Abstract
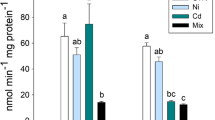
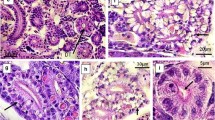
The present study is focused on determining the acute and chronic toxicity of nickel (Ni) to fish fingerlings, Mugil cephalus. The 96-h median lethal concentration (LC50) for Ni was found to be 42.2 ± 3.9 mg L−1. Based on the chronic toxicity test for 30 days, “No Observed Effect Concentration”, “Lowest Observed Effect Concentration” and “Chronic value” were found to be 2.9 ± 0.14, 4.7 ± 0.14 and 3.7 ± 0.14 mg Ni L−1, respectively. The activities of biomarker enzymes including esterase, superoxide dismutase and malate dehydrogenase showed differential expression and cellular anomalies like hyperplasia and detachment of bipolar cells from photoreceptor cells in the retina of eye of mullet. Cellular anomalies in the retina of fish eye affect the primary function of retina, which is to convert light energy into nerve impulses transferred to the brain via the optic nerve, leading to loss or poor vision.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adil AW, Sikdar-Bar M, Borana K, Khan HA, Andrabi SSM, Pervaiz PA (2011) Histo-pathological alterations induced in gill epithelium of African catfish, Clarias gariepinus exposed to copper sulphate. Asian J Exp Biol Sci 2:278–282.
Ameur WB, Megdiche YEl, Lapuente Jde, Barhoumi B, Trabelsi S, Ennaceur S, Camps L, Serret J, Ramos-López D, Gonzalez-Linares J, Touil S, Driss MR, Borràs M (2015) Oxidative stress, genotoxicity and histopathology biomarker responses in Mugil cephalus and Dicentrarchus labrax gill exposed to persistent pollutants. A field study in the Bizerte Lagoon: Tunisia. Chemosphere. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.02.050
APHA (1999) Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 20th edn. American Public Health Association, New York
Au DWT, Wu RSS, Zhou BS, Lam PKS (1999) Relationship between ultrastructural changes and EROD activities in liver of fish exposed to Benzo[a]pyrene. Environ Pollut 104(2):235–247
Beauchamp C, Fridovich I (1971) Superoxide dismutase: Improved assays and an assay applicable to acrylamide gels. Anal Biochem Rev 44:276–287
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein–dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Cardin JA (1985) Results of acute toxicity tests conducted with Nickel at ERL, Narragansett. U.S.EPA, Narragansett, RI: 1
Choudhury S, Thomas JK, Sylvain NJ, Ponomarenko O, Gordon RA, Heald SM, Janz DM, Krone PH, Coulthard I, George GN, Pickering IJ (2015) Selenium preferentially accumulates in the eye lens following embryonic exposure: a confocal X-ray fluorescence imaging study. Environ Sci Technol. doi:10.1021/es503848s
Davies KJ (1995) Oxidative stress: the paradox of aerobic life. Biochem Soc Symp 61:1–31
Dunnett CW (1964) New tables for multiple comparisons with a control. Biometrics 20:482–491
Finney DJ (1971) Probit analysis. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Gernhofer M, Pawert M, Schramm M, Muller E, Triebskorn R (2001) Ultra-structural biomarkers as tool to characterize the health status of fish in contaminated streams. J Aquat Ecol 8:241–260
Grasshoff K, Kremling K, Ehrhardt M (1999) Methods of sea water analysis, Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH, Weinheim, pp. 419–600
Hansen DJ (1983) Section on Acute Toxicity Tests to be Inserted in the April 1983 Report on Site Specific FAV’s. U.S. EPA, Narragansett, RI: 7.
