Abstract
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a complex neurodegenerative disorder featuring both motor and nonmotor symptoms associated with a progressive loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra pars compacta. Conventionally, PD treatment options have focused on dopamine replacement and provide only symptomatic relief. However, disease-modifying therapies are still unavailable. Mechanistically, genetic and environmental factors can produce oxidative stress which has been implicated as a core contributor to the initiation and progression of PD through the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons. Importantly, nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2 (Nrf2) is essential for maintaining redox homeostasis by binding to the antioxidant response element which exists in the promoter regions of most genes coding for antioxidant enzymes. Furthermore, protein kinase C, mitogen-activated protein kinases, and phosphotidylinositol 3-kinase have been implicated in the regulation of Nrf2 activity during PD. Here, we review the evidence supporting the regulation of Nrf2 through Keap1-dependent and Keap1-independent mechanisms. We also address that targeting Nrf2 may provide a therapeutic option to mitigate oxidative stress-associated PD. Finally, we discuss currently known classes of small molecule activators of Nrf2, including Nrf2-activating compounds in PD.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 6-OHDA:
-
6-Hydroxydopamine
- ARE:
-
Antioxidant response element
- BTB:
-
Bric-a-brac-Tramtrack-Broad
- β-TrCP:
-
β-Transducin repeat-containing protein
- CNC-bZIP:
-
Cap “n” collar basic leucine zipper
- CoA:
-
Coenzyme A
- CRLs:
-
Cullin-ring ubiquitin ligases
- DGR:
-
Double glycine repeat
- DMF:
-
Dimethyl fumarate
- EGCG:
-
Epigallocatechin gallate
- ERK1/2:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase 1/2
- GCLc:
-
Catalytic subunit of glutamate cysteine ligase
- GFAP:
-
Glial fibrillary acidic protein
- GPx:
-
Glutathione peroxidase
- GR:
-
Glutathione reductase
- GSH:
-
Glutathione
- GSK-3:
-
Glycogen synthase kinase 3
- GST:
-
Glutathione S-transferase
- HO-1:
-
Heme oxygenase-1
- IVR:
-
Intervening region
- Keap1:
-
Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1
- KO:
-
Knockout
- LC3:
-
Light chain 3
- Maf:
-
Musculoaponeurotic fibrosarcoma
- MAPKs:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinases
- MPTP:
-
1-Methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6- tetrahydropyridine
- Neh:
-
Nrf2-ECH homology
- NES:
-
Nuclear export signal
- NLS:
-
Nuclear localization sequence
- Nrf2:
-
Nuclear factor erythroid 2–related factor 2
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- Rbx1:
-
RING box protein-1
- ROC1:
-
Regulator of cullin-1
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RXRα:
-
Retinoid X receptor α
- SFN:
-
Sulforaphane
- SN:
-
Substantia nigra
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- tBHQ:
-
Tert-butylhydroquinone
References
Parkinson J (2002) An essay on the shaking palsy. 1817. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 14:223–236
Valent F, Devigili G, Rinaldo S, Del Zotto S, Tullio A, Eleopra R (2018) The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease in the Italian region Friuli Venezia Giulia: a population-based study with administrative data. Neurol Sci 39:699–704
Yang Y, Jiang S, Yan J, Li Y, Xin Z, Lin Y, Qu Y (2015) An overview of the molecular mechanisms and novel roles of Nrf2 in neurodegenerative disorders. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 26:47–57
Luk KC (2019) Oxidative stress and α-synuclein conspire in vulnerable neurons to promote Parkinson’s disease progression. J Clin Invest 130:3530–3531
