Abstract
Key message
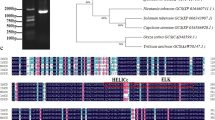
BrKCS6 encoding 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthases was cloned through MutMap and KASP analysis, and its function was verified via allelic mutants in Chinese cabbage.
Abstract
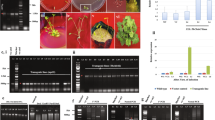
Bright and glossy green appearance is an attractive commodity character for leafy vegetables and is mainly caused by the absence of epicuticular wax crystals. In this study, two allelic epicuticular wax crystal deficiency mutants, wdm9 and wdm10, were obtained from an EMS mutagenesis population of Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Genetic analysis revealed that the mutant phenotype was controlled by a recessive nuclear gene. BrKCS6 encoding 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthases was identified as the candidate gene by MutMap and KASP analysis. A SNP (G to A) on BrKCS6 in wdm9 led to the amino acid substitution from serine (S) to phenylalanine (F), and another SNP (G to A) in wdm10 resulted in the amino acid substitution from serine (S) to leucine (L). Both SNPs are located in the ACP_syn_III_C conserved domain, corresponding to two highly conserved sites among BrKCS6 and its homologs. These two amino acid substitutions changed the secondary structure and the three-dimensional structure of BrKCS6 protein. qRT-PCR results showed that the relative expression of BrKCS6 significantly decreased in the flower, stem, and leaves in mutant, and the relative expressions of the downstream key genes of BrKCS6 were down-regulated in mutant. We were the first to clone the precious glossy bright gene BrKCS6 which has a great potential for commodity quality breeding in Chinese cabbage.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The plant material and datasets employed in this study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Bach L, Michaelson LV, Haslam R, Bellec Y, Gissot L, Marion J, Da Costa M, Boutin J-P (2008) The very-long-chain hydroxy fatty acyl-CoA dehydratase PASTICCINO2 is essential and limiting for plant development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:14727–14731
Bernard A, Domergue F, Pascal S, Jetter R, Renne C, Faure JD, Haslam RP, Napier JA, Lessire R, Joubes J (2012) Reconstitution of plant alkane biosynthesis in yeast demonstrates that Arabidopsis ECERIFERUM1 and ECERIFERUM3 are core components of a very-long-chain alkane synthesis complex. Plant Cell 24:3106–3118
Dellaert L, Van Es J, Koornneef M (1979) Eceriferum mutants in Arabidopsis thaliana (L.) Heynh. II. Phenotypic and genetic analysis. Arabid Inf Serv 16:10–26
Dong X, Ji J, Yang L, Fang Z, Zhuang M, Zhang Y, Lv H, Wang Y, Sun P, Tang J, Liu D, Liu Y, Li Z (2019) Fine-mapping and transcriptome analysis of BoGL-3, a wax-less gene in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). Mol Genet Genom 294:1231–1239
Fehling E, Mukherjee KD (1991) Acyl-CoA elongase from a higher plant (Lunaria annua): metabolic intermediates of very-long-chain acyl-CoA products and substrate specificity. Biochim Biophys Acta 1082:239–246
Fiebig A, Mayfield J, Miley N, Chau S, Fischer R, Preuss D (2000) Alterations in CER6, a gene identical to CUT1, differentially affect long-chain lipid content on the surface of pollen and stems. Plant Cell 12:2001–2008
Fu W, Huang S, Gao Y, Zhang M, Qu G, Wang N, Liu Z, Feng H (2020) Role of BrSDG8 on bolting in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa). Theor Appl Genet 133:2937–2948
Gan L, Zhu S, Zhao Z, Liu L, Wang X, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Wang J, Wang J, Guo X, Wan J (2017) Wax Crystal-Sparse Leaf 4, encoding a beta-ketoacyl-coenzyme A synthase 6, is involved in rice cuticular wax accumulation. Plant Cell Rep 36:1655–1666
Gao Y, Qu G, Huang S, Liu Z, Fu W, Zhang M, Feng H (2022) BrCPS1 function in leafy head formation was verified by two allelic mutations in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Front Plant Sci 13:889798
Guo W, Wu Q, Yang L, Hu W, Liu D, Liu Y (2020) Ectopic expression of CsKCS6 from navel orange promotes the production of very-long-chain fatty acids (VLCFAs) and increases the abiotic stress tolerance of Arabidopsis thaliana. Front Plant Sci 11:564656
Han F, Huang J, Xie Q, Liu Y, Fang Z, Yang L, Zhuang M, Zhang Y, Lv H, Wang Y, Ji J, Li Z (2021) Genetic mapping and candidate gene identification of BoGL5, a gene essential for cuticular wax biosynthesis in broccoli. BMC Genom 22:811
