Abstract
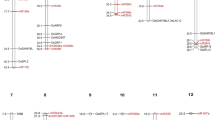
Well-saturated linkage maps especially those based on expressed sequence tag (EST)-derived genic molecular markers (GMMs) are a pre-requisite for molecular breeding. This is especially true in important legumes such as chickpea where few simple sequence repeats (SSR) and even fewer GMM-based maps have been developed. Therefore, in this study, 2,496 ESTs were generated from chickpea seeds and utilized for the development of 487 novel EST-derived functional markers which included 125 EST-SSRs, 151 intron targeted primers (ITPs), 109 expressed sequence tag polymorphisms (ESTPs), and 102 single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs). Whereas EST-SSRs, ITPs, and ESTPs were developed by in silico analysis of the developed EST sequences, SNPs were identified by allele resequencing and their genotyping was performed using the Illumina GoldenGate Assay. Parental polymorphism was analyzed between C. arietinum ICC4958 and C. reticulatum PI489777, parents of the reference chickpea mapping population, using a total of 872 markers: 487 new gene-based markers developed in this study along with 385 previously published markers, of which 318 (36.5%) were found to be polymorphic and were used for genotyping. The genotypic data were integrated with the previously published data of 108 markers and an advanced linkage map was generated that contained 406 loci distributed on eight linkage groups that spanned 1,497.7 cM. The average marker density was 3.68 cM and the average number of markers per LG was 50.8. Among the mapped markers, 303 new genomic locations were defined that included 177 gene-based and 126 gSSRs (genomic SSRs) thereby producing the most advanced gene-rich map of chickpea solely based on co-dominant markers.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad F, Gaur P, Croser J (2005) Chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Genetic resources, chromosome engineering and crop improvement—grain legumes, vol 1. CRC Press, USA, pp 185–214
Akhunov E, Nicolet C, Dvorak J (2009) Single nucleotide polymorphism genotyping in polyploidy wheat with the Illumina GoldenGate Assay. Theor Appl Genet 119:507–517
Areshchenkova T, Ganal MW (2002) Comparative analysis of polymorphism and chromosomal location of tomato microsatellite markers isolated from different sources. Theor Appl Genet 104:229–235
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Rep 9:208–218
Ashraf N, Ghai D, Barman P, Basu S, Gangisetty N, Mandal MK, Chakraborty N, Datta A, Chakraborty S (2009) Comparative analysis of genotype dependent expressed sequence tags and stress-responsive transcriptome of chickpea wilt illustrate predicted and unexpected genes and novel regulators of plant immunity. BMC Genomics 10:415
Brown GR, Kadel EE III, Bassoni DL, Kiehne KL, Temesgen B, van Buijtenen JP, Sewell MM, Marshall KA, Neale DB (2001) Anchored reference loci in loblolly Pine (Pinus taeda L.) for integrating pine genomics. Genetics 159:799–809
Bryan GJ, Stephenson P, Collins A, Kirby J, Smith JB, Gale MD (1999) Low levels of DNA sequence variation among adapted genotypes of hexaploid wheat. Theor Appl Genet 99:192–198
Buhariwalla HK, Jayashree B, Eshwar K, Crouch JH (2005) Development of ESTs from chickpea roots and their use in diversity analysis of the Cicer genus. BMC Plant Biol 5:16
Chakravarti A, Lasher LK, Reefer JE (1991) A maximum likelihood method for estimating genome length using genetic linkage data. Genetics 128:175–182
Cho YG, Ishii T, Temnykh S, Chen X, Lipovich L, McCouch SR, Park WD, Ayres N, Cartinhour S (2000) Diversity of microsatellites derived from genomic libraries and GenBank sequences in rice (Oryza sativa L.). Theor Appl Genet 100:713–722
