://archives.sensorsmag.com/articles/0503/16/
Smith G, Lee S (2005) A method for detecting tool wear on a CNC lathe using a doppler radar detector. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 25:270–280
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
All rights reserved. This study, or parts thereof, may not be reproduced in any form without written permission of the authors. This paper has not been published nor has it been submitted for publication elsewhere.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, J.Z., Chen, J.C. Tool condition monitoring in an end-milling operation based on the vibration signal collected through a microcontroller-based data acquisition system. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 39, 118–128 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1186-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-007-1186-6