Abstract
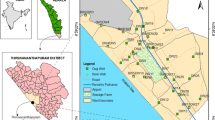
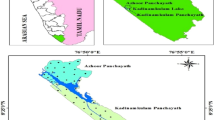
The aim of the present study is to investigate the pollution vulnerability of groundwater aquifers in the coastal regions of Tuticorin city, Tamil Nadu, India. Fourteen samples were analyzed to determine the concentration of trace elements (Pb, Zn, Cd, Hg, Cr and Cu) in the groundwater. Among the total samples six were collected from industrial areas and eight from non-industrial areas of Tuticorin city. The concentration of trace element ranges from 0.01 to 0.19 mg/kg−1 for Pb, from 0.01 to 0.16 mg/kg−1 for Zn, from BDL to 0.21 mg/kg−1 for Cd, from BDL (Below Detection Limit) to 0.023 mg/kg−1 for Hg, from 0.02 to 0.18 mg/kg−1 for Cr and from 0.01 to 0.16 mg/kg−1 for Cu. The trace element concentration in groundwater is higher than the WHO suggested maximum permissible limit except Zn and Cu.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abollino A, Aceto M, Buoso S, Gasparon M, Green WJ, Malandrino M (2004) Distribution of major, minor and trace elements in lake environments of Antarctica. Antarct Sci 16(3):277–291
APHA (1995) Standard methods for the examination of water and waste water (19th edn). American Public Health Association, Washington DC
Das J (2003) Geochemistry of trace elements in the groundwater of Cuttack city, India. Water Air Soil Pollut 147:129–140
Krishna Kumar S, Chandrasekar N, Seralathan P, Godson PS, Magesh NS (2011) Hydrogeochemical study of shallow carbonate aquifers, Rameswaram Island, India. Environ Monit Assess. doi:10.1007/s10661-011-2249-6
Lars J (2003) Hazards of heavy metal contamination. Brit Med Bull 18:445–454
Leung CM, Jiao JJ (2006) Heavy metal and trace element distributions in groundwater in natural slopes and highly urbanized spaces in mid-levels area, Hong Kong. Water Res 40:753–767
Mandal A, Sengupta D (2006) An assessment of soil contamination due to heavy metals around a coal-fired thermal power plant in India. Environ Geol 51(3):409–420
Puthiyasekar C, Neelakandan MA, Poongothai S (2010) Heavy metal contamination in bore water due to industrial pollution and polluted and non polluted sea water intrusion in Thoothukudi and Tirunelveli of South Tamil Nadu, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 85:598–601
Ramesh R, Shiv Kumar K, Eswaramoorthi S, Purvaja GR (1995) Migration and contamination of major and trace elements in groundwater of Madras City, India. Environ Geol 25:126–136
World Health Organization (WHO) (1984) Guidelines for drinking water quality V. 1 Recommendations. Switzerland, Geneva, p 130
Yosumura S, Vartsky D, Ellis KJ, Cohn SH (1980) Cadmium in human beings, Cadmium in the environment. In: Nriagu JO (ed) Partz ecological cycling. Wiley, New York, pp 12–34
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Department of Science and Technology, New Delhi, India for providing financial support under WAR for WATER program (Project No: DST/WAR-W/SWI/010/2010).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Krishna Kumar, S., Magesh, N.S. & Chandrasekar, N. Trace Element Concentration in Groundwater, Tuticorin City, Tamil Nadu, India. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88, 876–879 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0614-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-012-0614-y