Abstract
Objective
Neutrophil function impairment is common in nonneutropenic critically ill patients. Whether granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) may be useful for preventing nosocomial infection in these patients is debated. The response of blood neutrophils from critically ill patients to G-CSF was investigated in vitro.
Design and setting
Prospective study, laboratory investigation in two intensive care units.
Patients
52 critically ill patients without immunosuppression.
Measurements
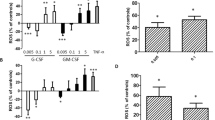
Neutrophils obtained from 52 patients on the 5th day of their intensive care unit stay were incubated with and without G-CSF (1, 10, 100 ng/ml). Reactive oxygen species (ROS) release and bactericidal activity against Staphylococcus aureus and Pseudomonas aeruginosa were evaluated. Plasma cytokines (interleukin 10, tumor necrosis factor α, and G-CSF) were measured.
Results
Median values (25th–75th percentiles) indicated no stimulatory effect of G-CSF on neutrophil bactericidal activity against either organism: S. aureus, 100% (95–109) of the unstimulated condition with 1 ng/ml G-CSF, and P. aeruginosa , 102% (98–109) with 1 ng/ml G-CSF. However, wide interindividual variability was found, ranging from marked inhibition to marked stimulation. Similar variability was found for ROS release. No correlations were found between ROS release and bactericidal activities against either bacterial strain. Inhibition of neutrophil bactericidal activity by G-CSF was associated with significantly higher plasma interleukin 10 concentrations. Plasma G-CSF levels were significantly higher in patients whose neutrophil bactericidal activity was unresponsive to G-CSF, suggesting G-CSF receptor downregulation.
Conclusions
The effect of G-CSF on in vitro neutrophil bactericidal activity varied widely, depending on endogenous levels of G-CSF and was not predictable based on severity scores.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Root RK, DC Dale (1999) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor: comparisons and potential for use in the treatment of infections in nonneutropenic patients. J Infect Dis 179 [Suppl 2]:S342–S352
Nelson S, SM Belknap, RW Carlson, D Dale, B DeBoisblanc, S Farkas, N Fotheringham, H Ho, T Marrie, H Movahhed, R Root, J Wilson (1998) A randomized controlled trial of Filgrastim as an adjunct to antibiotics for treatment of hospitalized patients with community-acquired pneumonia. J Infect Dis 178:1075–1080
Esposito C, SM Banks, PQ Eichacker (1998) Prophylactic granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in critically ill patients: not time yet. Crit Care Med 26:636–637
Solberg CO, KB Hellum (1972) Neutrophil granulocyte function in bacterial infections. Lancet II:727–730
Simms HH, R D'Amico (1997) Posttraumatic auto-oxidative polymorphonuclear neutrophil receptor injury predicts the development of nosocomial infection. Arch Surg 132:171–177
Stephan F, K Yang, J Tankovic, CJ Soussy, G Dhonneur, P Duvaldestin, L Brochard, C Brun-Buisson, A Harf, C Delclaux (2002) Impairment of polymorphonuclear neutrophil functions precedes nosocomial infections in critically ill patients. Crit Care Med 30:315–322
Heard SO, MP Fink, RL Gamelli, JS Solomkin, M Joshi, AL Trask, TC Fabian, LD Hudson, KB Gerold, ED Logan (1998) Effect of prophylactic administration of recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (filgrastim) on the frequency of nosocomial infections in patients with acute traumatic brain injury or cerebral hemorrhage. Crit Care Med 26:748–754
Pettila V, O Takkunen, T Varpula, A Markkola, K Porkka, V Valtonen (2000) Safety of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (filgrastim) in intubated patients in the intensive care unit: interim analysis of a prospective, placebo-controlled, double-blind study. Crit Care Med 28:3620–3655
Richards MJ, JR Edwards, DH Culver, RP Gaynes (1999) Nosocomial infections in medical intensive care units in the United States. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System. Crit Care Med 27:887–892
Quie PG, JG White, G Holmes, RA Good (1967) in vitro bactericidal capacity of human polymorphonuclear leukocytes: diminished activity in chronic granulomatous disease of childhood. J Clin Invest 46:668
Mizgerd JP, JD Brain (1995) Reactive oxygen species in the killing of Pseudomonas aeruginosa by human leukocytes. Curr Microbiol 31:124–128
Le Gall JR, S Lemeshow, F Saulnier (1993) A new simplified acute physiology score (SAPS II) based on a European/North American multicenter study. JAMA 270:2957–2963
Vincent JL, R Moreno, J Takala, S Willatts, A De Mendonca, H Bruining, CK Reinhart, PM Suter, LG Thijs (1996) The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. On behalf of the Working Group on Sepsis-Related Problems of the European Society of Intensive Care Medicine. Intensive Care Med 22:707–710
Gross-Weege W, K Dumon, A Dahmen, EM Schneider, HD Röher (1997) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) serum levels in surgical intensive care patients. Infection 25:213–216
