Abstract
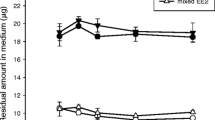
This paper investigates the effect of estrone (E1), 17β-estradiol (E2) and 17α-ethinylestradiol (EE2) individually and mixed at equal proportions (1:1:1) on Desmodesmus subspicatus and Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata in single and combined cultures (S+) at different exposure times based on algal growth (in vivo chlorophyll fluorescence and cell counting) and coenobium formation. EE2 and E2 were more toxic to individual and combined (S+) cultures than was E1. The frequency of coenobium formation by D. subspicatus increased significantly for all estrogens and all concentrations. After 96 h, D. subspicatus prevailed in S+. The results of the exposure to E+ suggested a less-than-additive effect on D. subspicatus and S+ and additive effect on P. subcapitata. Toxic effects occurred for both species exposed to E+ with individual estrogen concentrations below the NOEC of each species. Assays must include changes in response due to the exposure of more than one species to more than one estrogen.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altmann D, Schaar H, Bartel C et al (2012) Impact of ozonation on ecotoxicity and endocrine activity of tertiary treated wastewater effluent. Water Res 46:3693–3702. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2012.04.017
Buchanan JJ, Slater FR, Bai X, Pratt S (2013) Algal growth and community structure in a mixed-culture system using coal seam gas water as the water source. Environ Technol 34:695–701. doi:10.1080/09593330.2012.715676
Christen V, Hickmann S, Rechenberg B, Fent K (2010) Highly active human pharmaceuticals in aquatic systems: a concept for their identification based on their mode of action. Aquat Toxicol 96:167–181. doi:10.1016/j.aquatox.2009.11.021
Cleuvers M (2004) Mixture toxicity of the anti-inflammatory drugs diclofenac, ibuprofen, naproxen, and acetylsalicylic acid. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 59:309–315. doi:10.1016/S0147-6513(03)00141-6
Gressler PD, Bjerk TR, Schneider RDCS, et al (2013) Cultivation of Desmodesmus subspicatus in a tubular photobioreactor for bioremediation and microalgae oil production. Environ Technol 1–11. doi:10.1080/09593330.2013.822523
Hallgren P, Sorita Z, Berglund O, Persson A (2012) Effects of 17α-ethinylestradiol on individual life-history parameters and estimated population growth rates of the freshwater gastropods Radix balthica and Bithynia tentaculata. Ecotoxicology 21:803–810. doi:10.1007/s10646-011-0841-8
Kaczala F, Salomon PS, Marques M et al (2011) Effects from log-yard stormwater runoff on the microalgae Scenedesmus subspicatus: intra-storm magnitude and variability. J Hazard Mater 185:732–739. doi:10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.080
Kaur S, Sarkar M, Srivastava RB et al (2012) Fatty acid profiling and molecular characterization of some freshwater microalgae from India with potential for biodiesel production. New Biotechnol 29:332–344. doi:10.1016/j.nbt.2011.10.009
Lai KM, Scrimshaw MD, Lester JN (2002) Biotransformation and bioconcentration of steroid estrogens by Chlorella vulgaris. Appl Environ Microbiol 68:859–864. doi:10.1128/AEM.68.2.859
Laohaprapanon S, Kaczala F, Salomon PS et al (2012) Wastewater generated during cleaning/washing procedures in a wood-floor industry: toxicity on the microalgae Desmodesmus subspicatus. Environ Technol 33:2439–2446. doi:10.1080/09593330.2012.671853
Lindqvist N, Tuhkanen T, Kronberg L (2005) Occurrence of acidic pharmaceuticals in raw and treated sewages and in receiving waters. Water Res 39:2219–2228. doi:10.1016/j.watres.2005.04.003
López-Rodas V, Perdigones N, Marvá F et al (2008) Adaptation of phytoplankton to novel residual materials of water pollution: an experimental model analysing the evolution of an experimental microalgal population under formaldehyde contamination. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 80:158–162. doi:10.1007/s00128-007-9336-y
