Abstract
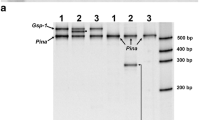
DNA from six hexaploid, tetraploid and diploid species of Aegilops with the C, D, S, M and U genomes was amplified with specific PCR primers to identify sequences encoding puroindolines (Pins) a and b and grain softness protein (GSP), all of which are encoded by genes at the Ha (hardness) locus, with Ae. tauschii (DD) and bread wheat (T. aestivum) (AABBDD) cv Hiline being studied as controls. Seven new allelic forms of Pin a and Pin b were identified, including forms with mutations within or close to the tryptophan motif. In addition, five new forms of GSP were detected. In all species both genomic DNA from leaves and cDNA from developing grain were analysed. This revealed the presence of both silent genes (with premature stop codons) and multiple genes, with the latter being confirmed by Southern blot analysis. Freeze fracture analysis demonstrated that all except one accession (Ae. sharonensis) were soft textured. However, this difference cannot be accounted for by the sequences of the Pin alleles present in this line.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Beecher B, Smidansky ED, See D, Blake TK and Giroux MJ (2001) Mapping and sequence analysis of barley hordoindolines. Theor Appl Genet 102:833–840
Beecher B, Bettge A, Smidansky E and Giroux MJ (2002) Expression of wild-type pin b sequence in transgenic wheat complements a hard phenotype. Theor Appl Genet 105:870–877
Blochet J-E, Chevalier C, Forest E, Pebay-Peyroula E, Gautier M-F, Joudrier P, Pezolet M and Marion D (1993) Complete amino acid sequence of puroindoline, a new basic and cystine-rich protein with a unique tryptophan-rich domain, isolated from wheat endosperm by Triton X-114 phase partitioning. FEBS Lett 329:336–340
Brennan CS, Harris N, Smith D and Shewry PR (1996) Structural differences in the mature endosperms of good and poor malting barley cultivars. J Cereal Sci 24:171–177
Caldwell KS, Langridge P and Powell W (2004) Comparative sequence analysis of the region harbouring the hardness locus in barley and its colinear region in rice. Plant Physiol 136:3177–3190
Chang S, Puryear J and Cairney J (1993) A simple and efficient method for isolating RNA from pine trees. Plant Mol Biol Rep 11:113–116
Chantret N, Cenci A, Sabot F, Anderson O, Dubcovsky J (2004) Sequencing of the Triticum monococcum Hardness locus reveals good microlinearity with rice. Mol Gen Genom 271:377–386
Darlington HF, Rouster J, Hoffmann L, Halford NG, Shewry PR and Simpson D (2001) Identification and molecular characterisation of hordoindolines from barley grain. Plant Mol Biol 47:785–794
Fido RJ, Tatham AS, Shewry PR (1995) Western blotting analysis. In: Jones H (ed) Methods in molecular biology. Humana, Totowa, pp 423–437
Gautier M-F, Aleman M-E, Guirao A, Marion D, and Joudier P (1994) Triticum aestivum puroindolines, two basic cystine-rich seed proteins: cDNA analysis and developmental gene expression. Plant Mol Biol 25:43–57
Gautier M-F, Cosson P, Guirao A, Alary R and Joudrier P (2000) Puroindoline genes are highly conserved in diploid ancestor wheats and related species but absent in tetraploid Triticum species. Plant Sci 153:81–91
Giroux MJ and Morris CF (1997) A glycine to serine change in puroindoline b is associated with wheat grain hardness and low levels of starch-surface friabilin. Theor Appl Genet 95:857–864
Giroux MJ and Morris CF (1998) Wheat grain hardness results from highly conserved mutations in the friabilin components puroindoline a and b. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:6262–6266
Greenwell P and Schofield JD (1986) A starch granule protein associated with endosperm softness in wheat. Cereal Chem 63:379–380
Jolly CJ, Rahman S, Kortt V and Higgins TJV (1993) Characterisation of the wheat M r 15000 ‘grain softness protein’ and analysis of the relationship between its accumulation in the whole seed and grain softness. Theor Appl Genet 86:589–597
Jolly CJ, Glenn GM and Rahman S (1996) GSP-1 genes are linked to the grain hardness locus (Ha) on wheat chromosome 5D. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:2408–2413
Kieliszewski MJ (2001) The latest hype on Hyp-it 0-glycosylation codes. Phytochemistry 57:319–323
Kooijman M, Orsel R, Hessing M, Hamer RJ and Bekkers ACAPA (1997) Spectroscopic characterisation of the lipid-binding properties of wheat puroindolines. J Cereal Sci 26:145–159
Krishnamurthy K and Giroux MJ (2001) Expression of wheat puroindoline genes in transgenic rice enhances grain softness. Nat Biotechnol 19:1–5
