Abstract
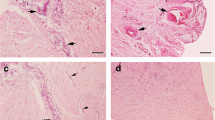
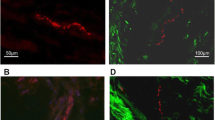
The etiology of pain in anterior knee pain syndrome is a matter of controversy. The normal, articular cartilage is aneural, so defects in the surface are not thought to produce pain. Some authors have sought the origin of the pain in soft tissue structures around the knee. Knowledge of the distribution of nociceptive nerve fibers around the knee would provide insight for treating anterior knee pain syndrome. Twenty consecutive patients (28 knees), all women, with anterior knee pain syndrome (group I) participated in the study. For comparison we used two groups of patients: 20 patients with an osteoarthritic knee (group II) and 20 patients with anterior cruciate ligament rupture or meniscal lesion with no history of pain in the anterior compartment (group III). Immunohistochemical techniques using a monoclonal antibody to substance-P (SP) were employed to identify nociceptive fibers. For statistical analyses we used the one-way ANOVA test, which was corrected with the LSD test, at the level of significance P < 0.05. Results of the study demonstrate that SP-immunoreactive nerve fibers are widespread within the soft tissues around the knee. These tissues include the retinaculum, synovium, fat pad and, in some circumstances, bone. In cases of anterior knee pain, the presence of neuropeptide-containing fibers was statistically significant in the medial retinaculum (P < 0.005) and in the fat pad (P < 0.001) compared to group III, and compared to group II (P < 0.05 and P < 0.007, respectively). For lateral retinaculum this relationship was not so statistically strong (P < 0.02) and was equal in comparison between anterior knee pain patients (group I) and group II or group III. There were no statistically significant differences in the distribution of substance-P nerve fibers in the fat pad, lateral and medial retinaculum or synovium between groups II and III. The results of this study provide immunohistochemical evidence suggesting that pain may originate in the fat pad and medial retinaculum of many patients with anterior knee pain syndrome.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 17 December 1997 Accepted: 20 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Witoński, D., Wągrowska-Danielewicz, M. Distribution of substance-P nerve fibers in the knee joint in patients with anterior knee pain syndrome A preliminary report. Knee Surgery 7, 177–183 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s001670050144
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s001670050144