Cho S, Chen W, Muehlbauer F (2004) Pathotype-specific genetic factors in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) for quantitative resistance to ascochyta blight. Theor Appl Genet 109:733–739
Choi HK, Kim D, Uhm T, Limpens E, Lim H, Mun JH, Kalo P, Penmetsa RV, Seres A, Kulikova O, Roe BA, Bisseling T, Kiss GB, Cook DR (2004) A sequence-based genetic map of Medicago truncatula and comparison of marker colinearity with M. sativa. Genetics 166:1463–1502
Choi IY, Hyten DL, Matukumalli LK, Song Q, Chaky JM, Quigley CV, Chase K, Lark KG, Reiter RS, Yoon MS, Hwang EY, Yi SI, Young ND, Shoemaker RC, van Tassel CP, Specht JE, Cregan PB (2007) A soybean transcript map: gene distribution, haplotype and single-nucleotide polymorphism analysis. Genetics 176:685–696
Choudhary S, Sethy NK, Shokeen B, Bhatia S (2009) Development of chickpea EST-SSR markers and analysis of allelic variation across related species. Theor Appl Genet 118:591–608
Coram T, Pang E (2005) Isolation and analysis of candidate ascochyta blight defense genes in chickpea, Part I. Generation and analysis of an expressed sequence tag (EST) library. Physiol Mol Plant Pathol 66:192–200
Deokar AA, Kondawar V, Jain PK, Karuppayil SM, Raju NL, Vadez V, Varshney RK, Srinivasan R (2011) Comparative analysis of expressed sequence tags (ESTs) between drought-tolerant and susceptible genotypes of chickpea under terminal drought stress. BMC Plant Biol 11:70
Doyle JJ, Doyle JL (1987) A rapid DNA isolation procedure for small quantities of fresh leaf tissue. Phytochem Bull 19:11–15
Eckert AJ, Pande B, Ersoz SE, Wright MH, Rashbrook VK, Nicolet MC, Neale DB (2009) High-throughput genotyping and mapping of single nucleotide polymorphisms in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). Tree Genet Genomes 5:225–234
Fan JB, Oliphant A, Shen R, Kermani BG, Garcia F, Gunderson KL, Hansen M, Steemers F, Butler SL, Deloukas P, Galver L, Hunt S, McBride C, Bibikova M, Rubano T, Chen J, Wickham E, Doucet D, Chang W, Campbell D, Zhang B, Kruglyak S, Bentley D, Haas J, Rigault P, Zhou L, Stuelpnagel J, Chee MS (2003) Highly parallel SNP genotyping. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 68:69–78
Flandez-Galvez H, Ford R, Pang E, Taylor P (2003) An intraspecific linkage map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genome based on sequence tagged microsatellite site and resistance gene analog markers. Theor Appl Genet 106:1447–1456
Fredslund J, Madsen LH, Hougaard BK, Nielsen AM, Bertioli D, Sandal N, Stougaard J, Schauser L (2006) GeMprospector—online design of cross species genetic marker candidates in legumes and grasses. Nucleic Acids Res 34:670–675
Galasso I, Frediani M, Maggiani M, Cremoni R, Pignone D (1996) Chromatin characterization by banding techniques, in situ hybridization, and nuclear DNA content in Cicer L. (Leguminosae). Genome 39:258–265
Garg R, Patel RK, Tyagi AK, Jain M (2011a) De novo assembly of chickpea transcriptome using short reads for gene discovery and marker identification. DNA Res 18:53–63
Garg R, Patel RK, Jhanwar S, Priya P, Bhattacharjee A, Yadav G, Bhatia S, Chattopadhyay D, Tyagi AK, Jain M (2011b) Gene discovery and tissue-specific transcriptome analysis in chickpea with massively parallel pyrosequencing and web resource development. Plant Physiol. doi:10.1104/pp.111.178616
Gaur R, Sethy NK, Choudhary S, Shokeen B, Gupta V, Bhatia S (2011) Advancing the STMS genomic resources for defining new locations on the intraspecific genetic linkage map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). BMC Genomics 12:117