Faulkner LB, F Tucci, A Tamburini, V Tintori, AA Lippi, F Bambi, F Malentacca, C Azzari, AMG Gelli, F Genovese, G Bernini (1998) G-CSF serum pharmacokinetics during peripheral blood progenitor cell mobilization: neutrophil count-adjusted dosage might potentially improve mobilization and be more cost-effective. Bone Marrow Transplant 21:1091–1095
Döcke WD, F Randow, U Syrbe, D Krausch, K Asadullah, P Reinke, HD Volk, W Kox (1997) Monocyte deactivation in septic patients: restauration by INF-γ treatment. Nat Med 3:678–681
Munford RS, J Pugin (2001) Normal responses to injury prevent systemic inflammation and can be immunosuppressive. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 163:316–321
Lejeune M, A Ferster, B Cantinieaux, E Sariban (1998) Prolonged but reversible neutrophil dysfunctions differentially sensitive to granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in children with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia. Br J Haematol 102:1284–1291
Roilides E, TJ Walsh, PA Pizzo, M Rubin (1991) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances the phagocytic and bactericidal activity of normal and defective human neutrophils. J Infect Dis 163:579–583
Lejeune M, E Sariban, B Cantinieaux, A Ferster, C Devalck, P Fondu (1996) Defective polymorphonuclear leukocyte functions in children receiving chemotherapy for cancer are partially restored by recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor in vitro. J Infect Dis 174:800–805
Anding K, A Kropec, E Schmidt-Eisenlohr, A Benzing, K Geiger, F Daschner (1993) Enhancement of in vitro bactericidal activity of neutrophils from trauma patients in the presence of granulocyte colony-stimulating factor. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 12:121–124
Ishikawa K, H Tanaka, T Matsuoka, T Shimazu, T Yoshioka, H Sugimoto (1998) Recombinant human granulocyte colony-stimulating factor attenuates inflammatory responses in septic patients with neutropenia. J Trauma 44:1047–1054–
Hollenstein U, M Homoncik, PJ Stohlawetz, C Marsik, A Sieder, HG Eichler, B Jilma (2000) Endotoxin down-modulates granulocyte colony-stimulating factor receptor (CD114) on human neutrophils. J Infect Dis 182:343–346
Jilma B, N Hergovich, M Homoncik, P Jilma-Stohlawetz, C Kreuzer, HG Eichler, M Zellner, J Pugin (2000) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor (G-CSF) downregulates its receptor (CD114) on neutrophils and induces gelatinase B release in humans. Br J Haematol 111:314–320
Weiss M, EM Schneider, J Tarnow, S Mettler, M Krone, A Teschemacher, H Lemoine (1996) Is inhibition of oxygen radical production of neutrophils by sympathomimetics mediated via beta-2 adrenoceptors? J Pharmacol Exp Ther 278:1105–1113
Olas B, B Wachowicz, A Buczynski (2000) The effects of granulocyte colony stimulating factor on chemiluminescence and lipid peroxidation of blood platelets treated with cisplatin. Anticancer Drugs 11:79–84
Cassatella MA (1998) The neutrophil: one of the cellular targets of interleukin-10. Int J Clin Lab Res 28:148–161
Giannoudis PV, RM Smith, SL Perry, AJ Windsor, RA Dickson, MC Bellamy (2000) Immediate IL-10 expression following major orthopaedic trauma: relationship to anti-inflammatory response and subsequent development of sepsis. Intensive Care Med 26:1076–1081
Boneberg EM, L Hareng, F Gantner, A Wendel, T Hartung (2000) Human monocytes express functional receptors for granulocyte colony-stimulating factor that mediate suppression of monokines and interferon-gamma. Blood 95:270–276
Karzai W, BU von Specht, C Parent, J Haberstroh, K Wollersen, C Natanson, SM Banks, PQ Eichacker (1999) G-CSF during Escherichia coli versus Staphylococcus aureus pneumonia in rats has fundamentally different and opposite effects. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 159:1377–1382
Vincent JL, DJ Bihari, PM Suter, HA Bruining, J White, MH Nicolas-Chanoin, M Wolff, RC Spencer, M Hemmer (1995) The prevalence of nosocomial infection in intensive care units in Europe. Results of the European Prevalence of Infection in Intensive Care (EPIC) Study. EPIC International Advisory Committee. JAMA 274:639–644
Girou E, M Pinsard, I Auriant, M Canonne (1996) Influence of the severity of illness measured by the Simplified Acute Physiology Score (SAPS) on occurrence of nosocomial infections in ICU patients. J Hosp Infect 34:131–137
Attalah HL, E Azoulay, C Lasclos, H Jouault, CJ Soussy, T Guillot, L Brochard, C Brun-Buisson, A Harf, C Delclaux (2002) Granulocyte colony-stimulating factor enhances host defenses against lung bacterial superinfection following peritonitis in non-neutropenic rats. Crit Care Med 30:2107–2114
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This study was supported by a grant from Aventis France
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, K., Azoulay, É., Attalah, L. et al. Bactericidal activity response of blood neutrophils from critically ill patients to in vitro granulocyte colony-stimulating factor stimulation. Intensive Care Med 29, 396–402 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-002-1623-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00134-002-1623-9