Abstract
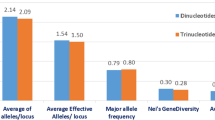
Southwestern Europe has been considered as a secondary centre of genetic diversity for the common bean. The dispersal of domesticated materials from their centres of origin provides an experimental system that reveals how human selection during cultivation and adaptation to novel environments affects the genetic composition. In this paper, our goal was to elucidate how distinct events could modify the structure and level of genetic diversity in the common bean. The genome-wide genetic composition was analysed at 42 microsatellite loci in individuals of 22 landraces of domesticated common bean from the Mesoamerican gene pool. The accessions were also characterised for phaseolin seed protein and for nine allozyme polymorphisms and phenotypic traits. One of this study’s important findings was the complementary information obtained from all the polymorphisms examined. Most of the markers found to be potentially under the influence of selection were located in the proximity of previously mapped genes and quantitative trait loci (QTLs) related to important agronomic traits, which indicates that population genomics approaches are very efficient in detecting QTLs. As it was revealed by outlier simple sequence repeats, loci analysis with STRUCTURE software and multivariate analysis of phenotypic data, the landraces were grouped into three clusters according to seed size and shape, vegetative growth habit and genetic resistance. A total of 151 alleles were detected with an average of 4 alleles per locus and an average polymorphism information content of 0.31. Using a model-based approach, on the basis of neutral markers implemented in the software STRUCTURE, three clusters were inferred, which were in good agreement with multivariate analysis. Geographic and genetic distances were congruent with the exception of a few putative hybrids identified in this study, suggesting a predominant effect of isolation by distance. Genomic scans using both markers linked to genes affected by selection (outlier) and neutral markers showed advantages relative to other approaches, since they help to create a more complete picture of how adaptation to environmental conditions has sculpted the common bean genomes in southern Europe. The use of outlier loci also gives a clue about what selective forces gave rise to the actual phenotypes of the analysed landraces.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Afanador L, Hadley S, Kelly JD (1993) Adoption of a mini-prep DNA extraction method for RAPD marker analysis in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Bean Improv Coop 36:10–11
Antao T, Lopes A, Lopes RJ, Beja-Pereira A (2008) LOSITAN: A workbench to detect molecular adaptation based on a Fst-outlier method. BMC Bioinformatics 9:323
Balardin RS, Kelly JD (1998) Interaction between Colletotrichum lindemuthianum races and gene pool diversity in Phaseolus vulgaris. J Am Soc Hortic Sci 123:1038–1047
Beaumont MA, Nichols RA (1996) Evaluating loci for use in the genetic analysis of population structure. Proc R Soc B 263:1619–1626
Beaver JS, Kelly JD (1994) Comparison of selection methods for dry bean landraces derived from crosses between gene pools. Crop Sci 25:923–926
Becerra Velasquez L, Gepts P (1994) RFLP diversity of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) in its centers of origin. Genome 37:256–263
Beebe S, Toro O, González AV, Chacón MI, Debouck D (1997) Wildweed-crop complex of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L., Fabaceae) in the Andes of Peru and Colombia, and their implications for conservation and breeding. Genet Resour Crop Evol 44:73–91
Beebe SE, Skroch PW, Tohme J, Duque MC, Pedraza F, Nienhuis J (2000) Structure of genetic diversity among common bean landraces of Middle American origin based on correspondence analysis of RAPD. Crop Sci 40:264–273
Beebe SE, Rengifo J, Gaitan E, Duque MC, Tohme J (2001) Diversity and origin of Andean landraces of common bean. Crop Sci 41:854–862
Blair MW, Pedraza F, Buendia H, Gaitan E, Beebe S, Gepts P, Tohme J (2003) Development of a genome wide anchored microsatellite for common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L). Theor Appl Genet 107:1362–1374