Lürling M (1998) Effect of grazing-associated infochemicals on growth and morphological development in Scenedesmus acutus (Chlorophyceae). J Phycol 34:578–586
Matozzo V, Gagné F, Marin MG et al (2008) Vitellogenin as a biomarker of exposure to estrogenic compounds in aquatic invertebrates: a review. Environ Int 34:531–545. doi:10.1016/j.envint.2007.09.008
Migowska N, Caban M, Stepnowski P, Kumirska J (2012) Simultaneous analysis of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and estrogenic hormones in water and wastewater samples using gas chromatography–mass spectrometry and gas chromatography with electron capture detection. Sci Total Environ 441:77–88. doi:10.1016/j.scitotenv.2012.09.043
OECD (2011) Guidelines for the testing of chemical: freshwater algae and cyanobacteria, growth inhibition test. OECD 201:1–25. doi:10.1787/9789264069923-en
Park JBK, Craggs RJ, Shilton a N (2011) Wastewater treatment high rate algal ponds for biofuel production. Bioresour Technol 102:35–42. doi:10.1016/j.biortech.2010.06.158
Pavlić Z, Vidaković-Cifrek Z, Puntarić D (2005) Toxicity of surfactants to green microalgae Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata and Scenedesmus subspicatus and to marine diatoms Phaeodactylum tricornutum and Skeletonema costatum. Chemosphere 61:1061–1068. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2005.03.051
Peña-Castro JM, Martínez-Jerónimo F, Esparza-García F, Cañizares-Villanueva RO (2004) Phenotypic plasticity in Scenedesmus incrassatulus (Chlorophyceae) in response to heavy metals stress. Chemosphere 57:1629–1636. doi:10.1016/j.chemosphere.2004.06.041
Ra J-S, Lee S-H, Lee J et al (2011) Occurrence of estrogenic chemicals in South Korean surface waters and municipal wastewaters. J Environ Monit 13:101–109. doi:10.1039/c0em00204f
Rose J, Holbech H, Lindholst C et al (2002) Vitellogenin induction by 17β-estradiol and 17α-ethinylestradiol in male zebrafish (Danio rerio). Comp Biochem Physiol Part C Toxicol Pharmacol 131:531–539
Salomão ALS, Marques M, Severo RG, da Cruz Roque OC (2012) Engineered ecosystem for on-site wastewater treatment in tropical areas. Water Sci Technol 66:2131–2137. doi:10.2166/wst.2012.434
Shi W, Wang L, Rousseau DPL, Lens PNL (2010) Removal of estrone, 17α-ethinylestradiol, and 17β-estradiol in algae and duckweed-based wastewater treatment systems. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 17:824–833
Souza MS, Hallgren P, Balseiro E, Hansson L-A (2013) Low concentrations, potential ecological consequences: synthetic estrogens alter life-history and demographic structures of aquatic invertebrates. Environ Pollut 178:237–243. doi:10.1016/j.envpol.2013.03.038
Ternes TA, Stumpf M, Mueller J et al (1999) Behavior and occurrence of estrogens in municipal sewage treatment plants-I. Investigations in Germany, Canada and Brazil. Sci Total Environ 225:81–90
Xu N, Xu YF, Li J, Tao HC (2012) Removal of estrogens in municipal wastewater treatment plants: a Chinese perspective. Environ Pollut 165:215–224
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the financial support from the National Council for Scientific and Technological Development-CNPq (Process No 556660/2009-9), the Carlos Chagas Filho Foundation for Supporting Research in the State of Rio de Janeiro-FAPERJ and the Swedish Foundation for International Cooperation in Research and Higher Education-STINT. The material made available by Prof. Edna Graneli and the technical support from Ms. Christina Esplund from the Marine Department, Linnaeus University in Sweden are also acknowledged.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
This experiment complied with the current laws of the country in which it was performed.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salomão, A.L.d., Soroldoni, S., Marques, M. et al. Effects of Single and Mixed Estrogens on Single and Combined Cultures of D. subspicatus and P. subcapitata . Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 93, 215–221 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1294-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-014-1294-6