Abstract
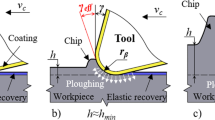
Diamond tools are used in ultra precision machining for their outstanding hardness and crystalline structure, which enable the fabrication of very sharp cutting edges. Single crystal diamond tools are thus extremely useful to machine electroless nickel-plated dies which are generally used for making molds for optical components. This paper deals with the objective to evaluate the performance and suitability of a single crystal diamond tool during microgrooving on electroless nickel plated workpieces. Effects of different machining parameters on overall machining performance were also investigated. The experimental results revealed that long distance (50 km) machining of microgrooves on electroless nickel is possible with a single crystal diamond tool without any significant tool wear. Some groove wear on the rake face were found after machining 28.5 km. No evidence of chipping or wear had been observed on the flank face during the total machining length. The surface roughness range of the machined workpieces was found to be 4–6 nm. Both thrust and cutting components of the machining forces showed an increasing trend with increasing machining distance, though magnitude of the thrust forces were found to increase more than the cutting forces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ikawa N, Donaldson RR, Kumanduri R, Konig W, Mckeown PA, Moriwaki T, Stowers IF (1991) Ultra-precision metal cutting - the past, the present and the future. Ann CIRP 40(2):587–593
Weule H, Hüntrup V, Tritschler H (2001) Micro-cutting of steel to meet new requirements in miniaturization. Annals CIRP 50(1):61–65
Childress FG, Eary SH, McLaughlin JE (1978) Cleaning and protecting LASL laser mirrors. Y/DA-7591, Union Carbide Corporation-Nuclear Division, Oak Ridge Y-12 Plant, Oak Ridge, TN
Casstevens JM, Daugherty CE (1978) Diamond turning optical surfaces on electroless nickel. Precis Mach Optics SPIE 159:109–113
Syn CK, Taylor JS, Donaldson RR (1986) Diamond tool wear vs. cutting distance on electrolesss nickel-mirrors. Proc SPIE on Ultra-Precision Machining and Automated Fabrication of Optics 676:128–140
Wada R, Kodama H, Nakamura K (1980) Wear characteristics of single crystal diamond tool. Ann CIRP 29(1):47–52
Li XP, Rahman M, Liu K, Neo KS, Chan CC (2003) Nano-precision measurement of diamond tool edge radius for wafer fabrication. J Mater Process Technol 140:358–362
Oomen JM, Eisses J (1992) Wear of monocrystalline diamond tools during ultra-precision machining of non ferrous metals. Precis Eng 14(4):206–218
Pramanik A, Neo KS, Rahman M, Li XP, Sawa M, Maeda Y (2003) Cutting performance of diamond tools during ultra-precision turning of electroless-nickel plated die materials. J Mater Process Technol 140(1-3) :308–313
Cheung CF, Lee WB (2001) Characterisation of nanosurface generation in single-point diamond turning. J Mach Tools Manuf 41:851–875
Bhattacharya A (1996) Metal cutting theory and practice. New Central Book Agency, Calcutta,
Jared BH, Dow TA (2000) Investigation and prediction of chip geometry in diamond turning. Precis Eng 24:88–96
Trent EM, Wright PK (2000) Metal cutting, 4th ed. Butterworth-Heinemann, MA,
Syn CK, Dini JW, Taylor JS, Mara GL, Vandervoort RR, Donaldson RR (1985) Influence of phosphorous content and heat treatment on the machinability of electroless nickel deposits. Proc Electroless Nickel Conference IV, Chicago, IL, 1-5 May 1985
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rezaur Rahman, K., Rahman, M., Neo, K. et al. Microgrooving on electroless nickel plated materials using a single crystal diamond tool. Int J Adv Manuf Technol 27, 911–917 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-004-2273-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00170-004-2273-6