Blair MW, Giraldo MC, Buendia HF, Tovar E, Duque MC, Beebe S (2006a) Microsatellite marker diversity in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Theor Appl Genet 113:100–109
Blair MW, Iriarte G, Beebe S (2006b) QTL analysis of yield traits in an advanced backcross landrace derived from a cultivated Andean wild common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L) cross. Theor Appl Genet 112:1149–1163
Blair MW, Fregene MA, Beebe SE, Ceballos H (2007) Marker-Assisted Selection in Common Beans and Cassava. Chap. 7. In: Guimaraes E (ed) Marker-assisted selection (MAS) in crops, livestock, forestry and fish: Current status and the way forward. FAO, Rome, Italy
Bonin A, Taberlet P, Claude M, Pompanon F (2006) Explorative genome scans to detect candidate loci for adaptation along a gradient of altitude in the common frog (Rana temporaria). Mol Biol Evol 23(4):773–783
Brown JWS, Ma Y, Bliss FA (1981) Genetic variation in the subunits of globulin 1-storage protein of French bean. Theor Appl Genet 59:83–88
Buso GSC, Amaral ZPS, Brondani RPV, Ferreira ME (2006) Microsatellite markers for the common bean - Phaseolus vulgaris. Mol Ecol Notes 6:252–254
Caixeta ET, Borem A, Alzate-Marin AL, Fagundes S (2005) Allelic relationships for genes that confer resistance to angular leaf sport in common bean. Euphytica 145:237–245
Campbell D, Bernatchez L (2004) Generic Scan Using AFLP Markers as a Means to Assess the Role of Directional Selection in the Divergence of Sympatric Whitefish Ecotypes. Mol Biol Evol 21(5):945–956
Chacón MI, Pickersgill S, Debouck D (2005) Domestication patterns in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) and the origin of Mesoamerican and Andean cultivated races. Theor Appl Genet 110:432–444
Checa C, Blair MW (2008) Mapping QTL for climbing ability and component traits in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Molecular Breed 22:201–215
Chen Y, Nelson RL (2005) Relationship between origin and genetic diversity in chinese soybean germplasm. Crop Sci 45:1645–1651
Crow JF, Aoki K (1984) Group selection for a polygenic behavioral trait: estimating the degree of landrace subdivision. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:6073–6077
Debouck DG, Araya Villalobos R, Ocampo Sánchez RA, González UWG (1989) Collecting Phaseolus in Costa Rica. FAO/IBPGR Plant Genet Resour Newsl 78(79):44–46
Díaz LM, Blair MW (2006) Race structure within the Mesoamerican gene pool of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as determined by microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 114:143–154
Evano G, Regnaut S, Goudet J (2005) Detecting the number of clusters of individuals using the software STRUCTURE: a simulation study. Mol Ecol 14:2611–2620
Freyre R, Ríos R, Guzmán L, Debouck DG, Gepts P (1996) Ecogeographic distribution of Phaseolus spp. (Fabaceae) in Bolivia. Econ Bot 50:195–215
Freyre R, Skroch P, Geffroy V, Adam-Blondon A-F, Shirmohamadali A, Johnson W, Llaca V, Nodari R, Pereira P, Tsai S-M, Tohme J, Dron M, Nienhuis J, Vallejos C, Gepts P (1998) Towards an integrated linkage map of common bean. 4. Development of a core linkage map and alignment of RFLP maps. Theor Appl Genet 97:847–856
Gaitán-Sólis E, Duque MC, Edwards K, Tohme J (2002) Microsatellite repeats in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): isolation, characterization, and cross-species amplification in Phaseolus spp. Crop Sci 42:2128–2136
Geffroy V, Sicard D, de Oliveira JCF, Sevgnac M, Cohen S, Gepts P, Neema C, Langin T, Dron M (1999) Identification of an ancestral resistance gene cluster involved in the co-evolution process between Phaseolus vulgaris and its fungal pathogen Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Mol Plant Microb Interact 12:774–784
Gepts P (1988) Phaseolin as an evolutionary marker. In: Resources of Phaseolus beans. Kluwer, Dordtrecht, pp 215–241
Gepts P (2004) Domestication as a long-term selection experiment. Plant Breed Rev 24(part 2):1–44
