Abstract
Understanding the population structure and linkage disequilibrium (LD) is a prerequisite for association mapping of complex traits in a target population. In this study, we assessed the genetic diversity, population structure and the extent of LD in a panel of 192 inbred lines of Brassica napus from all over the world using 451 single-locus microsatellite markers. The inbred lines could be divided into P1 and P2 groups by a model-based population structure analysis. Out of the 142 inbred lines in the P1 group, 126 lines were from China and Japan, and the remaining 16 lines were from Europe, Canada and Australia. In the P2 group, 33 out of the 50 lines were from Europe, Canada, and Australia, and the remaining 17 lines were from China. Structure analysis further divided each group into two subgroups. AMOVA, pairwise F ST and neutrality analyses confirmed the differentiation between groups and subgroups. More than 80 % of the pairwise kinship estimates between inbred lines were <0.05, indicating that relative kinship is weak in our panel. Only 6 % linked marker pairs showed LD, suggesting the low level of LD in this association panel. The LD decayed within 0.5–1 cM at the genome level, and varied considerably across each group and subgroup, due to the population size, genetic background and genetic drift. The characterization of the population structure and LD patterns would be useful for performing association studies for complex agronomic traits in rapeseed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Black WC, Krafsur ES (1985) A FORTRAN program for analysis of genotypic frequencies and description of the breeding structure of populations. Theor Appl Genet 70:484–490
Bradbury PJ, Zhang Z, Kroon DE, Casstevens TM, Ramdoss Y, Buckler ES (2007) TASSEL: software for association mapping of complex traits in diverse samples. Bioinformatics 23:2633–2635
Chen S, Nelson MN, Ghamkhar K, Fu T, Cowling WA (2008) Divergent patterns of allelic diversity from similar origins: the case of oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.) in China and Australia. Genome 51:1–10
Chen S, Zou J, Cowling WA, Meng J (2010) Allelic diversity in a novel gene pool of canola-quality Brassica napus enriched with alleles from B. rapa and B. carinata. Crop Pasture Sci 61:483–492
Cheng X, Xu J, Xia S, Gu J, Yang Y, Fu J, Qian X, Zhang S, Wu J, Liu K (2009) Development and genetic mapping of microsatellite markers from genome survey sequences in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 118:1121–1131
Cowling W (2007) Genetic diversity in Australian canola and implications for crop breeding for changing future environments. Field Crops Res 104:103–111
Delourme R, Falentin C, Huteau V, Clouet V, Horvais R, Gandon B, Specel S, Hanneton L, Dheu JE, Deschamps M, Margale E, Vincourt P, Renard M (2006) Genetic control of oil content in oilseed rape (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 113:1331–1345
Ecke W, Clemens R, Honsdorf N, Becker H (2010) Extent and structure of linkage disequilibrium in canola quality winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Theor Appl Genet 120:921–931
Ersoz ES, Yu J, Buckler ES (2007) Applications of linkage disequilibrium and association mapping in crop plants. Genomics-assisted crop improvement Springer, Dordrecht, pp 97–120
Evanno G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software structure: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Ewens WJ (1972) The sampling theory of selectively neutral alleles. Theor Popul Biol 3:87–112
Excoffier L, Laval G, Schneider S (2005) Arlequin version 3.0: an integrated software package for population genetics data analysis. Evol Bioinform Online 1:47–50
Fan C, Cai G, Qin J, Li Q, Yang M, Wu J, Fu T, Liu K, Zhou Y (2010) Mapping of quantitative trait loci and development of allele-specific markers for seed weight in Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 121:1289–1301
Flint-Garcia SA, Thornsberry JM, Iv B SE (2003) Structure of linkage disequilibrium in plants. Ann Rev Plant Biol 54:357–374
Fukunaga K, Hill J, Vigouroux Y, Matsuoka Y, Sanchez GJ, Liu K, Buckler ES, Doebley J (2005) Genetic diversity and population structure of teosinte. Genetics 169:2241–2254
Hardy OJ, Vekemans X (2002) SPAGeDi: a versatile computer program to analyse spatial genetic structure at the individual or population levels. Mol Ecol Notes 2:618–620
Hasan M, Seyis F, Badani AG, Pons-Kühnemann J, Friedt W, Lühs W, Snowdon RJ (2006) Analysis of genetic diversity in the Brassica napus L. gene pool using SSR markers. Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:793–802
Hasan M, Friedt W, Pons-Kühnemann J, Freitag NM, Link K, Snowdon RJ (2008) Association of gene-linked SSR markers to seed glucosinolate content in oilseed rape (Brassica napus ssp. napus). Theor Appl Genet 116:1035–1049