Law CN, Young CF, Brown JWS, Snape JW and Worland JW (1978) The study of grain protein control in wheat using whole chromosome substitution lines. Seed protein improvement by nuclear techniques, International Atomic Energy Agency, Vienna, Austria, pp 483–502
Lillemo M and Morris CF (2000) A leucine to proline mutation in puroindoline b is frequently present in hard wheats from Northern Europe. Theor Appl Genet 100:1100–1107
Lillemo M, Simeone MC and Morris CF (2002) Analysis of puroindoline a and b sequences from Triticum aestivum cv ‘Penawara‘ and related diploid taxa. Euphytica 126:321–331
Massa AN and Morris CF (2004) Relationship between sequence polymorphism of GSP-1 and puroindolines in Triticum aestivum and Aegilops tauschii. In: Lafiandra D, Masci S, D’Ovidio R (eds) The gluten proteins. RSC, Cambridge, pp 461–464
Massa AN, Morris CF and Gill BS (2004) Sequence diversity of Puroindoline-a, Puroindoline-b and the grain softness protein genes in Aegilops tauschii Coss. Crop Sci 44:1808–1816
Morris CF (2002) Puroindolines: the molecular genetic basis of wheat grain hardness. Plant Mol Biol 48:633–647
Oda S and Schofield JD (1997) Characterisation of friabilin polypeptides. J Cereal Sci 26:29–36
Pogna N, Gazza L, Corona V, Zanier R, Niglio A. E Mei, Palumbo M and Boggini G (2002) Puroindolines and kernel hardness in wheat species. In: Ng PKW, Wrigley CW (eds), Wheat Quality Elucidation: The Bushuk Legacy. AACC, St Paul, pp 155–169
Pomeranz Y and Williams PC (1990) Wheat hardness: its genetic, structural and biochemical background, measurement and significance. In: Pomeranz Y (ed), Advances in cereal science and technology, vol 10. AACC, St Paul, MN, USA, pp 471–548
Rahman S, Jolly CJ, Skerritt JH and Wallosheck A (1994) Cloning of a wheat 15-kDa grain softness protein (GSP). Eur J Biochem 223:917–925
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbour Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbour
Shewry PR, Tatham AS and Fido RJ (1995) Separation of plant proteins by electrophoresis. In: Jones H (eds), Methods in Molecular Biology. Humana, Totowa, pp 399–422
Stacey J and Isaac P (1994) Isolation of DNA from plants. In: Isaac EP (ed) Methods in molecular biology—protocols for nucleic acid analysis by non-radioactive probes. Humana, Totowa, NJ, USA, pp 9–15
Tanchak MA, Schernthaner JP, Giband M and Altosaar I (1998) Tryptophanins: isolation and molecular characterisation of oat cDNA clones encoding proteins structurally related to puroindoline and wheat grain softness proteins. Plant Sci 137:173–184
Tranquilli G, Lijavetzky D, Muzzi G and Dubcovsky J (1999) Genetic and physical characterisation of grain texture-related loci in diploid wheat. Mol. Gen. Genet. 262:846–850
Tranquilli G, Heaton J, Chicaiza O and Dubcovsky J (2002) Substitutions and deletions of genes related to grain hardness in wheat and their effect on grain texture. Crop Sci 42:1812–1817
Turnbull K-M, Gaborit T, Marion D and Rahman S (2000) Variation in puroindoline polypeptides in Australian wheat cultivars in relation to grain hardness. Aust J Plant Physiol 27:153–158
Turner M, Mukai Y, Leroy P, Charef B, Appels R and Rahman S (1999) The Ha locus of wheat: identification of a polymorphic region for tracing grain hardness in crosses. Genome 42:1242–1250
Turner AS, Bradburne RP, Fish L and Snape JW (2004) New quantitative trait loci influencing grain texture and protein content in bread wheat. J Cereal Sci 40:51–60
Van den Bulck K, Loosveld A-MA, Courtin C M, Proost P, Van Damme J, Robben J, Mort A and Delcour JA (2002) Amino acid sequence of wheat flour arabinogalactan-peptide, identical to part of grain softness protein GSP-1, leads to improved structural model. Cereal Chem 79:329–331
Acknowledgements
Rothamsted Research receives grant-aided support from the Biotechnology and Biological Sciences Research Council of the United Kingdom. We wish to thank Rothamsted International for providing a Fellowship for M Chen and Dr Nigel Halford for assistance with Table 3. We are also very grateful to Dr Huw Jones and Ms Caroline Sparks for advice and discussions and to Mrs Jean Devonshire for her assistance with the SEM.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by P. Langridge
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, M., Wilkinson, M., Tosi, P. et al. Novel puroindoline and grain softness protein alleles in Aegilops species with the C, D, S, M and U genomes. Theor Appl Genet 111, 1159–1166 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0047-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-005-0047-7