Gepts P, Bliss FA (1985) F1 hybrid weakness in the common bean: differential geographic origin suggests two gene pools in cultivated bean germplasm. J Hered 76:447–450
Gepts P, Bliss FA (1988) Dissemination pathways of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris, Fabaceae) deduced from phaseolin electrophoretic variability. II. Europe and Africa. Econ Bot 42:86–104
Gepts P, Osborn T, Rashka K, Bliss F (1986) Phaseolin–protein variability in wild forms and landraces of the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): evidence for multiple centers of domestication. Econ Bot 40:451–468
Guerra-Sanz JM (2004) Short communication - New SSR markers of Phaseolus vulgaris from sequence databases. Plant Breed 123:87–89
Guzmán P, Gilbertson RL, Nodari R, Johnson WC, Temple SR, Mandela D, Mkandawire ABC, Gepts P (1995) Characterization of variability in the fungus Phaseoisariopsis griseola suggests coevolution with the common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris). Phytopathology 85:600–607
Huang XQ, Börner A, Röder MS, Ganal MW (2002) Assessing genetic diversity of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) germplasm using microsatellite markers. Theor Appl Genet 105:699–707
Innes NL, Conway J, Taylor JD (1984) Resistance to halo blight in the Cambridge accessions V4604 and V4058 of Phaseolus beans. Ann Appl Biol 104:307–314
Islam FMA, Basford KE, Redden RJ, Gonzalez AV, Kroonenberg PM, Beebe SE (2002) Genetic variability in cultivated common bean beyond the two major gene pools. Genet Resour Crop Evol 49:271–283
Jarvis DI, Hodgkin T (1999) Wild relatives and crop cultivars: detecting natural introgression and farmer selection of new genetic combinations in agro-ecosystem. Mol Ecol 8:S159–S173
Khairallah M, Sears B, Adams M (1992) Mitochondrial restriction fragment length polymorphisms in wild Phaseolus vulgaris L.: insights on the domestication of the common bean. Theor Appl Genet 84:915–922
Koenig R, Gepts P (1989) Allozyme diversity in wild Phaseolus vulgaris: further evidence for two mayor centers of genetic diversity. Theor Appl Genet 78:809–817
Koinange EMK, Singh SP, Gepts P (1996) Genetic control of the domestication syndrome in common bean. Crop Sci 36:1037–1045
Kornegay J, White JW, Ortíz de la Cruz O (1992) Growth habit and gene pool effects on inheritance of yield in common bean. Euphytica 62:171–180
Kwak M, Gepts P (2009) Structure of genetic diversity in the two major gene pools of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L., Fabaceae). Theor Appl Genet 118:979–992
Li Z, Nelson RL (2001) Genetic diversity among soybean ac cessions from three countries measured by RAPDs. Crop Sci 41:1337–1347
Liu K, Muse S (2005) PowerMarker: an integrated analysis environment for genetic marker analysis. Bioinformatics Appl Note 21(9):2128–2129
Londo JP, Chiang YC, Hung KH, Chiang TY, Schaal BA (2006) Phylogeography of Asian wild rice, Oryza rufipogon, reveals multiple independent domestications of cultivated rice, Oryza sativa. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:9578–9583
Luikart G, England PR, Tallmon D (2003) The power and promise of population genomics: From genotyping to genome typing. Nat Rev Genet 4(12):981–994
Masi G, Logozzo P, Donini P, Spagnoletti Z (2009) Analysis of genetic structure in widely distributed common bean landraces with different plant growth habits using SSR and AFLP markers. Crop Sci 49:187–199
McClean PE, Lee RK, Miklas PN (2004) Sequence diversity analysis of dihydrofl avonol 4-reductase intron1 in common bean. Genome 47:266–280
Metais I, Hamon B, Jalouzot R, Peltier D (2002) Structure and level of genetic diversity in various bean types evidenced with microsatellite markers isolated from a genomic enriched library. Theor Appl Genet 104:1346–1352
Mitchell SE, Kresovich S, Jester CA, Hernandez CJ, Szewc-McFadden AK (1997) Application of multiplex PCR and fluorescence-based, semi-automated allele sizing technology for genotyping plant genetic resources. Crop Sci 37:617–624
Nei M (1978) Estimation of average heterozygocity and genetic distance from a small number of individuals. Genetics 89:583–590
Nielsen R (2005) Molecular signatures of natural selection. Annu Rev Genet 39:197–218