Honsdorf N, Becker HC, Ecke W (2010) Association mapping for phenological, morphological, and quality traits in canola quality winter rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Genome 53:899–907
Hu S, Yu C, Zhao H, Sun G, Zhao S, Vyvadilova M, Kucera V (2007) Genetic diversity of Brassica napus L. Germplasm from China and Europe assessed by some agronomically important characters. Euphytica 154:9–16
Huang X, Wei X, Sang T, Zhao Q, Feng Q, Zhao Y, Li C, Zhu C, Lu T, Zhang Z, Li M, Fan D, Guo Y, Wang A, Wang L, Deng L, Li W, Lu Y, Weng Q, Liu K, Huang T, Zhou T, Jing Y, Li W, Lin Z, Buckler ES, Qian Q, Zhang Q-F, Li J, Han B (2010) Genome-wide association studies of 14 agronomic traits in rice landraces. Nat Genet 42:961–967
Kalinowski S (2005) HP-RARE 1.0: a computer program for performing rarefaction on measures of allelic richness. Mol Ecol Notes 5:187–189
Lam H, Xu X, Liu X, Chen W, Yang G, Wong F-L, Li M-W, He W, Qin N, Wang B, Li J, Jian M, Wang J, Shao G, Wang J, Sun SS-M, Zhang G (2010) Resequencing of 31 wild and cultivated soybean genomes identifies patterns of genetic diversity and selection. Nat Genet 42:1053–1059
Li H, Chen X, Yang Y, Xu J, Gu J, Fu J, Qian X, Zhang S, Wu J, Liu K (2010) Development and genetic mapping of microsatellite markers from whole genome shotgun sequences in Brassica oleracea. Mol Breed. doi:10.1007/s11032-010-9509-y
Lijavetzky D, Cabezas JA, Ibanez A, Rodriguez V, Martinez-Zapater JM (2007) High throughput SNP discovery and genotyping in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) by combining a re-sequencing approach and SNPlex technology. BMC Genomics 8:424
Liu H (1984) Origin and evolution of rapeseeds. Acta Agron Sin 10:9–18
Liu H (1985) Rapeseed genetics and breeding. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai, pp 559–566
Liu A, Burke JM (2006) Patterns of nucleotide diversity in wild and cultivated sunflower. Genetics 173:321–330
Liu K, Muse SV (2005) PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics 21:2128–2129
Long Y, Shi J, Qiu D, Li R, Zhang C, Wang J, Hou J, Zhao J, Shi L, Park B-S, Choi SR, Lim YP, Meng J (2007) Flowering time quantitative trait loci analysis of oilseed Brassica in multiple environments and genome wide alignment with Arabidopsis. Genetics 177:2433–2444
Manly B (1985) The statistics of natural selection. Chapman and Hall, London
Mather KA, Caicedo AL, Polato NR, Olsen KM, McCouch S, Purugganan MD (2007) The extent of linkage disequilibrium in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Genetics 177:2223–2232
McNally KL, Childs KL, Bohnert R, Davidson RM, Zhao K, Ulat VJ, Zeller G, Clark RM, Hoen DR, Bureau TE, Stokowski R, Ballinger DG, Frazer KA, Cox DR, Padhukasahasram B, Bustamante CD, Weigel D, Mackill DJ, Bruskiewich RM, Rätsch G, Buell CR, Leung H, Leach JE (2009) Genomewide SNP variation reveals relationships among landraces and modern varieties of rice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:12273–12278
Myles S, Peiffer J, Brown PJ, Ersoz ES, Zhang Z, Costich DE, Buckler ES (2009) Association mapping: critical considerations shift from genotyping to experimental design. Plant Cell 21:2194–2202
Nordborg M, Borevitz JO, Bergelson J, Berry CC, Chory J, Hagenblad J, Kreitman M, Maloof JN, Noyes T, Oefner PJ, Stahl EA, Weigel D (2002) The extent of linkage disequilibrium in Arabidopsis thaliana. Nat Genet 30:190–193
Ohta T (1982) Linkage disequilibrium due to random genetic drift in finite subdivided populations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:1940–1944
Parkin IAP, Lydiate DJ, Trick M (2002) Assessing the level of collinearity between Arabidopsis thaliana and Brassica napus for A-thaliana chromosome 5. Genome 45:356–366
Pritchard J, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of population structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Radoev M, Becker HC, Ecke W (2008) Genetic analysis of heterosis for yield and yield components in rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) by QTL mapping. Genetics. doi:108.089680
Remington DL, Thornsberry JM, Matsuoka Y, Wilson LM, Whitt SR, Doebley J, Kresovich S, Goodman MM, Buckler Iv ES (2001) Structure of linkage disequilibrium and phenotypic associations in the maize genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:11479–11484
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599
The SAS Institute (1999) SAS/STAT User’s Guide, Version 8. SAS Institute, Cary
Trick M, Long Y, Meng JL, Bancroft I (2009) Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) discovery in the polyploid Brassica napus using Solexa transcriptome sequencing. Plant Biotechnol J 7:334–346
U (1935) Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jpn J Bot 7:389–425