Ge J, Zhang C, Sun YC, Zhang Q, Lv MW, Guo K, Li JL (2019) Cadmium exposure triggers mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in chicken (Gallus gallus) kidney via mitochondrial UPR inhibition and Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defense activation. Sci Total Environ 689:1160–1171
Zolnourian A, Galea I, Bulters D (2019) Neuroprotective role of the Nrf2 pathway in subarachnoid haemorrhage and its therapeutic potential. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:6218239
Von Otter M, Bergström P, Quattrone A, De Marco EV, Annesi G, Söderkvist P, Wettinger SB, Drozdzik M, Bialecka M, Nissbrandt H, Klein C, Nilsson M, Hammarsten O, Nilsson S, Zetterberg H (2014) Genetic associations of Nrf2-encoding NFE2L2 variants with Parkinson’s disease - a multicenter study. BMC Med Genet 15:131
Ahuja M, Ammal Kaidery N, Yang L, Calingasan N, Smirnova N, Gaisin A, Gaisina IN, Gazaryan I, Hushpulian DM, Kaddour-Djebbar I, Bollag WB, Morgan JC, Ratan RR, Starkov AA, Beal MF, Thomas B (2016) Distinct Nrf2 signaling mechanisms of fumaric acid esters and their role in neuroprotection against 1-methyl-4-Phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine-induced experimental Parkinson’s-like disease. J Neurosci 36:6332–6351
Gupta HV, Lyons KE, Wachter N, Pahwa R (2019) Long term response to levodopa in Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis 9:525–529
Sies H (2015) Oxidative stress: a concept in redox biology and medicine. Redox Biol 4:180–183
Scialo F, Mallikarjun V, Stefanatos R, Sanz A (2013) Regulation of lifespan by the mitochondrial electron transport chain: reactive oxygen species-dependent and reactive oxygen species-independent mechanisms. Antioxid Redox Signal 19:1953–1969
Zhao X, Zhang M, Li C, Jiang X, Su Y, Zhang Y (2019) Benefits of vitamins in the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2019:9426867
Abbott SK, Jenner AM, Spiro AS, Batterham M, Halliday GM, Garner B (2015) Fatty acid composition of the anterior cingulate cortex indicates a high susceptibility to lipid peroxidation in Parkinson’s disease. J Parkinsons Dis 5:175–185
Mythri RB, Venkateshappa C, Harish G, Mahadevan A, Muthane UB, Yasha TC, Srinivas Bharath MM, Shankar SK (2011) Evaluation of markers of oxidative stress, antioxidant function and astrocytic proliferation in the striatum and frontal cortex of Parkinson’s disease brains. Neurochem Res 36:1452–1463
Brouwer M, Huss A, van der Mark M, Nijssen PCG, Mulleners WM, Sas AMG, van Laar T, de Snoo GR, Kromhout H, Vermeulen RCH (2017) Environmental exposure to pesticides and the risk of Parkinson’s disease in the Netherlands. Environ Int 107:100–110
Dichtl S, Haschka D, Nairz M, Seifert M, Volani C, Lutz O, Weiss G (2018) Dopamine promotes cellular iron accumulation and oxidative stress responses in macrophages. Biochem Pharmacol 148:193–201
Yamato M, Kudo W, Shiba T, Yamada KI, Watanabe T, Utsumi H (2010) Determination of reactive oxygen species associated with the degeneration of dopaminergic neurons during dopamine metabolism. Free Radic Res 44:249–257
Guan X, Zhang Y, Wei H, Guo T, Zeng Q, Zhou C, Wang J, Gao T, Xuan M, Gu Q, Xu X, Huang P, Pu J, Zhang B, Liu C, Zhang M (2019) Iron-related nigral degeneration influences functional topology mediated by striatal dysfunction in Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 75:83–97
Moi P, Chan K, Asunis I, Cao A, Kan YW (1994) Isolation of NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2), a NF-E2-like basic leucine zipper transcriptional activator that binds to the tandem NF-E2/AP1 repeat of the beta-globin locus control region. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 91:9926–9930