Pañeda A, Rodríguez-Suárez C, Campa A, Ferreira JJ, Giraldez R (2008) Molecular markers linked to the fin gene controlling determinate growth habit in common bean. Euphytica 162:241–248
Papa R, Acosta J, Delgado-Salinas A, Gepts P (2005) A genome-wide analysis of differentiation between wild and domesticated Phaseolus vulgaris from Mesoamerica. Theor Appl Genet 111:1147–1158
Paredes OM, Gepts P (1995) Extensive introgression of Middle American germplasm into Chilean common bean landraces. Genet Resour Crop Evol 42:29–41
Pastor-Corrales MA (1991) Estandarización de variedades diferenciales y de designación de razas de Colletotrichum lindemuthianum. Phytopathology 81:694
Pastor-Corrales MA, Jara C, Singh SP (1998) Pathogenic variation in sources of and breeding for resistance to Phaeoisariopsis griseola causing angular leaf spot in common bean. Euphytica 103:161–171
Peakall R, Smouse PE (2006) GenAlEx 6: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research. Mol Ecol Notes 6:288–295
Piergiovanni A, Taranto G, Losavio FP, Pignone D (2006) Common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) landraces from Abruzzo and Lazio regions (Central Italy). Genet Resour Crop Evol 53:313–322
Pritchard JK, Wen W (2004) Documentation for the STRUCTURE software Version 2. Chicago. http://www.pritch.bsd.uchicagoedu/software/structure2_1.html
Pritchard JK, Stephens M, Donnelly P (2000) Inference of landrace structure using multilocus genotype data. Genetics 155:945–959
Rick CM, Holle M (1990) Andean Lycopersicon esculentum var. cerasiformie. Genetic variation and its evolutionary significance. Econ Bot 44:69–78
Rodiño P, Santalla M, González AM, De Ron AM, Singh SP (2006) Novel genetic variation in common bean from the Iberian Peninsula. Crop Sci 46:2540–2546
Rosales-Serna R, Hernandez-Delgado S, Gonzalez-Paz M, Acosta-Gallegos JA, Mayek-Perez N (2005) Genetic relationships and diversity revealed by AFLP markers in Mexican common bean bred cultivars. Crop Sci 45:1951–1957
Rossi M, Bitocchi E, Bellucci E, Nanni L, Rau D, Attene G, Papa R (2009) Linkage disequilibrium and population structure in wild and domesticated populations of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Evol Appl. doi:10.1111/j.1752-4571.2009.00082.x
Sánchez E, Sifres A, Casañas F, Nuez F (2008) The endangered future of organoleptically prestigious European landraces: Ganxet bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as an example of a crop originating in the Americas. Genet Resour Crop Evol 55:45–52
Santalla M, Rodiño AP, De Ron AM (2002) Allozyme evidence supporting southwestern Europe as a secondary center of genetic diversity for common bean. Theor Appl Genet 104:934–944
Schlötterer C (2003) Hitchhiking mapping—functional genomics from the population genetics perspective. Trends Genet 19:32–38
Sicard D, Nanni L, Porfiri O, Bulfon D, Papa R (2005) Genetic diversity of Phaseolus vulgaris L. and Phaseolus coccineus L. landraces in central Italy. Plant Breed 124:464–472
Singh SP (1995) Selection for seed yield in Middle American versus Andean x Middle American interracial common bean landraces. Plant Breed 114:269–271
Singh SP, Gutiérrez JA (1990) Effect of plant density on selection for seed yield in two landrace types of Phaseolus vulgaris L. Euphytica 51:173–178
Singh SP, Gepts P, Debouck DG (1991a) Races of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris, Fabaceae). Econ Bot 45:379–396
Singh SP, Gutiérrez JA, Molina A, Urrea C, Gepts P (1991b) Genetic diversity in cultivated common bean: II. Marker-based analysis of morphological and agronomic traits. Crop Sci 31:23–29
Singh S, Nodari R, Gepts P (1991c) Genetic diversity in cultivated common bean. I. Allozymes. Crop Sci 31:19–23
Singh SP, Terán H, Germán Muñoz C, Takegami JC (1999) Two cycles of recurrent selection for seed yield in common bean. Crop Sci 39:391–397
Slatkin M, Barton N (1989a) A comparison of three indirect methods for estimating average levels of gene flow. Evolution 43:1349–1368
Slatkin M, Barton NH (1989b) A comparison of three indirect methods for estimating the average level of gene flow. Evolution 43:1349–1368