Gujaria N, Kumar A, Dauthal P, Dubey A, Hiremath P, Bhanu Prakash A, Farmer A, Bhide M, Shah T, Gaur PM, Upadhyaya HD, Bhatia S, Cook DR, May GD, Varshney RK (2011) Development and use of genic molecular markers (GMMs) for construction of a transcript map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Theor Appl Genet 122:1577–1589
Guo W, Cai C, Wang C, Han Z, Song X, Wang K, Niu X, Wang C, Lu K, Shi B, Zhang T (2007) A microsatellite-based, gene-rich linkage map reveals genome structure, function, and evolution in Gossypium. Genetics 176:527–541
Gutierrez MV, Vaz Patto MC, Huguet T, Cubero JI, Moreno MT, Torres AM (2005) Cross-species amplification of Medicago truncatula microsatellites across three major pulse crops. Theor Appl Genet 110:1210–1217
Hiremath PJ, Farmer A, Cannon SB, Woodward J, Kudapa H, Tuteja R, Kumar A, BhanuPrakash A, Mulaosmanovic B, Gujaria N, Krishnamurthy L, Gaur PM, KaviKishor PB, Shah T, Srinivasan R, Lohse M, Xiao Y, Town CD, Cook DR, May GD, Varshney RK (2011) Large-scale transcriptome analysis in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.), an orphan legume crop of the semi-arid tropics of Asia and Africa. Plant Biotechnol J. doi:10.1111/j.1467-7652.2011.00625.x)
Holland JB, Helland SJ, Sharopova N, Rhyne DC (2001) Polymorphism of PCR-based markers targeting exons, introns, promoter regions and SSRs in maize and introns and repeat sequences in oat. Genome 44:1065–1076
Huang X, Madan A (1999) CAP3: a DNA sequence assembly program. Genome Res 9:868–877
Hüttel B, Winter P, Weising K, Choumane W, Weigand F, Kahl G (1999) Sequence-tagged microsatellite markers for chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Genome 42:210–217
Hyten DL, Song Q, Zhu Y, Choi IY, Nelson RL, Costa JM, Specht JE, Shoemaker RC, Cregan PB (2006) Impacts of genetic bottlenecks on soybean genome diversity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:16666–16671
Hyten DL, Song Q, Choi IY, Yoon MS, Cregan PB (2008) Highthroughput genotyping with the GoldenGate assay in the complex genome of soybean. Theor Appl Genet 116:945–952
Jander G, Norris SR, Rounsley SD, Bus DF, Levin IM, Last RL (2002) Arabidopsis map-based cloning in the postgenome era. Plant Physiol 129:440–450
Kantety RV, Rota ML, Matthews DE, Sorrells ME (2002) Data mining for simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags from barley, maize, sorghum and wheat. Plant Mol Biol 48:501–510
Kidwell KK, Echt CS, Osborn TC, McCoy TJ (1993) RFLP and RAPD linkage map of alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.) 2n=16. In: O’Brien SJ (ed) Genetic maps, vol 6. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, New York, pp 84–85
Kosambi D (1994) The estimation of map distances from recombination values. Ann Eugen 12:172–175
Kumpatla SP, Mukhopadhyay S (2005) Mining and survey of simple sequence repeats in expressed sequence tags of dicotyledonous species. Genome 48:985–998
Lambrides CJ, Godwin ID, Lawn RJ, Imre BC (2004) Segregation distortion in seed testa color in mungbean (Vigna radiata L. Wilcek). J Hered 95:532–535
Lichtenzveig J, Scheuring C, Dodge J, Abbo S, Zhang HB (2005) Construction of BAC and BIBAC libraries and their applications for generation of SSR markers for genome analysis of chickpea, Cicer arietinum L. Theor Appl Genet 110:492–510
Millan T, Clarke H, Siddique K, Buhariwalla H, Gaur P, Kumar J, Gil J, Kahl G, Winter P (2006) Chickpea molecular breeding: new tools and concepts. Euphytica 147(1):81–103