Luo L, Chen Y, Wang H, Wang S, Liu K, Li X, Wang XJ, Tang X (2018) Mkp-1 protects mice against toxin-induced liver damage by promoting the Nrf2 cytoprotective response. Free Radic Biol Med 115:361–370
Anuranjani BM (2014) Concerted action of Nrf2-ARE pathway, MRN complex, HMGB1 and inflammatory cytokines - implication in modification of radiation damage. Redox Biol 2:832–846
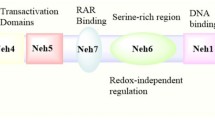
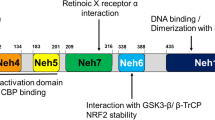
Nioi P, Nguyen T, Sherratt PJ, Pickett CB (2005) The carboxy-terminal Neh3 domain of Nrf2 is required for transcriptional activation. Mol Cell Biol 25:10895–10906
Kim JH, Yu S, Chen JD, Kong AN (2013) The nuclear cofactor RAC3/AIB1/SRC-3 enhances Nrf2 signaling by interacting with transactivation domains. Oncogene 32:514–527
Rada P, Rojo AI, Chowdhry S, McMahon M, Hayes JD, Cuadrado A (2011) SCF/{beta}-TrCP promotes glycogen synthase kinase 3-dependent degradation of the Nrf2 transcription factor in a Keap1-independent manner. Mol Cell Biol 31:1121–1133
Wang H, Liu K, Geng M, Gao P, Wu X, Hai Y, Li Y, Li Y, Luo L, Hayes JD, Wang XJ, Tang X (2013) RXRα inhibits the NRF2-ARE signaling pathway through a direct interaction with the Neh7 domain of NRF2. Cancer Res 73:3097–3108
Ma Q (2013) Role of Nrf2 in oxidative stress and toxicity. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:401–426
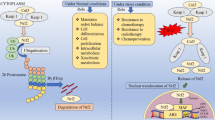
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Wakabayashi N (2005) Keap1, the sensor for electrophiles and oxidants that regulates the phase 2 response, is a zinc metalloprotein. Biochemistry 44:6889–6899
Ogura T, Tong KI, Mio K, Maruyama Y, Kurokawa H, Sato C, Yamamoto M (2010) Keap1 is a forked-stem dimer structure with two large spheres enclosing the intervening, double glycine repeat, and C-terminal domains. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:2842–2847
Zhang DD, Hannink M (2003) Distinct cysteine residues in Keap1 are required for Keap1-dependent ubiquitination of Nrf2 and for stabilization of Nrf2 by chemopreventive agents and oxidative stress. Mol Cell Biol 23:8137–8151
Kume T (2017) Therapeutic potential of the activators of the nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2-antioxidant response element pathway in brain disorders. Biol Pharm Bull 40:553–556
Wible RS, Tran QT, Fathima S, Sutter CH, Kensler TW, Sutter TR (2018) Pharmacogenomics of chemically distinct classes of Keap1-Nrf2 activators identify common and unique gene, protein, and pathway responses in vivo. Mol Pharmacol 93:297–308
Zhou W, Xu J, Tan M, Li H, Li H, Wei W, Sun Y (2018) UBE2M is a stress-inducible dual E2 for neddylation and ubiquitylation that promotes targeted degradation of UBE2F. Mol Cell 70:1008–1024
Tong KI, Kobayashi A, Katsuoka F, Yamamoto M (2006) Two-site substrate recognition model for the Keap1-Nrf2 system: a hinge and latch mechanism. Biol Chem 387:1311–1320
Rachakonda G, Xiong Y, Sekhar KR, Stamer SL, Liebler DC, Freeman ML (2008) Covalent modification at Cys151 dissociates the electrophile sensor Keap1 from the ubiquitin ligase CUL3. Chem Res Toxicol 21:705–710
Baird L, Llères D, Swift S, Dinkova-Kostova AT (2013) Regulatory flexibility in the Nrf2-mediated stress response is conferred by conformational cycling of the Keap1-Nrf2 protein complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:15259–15264
Taguchi K, Maher JM, Suzuki T, Kawatani Y, Motohashi H, Yamamoto M (2010) Genetic analysis of cytoprotective functions supported by graded expression of Keap1. Mol Cell Biol 30:3016–3026