Storz JF (2005) Using genome scans of DNA polymorphism to infer adaptive landrace divergence. Mol Ecol 14:671–688
Tohme J, González DO, Beebe S, Duque MC (1996) AFLP analysis of gene pools of a wild bean core collection. Crop Sci 36:1375–1384
CIAT (Centro Internacional de Agricultura Tropical) (1987) Standard Voysest O. 2000. Mejoramiento genético del frijol (Phaseolus vulgaris system for the evaluation of bean germplasm. Van Schoohoven L.): Legado de variedades de América Latina 1930–1999. Pastor- Corrales (compilers). CIAT. Cali, Colombia
van Schoonhoven A, Pastor-Corrales MA (1987) Standard system for the evaluation of bean germplasm. CIAT, Cali, Colombia
Vasemägi A, Nilsson J, Primmer CR (2005) Expressed sequence tag (EST) linked microsatellites as a source of gene associated polymorphisms for detecting signatures of divergent selection in Atlantic salmon (Salmo salar L.). Mol Biol Evol 22:1067–1076
Vavilov NI (1951) The origin, variation, immunity and breeding of cultivated plants. Chron Bot 13:1–366 Translated by K. Start
Vigouroux Y, MacMullen M, Hittinger CT, Houchins K, Schulz L, Kresovich S, Matsuoka Y, Doebley J (2002) Identifying genes of agronomic importance in maize by screening microsatellites for evidence of selection during domestication. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 99:9650–9655
Vitalis R, Dawson K, Boursot P (2001) Interpretation of variation across marker loci as evidence of selection. Genetics 158:1811–1823
Vitalis R, Dawson K, Boursot P, Belkhir K (2003) DetSel 1.0: a computer program to detect markers responding to selection. J Hered 94:429–431
Vitte C, Ishii T, Lamy F, Brar D, Panaud O (2004) Genomic paleontology provides evidence for two distinct origins of Asian rice (Oryza sativa L.). Mol Genet Genom 272:504–511
Wang L, Guan R, Zhangxiong L, Chang R, Qiu L (2006) Genetic Diversity of Chinese Cultivated Soybean Revealed by SSR Markers. Crop Sci 46:1032–1038
Weir BS, Cockerman C (1984) Estimating F-statistics for the analysis of landrace structure. Evolution 38:1358–1370
White JW, Singh SP, Pino C, Rios MJ, Buddenhagen I (1992) Effects of seed size and photoperiod response on crop growth and yield of common bean. Field Crops Res 23:159–175
Xu P, Tao DY, Hu FY, Zhou JW, Deng XN (2005) Interspecific hybridization of cultivated rice for breeding japonica rice in Yunnan province. Chin J Rice Sci 19(1):41–46
Yaish MWF, Pérez De La Vega M (2003) Isolation of (GA)n microsatellite sequences and description of a predicted MADS-box sequence isolated from common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Genet Mol Biol 26:337–342
Yu K, Park J, Poysa V, Gepts P (2000) Integration of simple sequence repeat (SSR) markers into a molecular linkage map of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). J Hered 91:429–434
Zizumbo-Villarreal D, Colunga-García Marín P, De la Cruz E, Payró Delgado-Valerio P, Gepts P (2005) Landrace structure and evolutionary dynamics of wild–weedy–domesticated complexes of common bean in a Mesoamerican region. Crop Sci 45:1073–1083
Acknowledgments
Research was supported by RF2006-00001, AGL2008-02091/AGR and INCITE07PXI403088ES projects from the Spanish Government and Xunta de Galicia, respectively. The authors are grateful to the Diputación Provincial de Pontevedra for farm facilities and María Lores for technical assistance. M. De La Fuente is grateful to the Xunta de Galicia for awarding her a fellowship grant, which allowed her to carry out this study. Special thanks to J.D. Kelly for anthracnose, S.P. Singh and P. Miklas for BCMV and BCMNV, and D. Fourier and J. Murillo for bacterial inocula.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by R. Varshney.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santalla, M., De Ron, A.M. & De La Fuente, M. Integration of genome and phenotypic scanning gives evidence of genetic structure in Mesoamerican common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) landraces from the southwest of Europe. Theor Appl Genet 120, 1635–1651 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1282-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-010-1282-0