Vigouroux Y, Jaqueth JS, Matsuoka Y, Smith OS, Beavis WD, Smith JSC, Doebley J (2002a) Rate and pattern of mutation at microsatellite loci in maize. Mol Biol Evol 19:1251–1260
Vigouroux Y, McMullen M, Hittinger CT, Houchins K, Schulz L, Kresovich S, Matsuoka Y, Doebley J (2002b) Identifying genes of agronomic importance in maize by screening microsatellites for evidence of selection during domestication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9650–9655
Wang F, Wang X, Chen X, Xiao Y, Li H, Zhang S, Xu J, Fu J, Huang L, Wu J, Liu K (2011) Abundance, marker development and genetic mapping of microsatellites from unigenes in Brassica napus. Mol Breed doi:10.1007/s11032-011-9658-7
Watterson GA (1978) The homozygosity test of neutrality. Genetics 88:405–417
Weir B, Cockerham C (1984) Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of population structure. Evolution 38:1358–1370
Wen W, Mei H, Feng F, Yu S, Huang Z, Wu J, Chen L, Xu X, Luo L (2009) Population structure and association mapping on chromosome 7 using a diverse panel of Chinese germplasm of rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 119:459–470
Xu J, Qian X, Wang X, Li R, Cheng X, Yang Y, Fu J, Zhang S, King GJ, Wu J, Liu K (2010) Construction of an integrated genetic linkage map for the A genome of Brassica napus using SSR markers derived from sequenced BACs in B. rapa. BMC Genomics 11:594
Yan J, Shah T, Warburton ML, Buckler ES, McMullen MD, Crouch J (2009) Genetic characterization and linkage disequilibrium estimation of a global maize collection using SNP markers. PLoS One 4:e8451
Yan J, Kandianis CB, Harjes CE, Bai L, Kim E-H, Yang X, Skinner DJ, Fu Z, Mitchell S, Li Q, Fernandez MGS, Zaharieva M, Babu R, Fu Y, Palacios N, Li J, DellaPenna D, Brutnell T, Buckler ES, Warburton ML, Rocheford T (2010) Rare genetic variation at Zea mays crtRB1 increases β-carotene in maize grain. Nat Genet 42:322–327
Yeh F, Yang R, Boyle T (1999) Popgene version 1.31, Microsoft window-based freeware for population genetic analysis. http://www.ualberta.ca/~fyeh/
Yu J, Pressoir G, Briggs WH, Bi IV, Yamasaki M, Doebley JF, McMullen MD, Gaut BS, Nielsen DM, Holland JB (2006) A unified mixed-model method for association mapping that accounts for multiple levels of relatedness. Nat Genet 38:203–208
Zhang D, Zhang H, Wang M, Sun J, Qi Y, Wang F, Wei X, Han L, Wang X, Li Z (2009) Genetic structure and differentiation of Oryza sativa L. in China revealed by microsatellites. Theor Appl Genet 119:1105–1117
Zou J, Jiang C, Cao Z, Li R, Long Y, Chen S, Meng J (2010) Association mapping of seed oil content in Brassica napus and comparison with quantitative trait loci identified from linkage mapping. Genome 53:908–916
Acknowledgments
We thank Prof. Jianbing Yan at Huazhong Agricultural University for his critical review of this manuscript, and sincerely thank Mayank Gautam for his critical reading of the manuscript. The research was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 31071452) and the Doctoral Fund of Ministry of Education of China (No. 20100146110019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by H. Becker.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
122_2012_1843_MOESM1_ESM.ppt
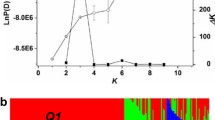
Supplemental Fig. 1 Estimation of LnP(D) and Δk in the total panel and inferred groups. a) the total panel; b) the P1 group; c) the P2 group. The blue and red curves represent LnP(D) and Δk, respectively. The bar indicates standard deviation. Supplementary material 1 (PPT 161 kb)
122_2012_1843_MOESM2_ESM.ppt
Supplemental Fig. 2 The PCA analysis on the different populations. a) the total panel; b) the P1 group; c) the P2 group. Colored points represent inbred lines belonging to different groups and subgroups. Supplementary material 2 (PPT 172 kb)
122_2012_1843_MOESM3_ESM.ppt
Supplemental Fig. 3 Unrooted Neigbour-Joining tree of 192 inbred lines. Colored lines correspond to assignments to different model-based subgroups. Supplementary material 3 (PPT 219 kb)
122_2012_1843_MOESM4_ESM.ppt
Supplemental Fig. 4 LD decays (r 2) in the inferred groups and subgroups. The r 2 value for markers with genetic distance of 0 cM is defined as 1. The dots are mean r 2 values for marker genetic intervals of 0 cM, 0-0.5 cM, 0.5-1 cM, 1-2 cM, 2-5 cM, 5-10 cM, 10-50 cM, 50-100 cM and 100-200 cM, respectively. The curves were drawn using the nonlinear regression model. G4 subgroup was not included in the analysis due to its small population size. Supplementary material 4 (PPT 147 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiao, Y., Cai, D., Yang, W. et al. Genetic structure and linkage disequilibrium pattern of a rapeseed (Brassica napus L.) association mapping panel revealed by microsatellites. Theor Appl Genet 125, 437–447 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1843-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1843-5