Millan T, Winter P, Jüngling R, Gil J, Rubio J, Cho S, Cobos MJ, Iruela M, Rajesh PN, Tekeoglu M, Kahl G, Muehlbauer FJ (2010) A consensus genetic map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) based on 10 mapping populations. Euphytica 175:175–189
Muchero W, Diop NN, Bhat PR, Fenton RD, Wanamaker S, Pottor VM, Hearne S, Cisse N, Fatokun C, Ehlers JD, Roberts PA, Close TJ (2009) A consensus genetic map of cowpea [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.] and synteny based on EST-derived SNPs. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:18159–18164
Namroud MC, Beaulieu J, Juge N, Laroche J, Bousquet J (2008) Scanning the genome for gene single nucleotide polymorphisms involved in adaptive population differentiation in white spruce. Mol Ecol 17:3599–3613
Nayak SN, Zhu H, Varghese N, Datta S, Choi H, Horres R, Jüngling R, Singh J, Kavi Kishore PB, Sivaramakrishnan S, Hoisington DA, Kahl G, Winter P, Cook DR, Varshney RK (2010) Integration of novel SSR and gene-based SNP marker loci in the chickpea genetic map and establishment of new anchor points with Medicago truncatula genome. Theor Appl Genet 120:1415–1441
Panjabi P, Jagannath A, Bisht NC, Padmaja KL, Sharma S, Gupta V, Pradhan AK, Pental D (2008) Comparative mapping of Brassica juncea and Arabidopsis thaliana using intron polymorphism (IP) markers: homoeologous relationships, diversification and evolution of the A, B and C Brassica genomes. BMC Genomics 9:113
Paran I, Goldman I, Tanksley S, Zamir D (1995) Recombinant inbred lines for genetic mapping in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 90:542–548
Park YH, Magdy E, Alabady S, Ulloa M, Sickler EB, Thea E, Wilkins A, Yu J, David E, Stelly M, Kohel RJ, El-Shihy OM, Cantrell RG (2005) Genetic mapping of new cotton fiber loci using EST-derived microsatellites in an interspecific recombinant inbred line cotton population. Mol Genet Genomics 274:428–441
Pavy N, Pelgas B, Beauseigle S, Blais S, Gagnon F, Gosselin I, Lamothe M, Isabel N, Bousquet J (2008) Enhancing genetic mapping of complex genomes through the design of highly-multiplexed SNP arrays: application to the large and unsequenced genomes of white spruce and black spruce. BMC Genomics 9:21
Pfaff T, Kahl G (2003) Mapping of gene-specific markers on the genetic map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Mol Gen Genomics 269:243–251
Radhika P, Gowda SJM, Kadoo NY, Mhase LB, Jamadagni BM, Sainani MN, Chandra S, Gupta VS (2007) Development of an integrated intraspecific map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) using two recombinant inbred line populations. Theor Appl Genet 115:209–216
Rajesh PN, Coyne C, Meksem K, Sharma KD, Gupta V, Muehlbauer FJ (2004) Construction of a HindIII bacterial artificial chromosome library and its use in identification of clones associated with disease resistance in chickpea. Theor Appl Genet 108:663–669
Ramsay L, Macaulay M, Ivanissevich DS, MacLean K, Cardle L, Fuller J, Edwards KJ, Tuvesson S, Morgante M, Massari A, Maestri E, Marmiroli N, Sjakste T, Ganal M, Powell W, Waugh R (2000) A simple sequence repeat-based linkage map of barley. Genetics 156:1997–2005
Riaz S, Dangl GS, Edwards KJ, Meredith CP (2004) A microsatellite marker based framework linkage map of Vitis vinifera L. Theor Appl Genet 108:864–872
Rostoks N, Ramsay L, MacKenzie K, Cardle L, Bhat PR, Roose ML, Svensson JT, Stein N, Varshney RK, Marshall DF, Graner A, Close TJ, Waugh R (2006) Recent history of artificial outcrossing facilitates whole-genome association mapping in elite inbred crop varieties. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18656–18661
Rozen S, Skaletsky HJ (1997) Primer 3. Code available at http://www.genome.wi.mit.edu/genome_software/other/primer3.html
