Abstract
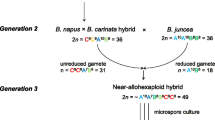
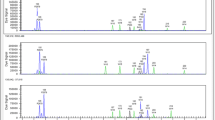
We analysed the products of male meiosis in microspore-derived progeny from a Brassica napus (AACnCn) × Brassica carinata (BBCcCc) interspecific hybrid (ABCnCc). Genotyping at 102 microsatellite marker loci and nuclear DNA contents provided strong evidence that 26 of the 28 progeny (93%) were derived from unreduced (2n) gametes. The high level of CnCc marker heterozygosity, and parallel spindles at Anaphase II in the ABCnCc hybrid, indicated that unreduced gametes were formed by first division restitution. The frequency of dyads at the tetrad stage of pollen development (2.6%) suggested that unreduced gametes were preferentially selected in microspore culture. Segregation of marker alleles in the microspore-derived progeny was consistent with homologous recombination between Cn and Cc chromosomes and homoeologous recombination involving A-, B- and C-genome chromosomes during meiosis in the ABCnCc hybrid. We discuss the potential for using microspore culture of unreduced gametes in interspecific hybrids to map Brassica centromeres through half-tetrad analysis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arumuganathan K, Earle ED (1991) Nuclear DNA content of some important plant species. Plant Mol Biol Reporter 9:208–218
Bino RJ, De Vries JN, Kraak HL, Van Pijlen JG (1992) Flow cytometric determination of nuclear replication stages in tomato seeds during priming and germination. Ann Bot 69:231–236
Bohuon EJR, Keith DJ, Parkin IAP, Sharpe AG, Lydiate DJ (1996) Alignment of the conserved C genomes of Brassica oleracea and Brassica napus. Theor Appl Genet 93:833–839
Bretagnolle F, Thompson JD (1995) Tansley Review No. 78. Gametes with the somatic chromosome number: mechanisms of their formation and role in the evolution of autopolypoid plants. New Phytolog 129:1–22
Chen W, Zhang Y, Liu X, Chen B, Tu J, Tingdong F (2007) Detection of QTL for six yield-related traits in oilseed rape (Brassica napus) using DH and immortalized F2 populations. Theor Appl Gen 115:849–858
Dolezel J, Bartos J (2005) Plant DNA flow cytometry and estimation of nuclear genome size. Ann Bot 95:99–110
Douches DS, Quiros CF (1988) Genetic strategies to determine the mode of 2n egg formation in diploid potatoes. Euphytica 38:247–260
Friedt W, Zarhloul MK (2005) Haploids in the Improvement of Crucifers. In: Palmer CE, Keller WA, Kasha KJ (eds) Haploids in crop improvement II. Springer, New York
Gamborg OL, Miller RA, Ojima J (1968) Nutrient requirements of suspension cultures of soybean root cells. Exp Cell Res 50:151–158
Ge X-H, Li Z-Y (2006) Extra divisions and nuclei fusions in microspores from Brassica allohexaploid (AABBCC) × Orychophragmus violaceus hybrids. Plant Cell Rep 25:1075–1080
Henry IM, Dilkes BP, Comai L (2006) Molecular karyotyping and aneuploidy detection in Arabidopsis thaliana using quantitative fluorescent polymerase chain reaction. Plant J 48:307–319
Heyn FJ (1977) Analysis of unreduced gametes in the Brassiceae by crosses between species and ploidy levels. Z Pflanzenzüchtg 78:13–30
Kubik TJ (1999) Evaluation of doubled haploid lines derived from interspecific crosses between Brassica napus and Brassica rapa. MSc thesis. University of Alberta, Edmonton, Canada. http://www.collectionscanada.ca/obj/s4/f2/dsk2/ftp01/MQ40073.pdf
Lagercrantz U, Lydiate DJ (1996) Comparative genome mapping in Brassica. Genetics 144:1903–1910
Leflon M, Eber F, Letanneur J, Chelysheva L, Coriton O, Huteau V, Ryder C, Barker G, Jenczewski E, Chèvre A (2006) Pairing and recombination at meiosis of Brassica rapa (AA) × Brassica napus (AACC) hybrids. Theor Appl Gen 113:1467–1480
Leitch AR, Leitch IJ (2008) Genomic plasticity and the diversity of polyploid plants. Science 320:481–483
Lowe AJ, Moule C, Trick M, Edwards KJ (2004) Efficient large-scale development of microsatellites for marker and mapping applications in Brassica crop species. Theor Appl Genet 108:1103–1112
Murray MG, Thompson WF (1980) Rapid isolation of high molecular weight plant DNA. Nucl Acids Res 8:4321–4326
Nagaharu U (1935) Genome analysis in Brassica with special reference to the experimental formation of B. napus and peculiar mode of fertilization. Jpn J Bot 7:389–452