Hooker TS, Millar AA, Kunst L (2002) Significance of the expression of the CER6 condensing enzyme for cuticular wax production in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 129:1568–1580
Huang H, Lü S, Ayaz A, Zheng M, Yang X, Zaman W, Zhao H (2022) Arabidopsis KCS5 and KCS6 Play redundant roles in wax synthesis. Int J Mol Sci 23:4450
Huang H, Yang X, Zheng M, Chen Z, Yang Z, Wu P, Jenks MA, Wang G, Feng T, Liu L, Yang P, Lu S, Zhao H (2023) An ancestral role for 3-KETOACYL-COA SYNTHASE3 as a negative regulator of plant cuticular wax synthesis. Plant Cell
Ji JL, Cao WX, Dong X, Liu ZZ, Fang ZY, Zhuang M, Zhang YY, Lv HH, Wang Y, Sun PT, Liu YM, Li ZS, Yang LM (2018) A 252-bp insertion in BoCER1 is responsible for the glossy phenotype in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). Mol Breed 38:128
Jiang D, Fang J, Lou L, Zhao J, Yuan S, Yin L, Sun W, Peng L, Guo B, Li X (2015) Characterization of a null allelic mutant of the rice NAL1 gene reveals its role in regulating cell division. PLoS ONE 10:e0118169
Jiao Y, Burow G, Gladman N, Acosta-Martinez V, Chen J, Burke J, Ware D, Xin Z (2017) Efficient identification of causal mutations through sequencing of bulked F2 from two allelic bloomless mutants of Sorghum bicolor. Front Plant Sci 8:2267
Kunst L, Samuels AL (2003) Biosynthesis and secretion of plant cuticular wax. Prog Lipid Res 42(1):51–80
Lee SB, Suh MC (2015) Advances in the understanding of cuticular waxes in Arabidopsis thaliana and crop species. Plant Cell Rep 34:557–572
Lee G, Piao R, Lee Y, Kim B, Seo J, Lee D, Jang S, Jin Z, Lee C, Chin JH, Koh HJ (2019) Identification and characterization of LARGE EMBRYO, a new gene controlling embryo size in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Rice 12:22
Leide J, Hildebrandt U, Reussing K, Riederer M, Vogg G (2007) The developmental pattern of tomato fruit wax accumulation and its impact on cuticular transpiration barrier properties: effects of a deficiency in a beta-ketoacyl-coenzyme A synthase (LeCER6). Plant Physiol 144:1667–1679
Lewandowska M, Keyl A, Feussner I (2020) Wax biosynthesis in response to danger: its regulation upon abiotic and biotic stress. New Phytol 227:698–713
Liu R, Yu S, Wei Y, Zhang F, Yu Y, Zhao X, Zhang D, Wang W (2012) Establishment of high frequency regeneration system from cotyledon in Brassica rapa L. Acta Agric Boreali-Occident Sin 21:118–123
Liu D, Tang J, Liu Z, Dong X, Zhuang M, Zhang Y, Lv H, Sun P, Liu Y, Li Z, Ye Z, Fang Z, Yang L (2017a) Cgl2 plays an essential role in cuticular wax biosynthesis in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). BMC Plant Biol 17:223
Liu Z, Fang Z, Zhuang M, Zhang Y, Lv H, Liu Y, Li Z, Sun P, Tang J, Liu D, Zhang Z, Yang L (2017b) Fine-mapping and analysis of Cgl1, a gene conferring glossy trait in cabbage (Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata). Front Plant Sci 8:239
Liu D, Dong X, Liu Z, Tang J, Zhuang M, Zhang Y, Lv H, Liu Y, Li Z, Fang Z, Yang L (2018) Fine mapping and candidate gene identification for wax biosynthesis locus, BoWax1 in Brassica oleracea L. var. capitata. Front Plant Sci 9:309
Liu CH, Song GX, Wang N, Huang SN, Gao Y, Fu W, Zhang MD, Feng H (2021) A single SNP in Brcer1 results in wax deficiency in Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis). Sci Hortic 282:110019
Millar A, Clemens S, Zachgo S, Giblin E, Taylor D, Kunst L (1999) CUT1, an Arabidopsis gene required for cuticular wax biosynthesis and pollen fertility, encodes a very-long-chain fatty acid condensing enzyme. Plant Cell 11:825–838
Pascal S, Bernard A, Sorel M, Pervent M, Vile D, Haslam RP, Napier JA, Lessire R, Domergue F, Joubes J (2013) The Arabidopsis cer26 mutant, like the cer2 mutant, is specifically affected in the very long chain fatty acid elongation process. Plant J 73:733–746
Preuss D, Lemieux B, Yen G, Davis RJ (1993) A conditional sterile mutation eliminates surface components from Arabidopsis pollen and disrupts cell signaling during fertilization. Genes Dev 7:974–985
Ram H, Soni P, Salvi P, Gandass N, Sharma A, Kaur A, Sharma TR (2019) Insertional mutagenesis approaches and their use in rice for functional genomics. Plants 8:310
Richardson A, Boscari A, Schreiber L, Kerstiens G, Jarvis M, Herzyk P, Fricke W (2007) Cloning and expression analysis of candidate genes involved in wax deposition along the growing barley (Hordeum vulgare) leaf. Planta 226:1459–1473