Ryan J (1997) A global perspective on pigeon pea and chickpea sustainable production systems: present status and future potential. In: Asthana A, Ali M (ed) Recent advances in pulses research. Indian Society for Pulses Research and Development, Kanpur, pp 1–31
Sachidanandam R, Weissman D, Schmidt SC, Kakol JM, Stein LD et al (2001) A map of human genome sequence variation containing 1.42 million single nucleotide polymorphisms. Nature 409:928–933
Senthilvel S, Jayashree B, Mahalakshmi V, Sathish Kumar P, Nakka S, Nepolean T, Hash CT (2008) Development and mapping of simple sequence repeat markers for pearl millet from data mining of expressed sequence tags. BMC Plant Biol 8:119–127
Sethy NK, Shokeen B, Bhatia S (2003) Isolation and characterization of sequence-tagged microsatellite sites markers in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Mol Ecol Notes 3:428–430
Sethy NK, Shokeen B, Edwards KJ, Bhatia S (2006) Development of microsatellite markers and analysis of intra-specific genetic variability in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Theor Appl Genet 112:1416–1428
Sharma PC, Winter P, Bunger T, Hüttel B, Weigand F, Weising K, Kahl G (1995) Abundance and polymorphism of di-, tri- and tetra- nucleotide tandem repeats in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). Theor Appl Genet 90:90–96
Shirasawa K, Asamizu E, Fukuoka H, Ohyama A, Sato S, Nakamura Y, Tabata S, Sasamoto S, Wada T, Kishida Y, Tsuruoka H, Fujishiro T, Yamada M, Isobe S (2010a) An interspecific linkage map of SSR and intronic polymorphism markers in tomato. Theor Appl Genet 121:731–739
Shirasawa K, Isobe S, Hirakawa H, Asamizu E, Fukuoka H, Just D, Rothan C, Sasamoto S, Fujishiro T, Kishida Y, Kohara M, Tsuruoka H, Wada T, Nakamura Y, Sato S, Tabata S (2010b) SNP discovery and linkage map construction in cultivated tomato. DNA Res 17:381–391
Shirasawa K, Oyama M, Hirakawa H, Sato S, Tabata S, Fujioka T, Kimizuka-Takagi C, Sasamoto S, Watanabe A, Kato M, Kishida Y, Kohara M, Takahashi C, Tsuruoka H, Wada T, Sakai T, Isobe S (2011) An EST-SSR linkage map of Raphanus sativus and comparative genomics of the Brassicaceae. DNA Res 18:221–232
Sraphet S, Boonchanawiwat A, Thanyasiriwat T, Boonseng O, Tabata S, Sasamoto S, Shirasawa K, Isobe S, Lightfoot DA, Tangphatsornruang S, Triwitayakorn K (2011) SSR and EST-SSR-based genetic linkage map of cassava (Manihot esculenta Crantz). Theor Appl Genet 122:1161–1170
Tanksley SD, Ganal MW, Prince JP, de Vicente MC, Bonierbale MW, Broun P, Fulton TM, Giovannoni JJ, Grandillo S, Martin GB, Messeguer R, Miller JC, Miller L, Paterson AH, Pineda O, Roder MS, Wing RA, Wu W, Young ND (1992) High density molecular linkage maps of the tomato and potato genomes. Genetics 132:1141–1160
Taran B, Warkentin TD, Tullu A, Vandenberg A (2007) Genetic mapping of Ascochyta blight resistance in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) using a simple sequence repeat map. Genome 50:26–34
Tekeoglu M, Rajesh PN, Muehlbauer FJ (2002) Integration of sequence tagged microsatellite sites to chickpea genetic map. Theor Appl Genet 105:847–854
Temesgen B, Brown GR, Harry DE, Kinlaw CS, Sewell MM, Neale DB (2001) Genetic mapping of expressed sequence tag polymorphism (ESTP) markers in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L.). Theor Appl Genet 102:664–675
Tian AG, Wang J, Cui P, Han YJ, Xu H, Cong LJ, Huang XG, Wang XL, Jiao YZ, Wang BJ, Wang YJ, Zhang JS, Chen SY (2004) Characterization of soybean genomic features by analysis of its expressed sequence tags. Theor Appl Genet 108:903–913