Nicolas SD, Le Mignon G, Eber F, Coriton O, Monod H, Clouet V, Huteau V, Lostanlen A, Delourme R, Chalhoub B, Ryder CD, Chèvre AM, Jenczewski E (2007) Homeologous recombination plays a major role in chromosome rearrangements that occur during meiosis of Brassica napus haploids. Genetics 175:487–503
Park T-H, Kim J-B, Hutten RCB, van Eck HJ, Jacobsen E, Visser RGF (2007) Genetic positioning of centromeres using half-tetrad analysis in a 4x–2x cross population of potato. Genetics 176:85–94
Parkin IAP, Sharpe AG, Lydiate DJ (2003) Patterns of genome duplication within the Brassica napus genome. Genome 46:291–303
Parkin IAP, Gulden SM, Sharpe AG, Lukens L, Trick M, Osborn TC, Lydiate DJ (2005) Segmental structure of the Brassica napus genome based on comparative analysis with Arabidopsis thaliana. Genetics 171:765–781
Pouilly N, Delourme R, Alix K, Jenczewski E (2008) Repetitive sequence-derived markers tag centromeres and telomeres and provide insights into chromosome evolution in Brassica napus. Chromosome Res 16:683–700
Prakash S, Chopra VL (1990) Reconstruction of allopolyploid Brassicas through non-homologous recombination: introgression of resistance to pod shatter in Brassica napus. Genet Res Camb 56:1–2
Prakash S, Chopra VL (1992) Genome manipulations. In: Labana KS, Banga SS, Banga SK (eds) Breeding oilseed Brassicas. Narosa Publishing House, New Delhi, pp 108–133
Schranz ME, Lysak MA, Mitchell-Olds T (2006) The ABC’s of comparative genomics in the Brassicaceae: building blocks of crucifer genomes. Trends Plant Sci 11:535–542
Sharpe AG, Parkin IAP, Keith DJ, Lydiate DJ (1995) Frequent nonreciprocal translocations in the amphidiploid genome of oilseed rape (Brassica napus). Genome 38:1112–1121
Snowdon R (2007) Cytogenetics and genome analysis in Brassica crops. Chromosome Res 15:85–95
Snowdon RJ, Friedrich T, Friedt W, Kohler W (2002) Identifying the chromosomes of the A- and C-genome diploid Brassica species B. rapa (syn. campestris) and B. oleracea in their amphidiploid B. napus. Theor Appl Genet 104:533–538
Udall JA, Quijada PA, Osborn TC (2005) Detection of chromosomal rearrangements derived from homeologous recombination in four mapping populations of Brassica napus L. Genetics 169:967–979
Yan G, Ferguson A, McNeilage M, Murray B (1997) Numerically unreduced (2n) gametes and sexual polyploidization in Actinidia. Euphytica 96:267–272
Zhou Y, Scarth R (1995) Microspore culture of hybrids between Brassica napus and B. campestris. Acta Bot Sinica 37:848–855
Ziolkowski PA, Kaczmarek M, Babula D, Sadowski J (2006) Genome evolution in Arabidopsis/Brassica: conservation and divergence of ancient rearranged segments and their breakpoints. Plant J 47:63–74
Acknowledgments
We thank Anouska Cousin (Canola Breeders Western Australia Pty Ltd) for technical guidance in microspore culture, and Dr. Paul Kron (University of Guelph, Canada) for technical guidance in flow cytometry. We thank Dr. Kathy Heel and Dr. Paul Rigby of the UWA Centre for Microscopy, Characterisation and Analysis for help in flow cytometry and pollen analysis. We also thank Dr. Anne-Marie Chèvre and Prof. Carlos Quiros for helpful suggestions in preparing this manuscript. The work was supported by the Australian Research Council Linkage Project LP0667805 with industry partners Norddeutsche Pflanzenzucht Hans-Georg Lembke KG (Germany) and the Council of Grain Grower Organisations Ltd (Australia). AEM and LT were supported by scholarships from the Cooperative Research Centre for Value Added Wheat. MNN and WAC were supported for this research by a grant from Export Grains Centre Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by C. Quiros.
An erratum to this article can be found at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1126-y
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nelson, M.N., Mason, A.S., Castello, MC. et al. Microspore culture preferentially selects unreduced (2n) gametes from an interspecific hybrid of Brassica napus L. × Brassica carinata Braun. Theor Appl Genet 119, 497–505 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1056-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1056-8