Riezman H (2007) The long and short of fatty acid synthesis. Cell 130:587–588
Rowland O, Zheng H, Hepworth SR, Lam P, Jetter R, Kunst L (2006) CER4 encodes an alcohol-forming fatty acyl-coenzyme A reductase involved in cuticular wax production in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 142:866–877
Serra O, Soler M, Hohn C, Franke R, Schreiber L, Prat S, Molinas M, Figueras M (2009) Silencing of StKCS6 in potato periderm leads to reduced chain lengths of suberin and wax compounds and increased peridermal transpiration. J Exp Bot 60:697–707
Tang GX, Zhou WJ, Li HZ, Mao BZ, Yoneyama K (2010) Medium, explant and genotype factors influencing shoot regeneration in oilseed Brassica spp. J Agron Crop Sci 189:351–358
Terauchi R, Abe A, Takagi H, Yoshida K, Kosugi S, Natsume S, Yaegashi H, Kanzaki H, Matsumura H, Mitsuoka C, Utsushi H, Tamiru M (2012) Whole genome sequencing and future breeding of rice. J Plant Biochem Biotechnol 21:10–14
Todd J, Post-Beittenmiller D, Jaworski JG (1999) KCS1 encodes a fatty acid elongase 3-ketoacyl-CoA synthase affecting wax biosynthesis in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 17:119–130
Wang CJ, Li HL, Li YX, Meng QF, Xie F, Xu YJ, Wan ZJ (2019) Genetic characterization and fine mapping BrCER4 in involved cuticular wax formation in purple cai-tai (Brassica rapa L. var. purpurea). Mol Breed 39:12
Xin Y, Tan C, Wang C, Wu Y, Huang S, Gao Y, Wang L, Wang N, Liu Z, Feng H (2022) BrAN contributes to leafy head formation by regulating leaf width in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp pekinensis). Hortic Res 9:uhac167
Xiong C, Xie Q, Yang Q, Sun P, Gao S, Li H, Zhang J, Wang T, Ye Z, Yang C (2020) WOOLLY, interacting with MYB transcription factor MYB31, regulates cuticular wax biosynthesis by modulating CER6 expression in tomato. Plant J 103:323–337
Xu H, Wang X, Zhao H, Liu F (2008) An intensive understanding of vacuum infiltration transformation of pakchoi (Brassica rapa ssp. chinensis). Plant Cell Rep 27:1369–1376
Xu L, Zeisler V, Schreiber L, Gao J, Hu K, Wen J, Yi B, Shen J, Ma C, Tu J, Fu T (2017) At5g02890 overexpression of the novel arabidopsis gene alters inflorescence stem wax composition and affects phytohormone homeostasis. Front Plant Sci 8:68
Yang S, Tang H, Wei X, Zhao Y, Wang Z, Su H, Niu L, Yuan Y, Zhang X (2022) BrWAX3, encoding a beta-ketoacyl-CoA synthase, plays an essential role in cuticular wax biosynthesis in Chinese cabbage. Int J Mol Sci 23:10938
Yeats TH, Rose JK (2013) The formation and function of plant cuticles. Plant Physiol 163:5–20
Zhang F-L, Takahata Y, Watanabe M, Xu J-B (2000) Agrobacterium-mediated transformation of cotyledonary explants of Chinese cabbage (Brassica campestris L. ssp. pekinensis). Plant Cell Rep 19:569–575
Zhang X, Wang Q, Zou C, Liu Z, Wang Y, Feng H (2013) Genetic analysis and preliminary mapping of wax gene on stem in Chinese cabbage. Mol Breed 32:867–874
Zhang C, Chen F, Zhao Z, Hu L, Liu H, Cheng Z, Weng Y, Chen P, Li Y (2018) Mutations in CsPID encoding a Ser/Thr protein kinase are responsible for round leaf shape in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Theor Appl Genet 131:1379–1389
Zhang S, Zhou F, Liu Z, Feng X, Li Y, Zhu P (2022) Inactivation of BoORP3a, an oxysterol-binding protein, causes a low wax phenotype in ornamental kale. Hortic Res 9:uhac219
Zhao Y, Huang S, Zhang M, Zhang Y, Feng H (2021) Mapping of a pale green mutant gene and its functional verification by allelic mutations in Chinese cabbage (Brassica rapa L. ssp. pekinensis). Front Plant Sci 12:699308
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31972405).
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 31972405).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HF and JR designed the experiments. GS performed the experiments, and SD wrote the manuscript. CL assisted in the screening of mutants. HF and JZ revised the manuscript. All authors reviewed and approved this submission.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Communicated by Esther van der Knaap.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Song, G., Dong, S., Liu, C. et al. BrKCS6 mutation conferred a bright glossy phenotype to Chinese cabbage. Theor Appl Genet 136, 216 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-023-04464-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-023-04464-1