Udupa SM, Baum M (2003) Genetic dissection of pathotype-specific resistance to Ascochyta blight disease in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 106:1196–1202
van Ooijen J (2006) JoinMap version 4.0: software for the calculation of genetic linkage maps. Plant Research International, Wageningen
Varshney RK, Graner A, Sorrells ME (2005) Genic microsatellite markers in plants: features and applications. Trends Biotechnol 23:48–55
Varshney RK, Marcel TC, Ramsay L, Russell J, Roder MS, Stein N, Waugh R, Langridge P, Niks RE, Graner A (2007) A high density barley microsatellite consensus map with 775 SSR loci. Theor Appl Genet 114:1091–1113
Varshney RK, Hiremath PJ, Lekha P, Kashiwagi J, Balaji J, Deokar AA, Vadez V, Xiao Y, Srinivasan R, Gaur PM, Siddique KH, Town CD, Hoisington DA (2009) A comprehensive resource of drought and salinity responsive ESTs for gene discovery and marker development in chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.). BMC Genomics 15:523
Wang X, Zhao X, Zhu J, Wu W (2005) Genome-wide investigation of intron length polymorphisms and their potential as molecular markers in rice (Oryza sativa L.). DNA Res 12:417–427
Wei H, Fu Y, Arora R (2005) Intron-flanking EST-PCR markers: from genetic marker development to gene structure analysis in Rhododendron. Theor Appl Genet 111:1347–1356
Winter P, Pfaff T, Udupa SM, Hüttel B, Sharma PC, Sahi S, Arreguin-Espinoza R, Weigand F, Muehlbauer FJ, Kahl G (1999) Characterization and mapping of sequence-tagged microsatellite sites in the chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genome. Mol Gen Genet 262:90–101
Winter P, Benko-Iseppon AM, Hüttel B, Ratnaparkhe M, Tullu A, Sonnante G, Pfaff T, Tekeoglu M, Santara D, Sant VJ, Rajesh PN, Kahl G, Muhelbauer FJ (2000) A linkage map of chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) genome based on recombinant inbred lines from a C. arietinum × C. reticulatum cross: localization of resistance genes for fusarium wilt races 4 and 5. Theor Appl Genet 101:1155–1163
Yang L, Jin G, Zhao X, Zheng Y, Xu Z, Wu W (2007) PIP: a database of potential intron polymorphism markers. Bioinformatics 23:2174–2177
Yi G, Lee JM, Lee S, Choi D, Kim BD (2006) Exploitation of pepper EST-SSRs and an SSR-based linkage map. Theor Appl Genet 114:113–130
Yu JK, Sun Q, Rota ML, Edwards H, Tefera H, Sorrells ME (2006) Expressed sequence tag analysis in tef (Eragrostis tef (Zucc) Trotter). Genome 49:365–372
Zhang X, Scheuring CF, Zhang M, Dong JJ, Zhang Y, Huang JJ, Lee MK, Abbo S, Sherman A, Shtienberg D, Chen W, Muehlbauer F, Zhang HB (2010) A BAC/BIBAC-based physical map of chickpea Cicer arietinum L. BMC Genomics 11:501
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by the National Institute of Plant Genome Research (NIPGR), New Delhi, India and also by the Department of Biotechnology (DBT), Government of India by means of a project grant (BT/PR9658/AGR/02/470/2007). We are thankful to Dr. Fred Muehlbauer, Washington State University, USA for providing the inter-specific chickpea mapping population and genotypic data of published STMS markers. The fellowships provided to SC by University Grants Commission (UGC), India, and SG by Council for Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), India is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by B. Diers.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary, S., Gaur, R., Gupta, S. et al. EST-derived genic molecular markers: development and utilization for generating an advanced transcript map of chickpea. Theor Appl Genet 124, 1449–1462 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1800-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-012-1800-3