Hunt JW, Anderson BS, Phillips BM, Tjeerderma RS, Puckett HM, Stephenson M, Tucker DW, Watson D (2002) Acute and chronic toxicity of nickel to marine organisms: implications for water quality criteria. Environ Toxicol Chem 21(11):2423–2430
Jin Y, Zhang X, Shu L, Chen L, Sun L, Qian H, Liu W, Fu Z (2010) Oxidative stress response and gene expression with atrazine exposure in adult female zebrafish (Danio rerio). Chemosphere 78:846–852. doi:10.1016/jchemosphere.2009.11.044
Joseph KO, Srivastava JP (1993) Mercury in the Ennore estuary and in fish from Madras coastal waters. J Environ Biol 14:55–62
Kannan KS, Lee KJ, Krishnamoorthy R, Purusothaman A, Shanthi K, Rao R (2007) Aerobic chromium reducingBacillus cereusisolated from the heavy metal contaminated Ennore Creek sediment, North of Chennai, Tamilnadu, South East India. Res J Microbiol 2(2):130–140
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 277:680–685
Livingstone DR (2001) Contaminant-stimulated reactive oxygen species production and oxidative damage in aquatic organisms. Mar Pollut Bull 42:656–666
Lopez-Galindo C, Vargas-Chacoff L, Nebot E, Casanueva JF, Rubio D, Mancera JM, Sole M (2010) Sublethal responses of the common mussel (Mytilus galloprovincialis) exposed to sodium hypochlorite and Mexel 432 used as antifoulants. Ecotoxicol Environ Safety. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2010.01.001
Mukhopadhyay D, Chattopadhyay A (2014) Induction of oxidative stress and related transcriptional effects of sodium fluoride in female Zebrafish liver. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s00128-014-1271-0
Padmini E, Usha Rani M, Vijaya Geetha B (2009) Studies on antioxidant status in Mugil cephalus in response to heavy metal pollution at Ennore estuary. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-008-0430-3
Palawski D, Hunn JB, Dwyer FJ (1985) Sensitivity of young striped bass to oranic and inorganic contaminants in fresh and saline water. Trans Am Fish Soc 114:748–753
PAN (Pesticide Network) Pesticides database (2012) Chemical toxicity studies on Aquatic Organisms. Toxicity studies for Nickel on All Organism Groups. http://www.pesticideinfo.org/.
Ridgway J, Shimmield G (2002) Estuaries as repositories of historical contamination and their impact on shelf Seas. Estuar Coast Shelf Sci. doi:10.1006/ecss.2002.1035
Seshan BRR, Usha N, Deepthi K (2011) Geochemical evidence of terrgenous influence in sediments of Buckingham canal, Ennore, South East Coast of India. Environ. Earth Sci. doi:10.1007/s12665-011-1258-7
Slaninova A, Smutna M, Modra H, Svobodova Z (2009) A review: oxidative stress in fish induced by pesticides. Neuroendocrinol Lett 30:2–12
Sprague JB (1973) The ABC’s of pollutant bioassay using fish. Biol Methods Assess Water Qual. doi:10.1520/STP34714S
Stephan CE, Mount DI, Hansen DJ, Gentile JH, Chapman GA, Brungs WA (1985) Guidelines for deriving numerical national water quality criteria for the protection of aquatic organisms and their uses. National Technical Information Service, Springfield, pp B85–B227049
Tu HT, Silvestre F, Wang N, Thome JP, Thanh N, Kestemont P (2010) A multi-biomarker approach to assess the impact of farming systems on black tiger shrimp (Peneaus monodon). Chemosphere. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2010.09.039
US Environmental Protection Agency (2002) Methods for measuring the acute toxicity of effluents and receiving waters to freshwater and marine organisms, 5th ed. October. U.S. EPA, Washington. 4303T. EPA-821-R-02-012.
Wendel JF, Weeden NF (1989) Visualization and interpretation of plant isozymes. In: Soltis DEDE, Soltis PS (eds) Isozymes in plant biology. Dioscordes Press, Oregon, pp 5–45
Zhihao Wu, Feng You, Hongjun Liu, Mengxia Liu, Jun Li, Peijun Zhang (2012) Effects of waterborne Fe(II) on juvenile turbot Scophthalmus maximus: analysis of respiratory rate, hematology and gill histology. Chin J Oceanol Limnol. doi:10.1007/s00343-012-1065-3
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Ministry of Earth Sciences, Government of India to provide funds for implementing the project on ‘Marine Ecotoxicology’. Thanks are also due to the Project Director, Integrated Coastal and Marine Area Management for constant encouragement and facilities provided for carrying out the work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagarjuna, A., Mohan, D. Biochemical and Histopathological Changes Induced by Nickel in the Striped Mullet, Mugil cephalus (Linnaeus 1758). Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 98, 33–40 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1961-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-016-1961-x