Zhang J, Hosoya T, Maruyama A, Nishikawa K, Maher JM, Ohta T, Motohashi H, Fukamizu A, Shibahara S, Itoh K, Yamamoto M (2007) Nrf2 Neh5 domain is differentially utilized in the transactivation of cytoprotective genes. Biochem J 404:459–466
Liu B, Jiang H, Lu J, Baiyun R, Li S, Lv Y, Li D, Wu H, Zhang Z (2018) Grape seed procyanidin extract ameliorates lead-induced liver injury via miRNA153 and AKT/GSK-3β/Fyn-mediated Nrf2 activation. J Nutr Biochem 52:115–123
Rada P, Rojo AI, Evrard-Todeschi N, Innamorato NG, Cotte A, Jaworski T, Tobón-Velasco JC, Devijver H, García-Mayoral MF, Van Leuven F, Hayes JD, Bertho G, Cuadrado A (2012) Structural and functional characterization of Nrf2 degradation by the glycogen synthase kinase 3/β-TrCP axis. Mol Cell Biol 32:3486–3499
Papaiahgari S, Zhang Q, Kleeberger SR, Cho HY, Reddy SP (2006) Hyperoxia stimulates an Nrf2-ARE transcriptional response via ROS-EGFR-PI3K-Akt/ERK MAP kinase signaling in pulmonary epithelial cells. Antioxid Redox Signal 8:43–52
Sun Z, Huang Z, Zhang DD (2009) Phosphorylation of Nrf2 at multiple sites by MAP kinases has a limited contribution in modulating the Nrf2-dependent antioxidant response. PLoS One 4:e6588
Zhang G, Yang W, Jiang F, Zou P, Zeng Y, Ling X, Zhou Z, Cao J, Ao L (2019) PERK regulates Nrf2/ARE antioxidant pathway against dibutyl phthalate-induced mitochondrial damage and apoptosis dependent of reactive oxygen species in mouse spermatocyte-derived cells. Toxicol Lett. 308:24–33
Lee Y, Weihl CC (2017) Regulation of SQSTM1/p62 via UBA domain ubiquitination and its role in disease. Autophagy 13:1615–1616
Pajares M, Jiménez-Moreno N, García-Yagüe ÁJ, Escoll M, de Ceballos ML, Van Leuven F, Rábano A, Yamamoto M, Rojo AI, Cuadrado A (2016) Transcription factor NFE2L2/NRF2 is a regulator of macroautophagy genes. Autophagy 12:1902–1916
Liao W, Wang Z, Fu Z, Ma H, Jiang M, Xu A, Zhang W (2019) p62/SQSTM1 protects against cisplatin-induced oxidative stress in kidneys by mediating the cross talk between autophagy and the Keap1-Nrf2 signalling pathway. Free Radic Res 53:800–814
Yamada M, Iwata M, Warabi E, Oishi H, Lira VA, Okutsu M (2019) p62/SQSTM1 and Nrf2 are essential for exercise-mediated enhancement of antioxidant protein expression in oxidative muscle. FASEB J 33:8022–8032
Pajares M, Rojo AI, Arias E, Díaz-Carretero A, Cuervo AM, Cuadrado A (2018) Transcription factor NFE2L2/NRF2 modulates chaperone-mediated autophagy through the regulation of LAMP2A. Autophagy 14:1310–1322
Li Y, Zhao Y, Cheng M, Qiao Y, Wang Y, Xiong W, Yue W (2018) Suppression of microRNA-144-3p attenuates oxygen-glucose deprivation/reoxygenation-induced neuronal injury by promoting Brg1/Nrf2/ARE signaling. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 32:e22044
Yamamoto S, Inoue J, Kawano T, Kozaki K, Omura K, Inazawa J (2014) The impact of miRNA-based molecular diagnostics and treatment of NRF2-stabilized tumors. Mol Cancer Res 12:58–68
Srinoun K, Sathirapongsasuti N, Paiboonsukwong K, Sretrirutchai S, Wongchanchailert M, Fucharoen S (2019) miR-144 regulates oxidative stress tolerance of thalassemic erythroid cell via targeting NRF2. Ann Hematol 98:2045–2052
Akdemir B, Nakajima Y, Inazawa J, Inoue J (2017) miR-432 Induces NRF2 stabilization by directly targeting KEAP1. Mol Cancer Res 15:1570–1578
Hayes JD, Dinkova-Kostova AT (2014) The Nrf2 regulatory network provides an interface between redox and intermediary metabolism. Trends Biochem Sci 39:199–218
Chen Y, Vartiainen NE, Ying W, Chan PH, Koistinaho J, Swanson RA (2001) Astrocytes protect neurons from nitric oxide toxicity by a glutathione-dependent mechanism. J Neurochem 77:1601–1610
Wang GQ, Zhang B, He XM, Li DD, Shi JS, Zhang F (2019) Naringenin targets on astroglial Nrf2 to support dopaminergic neurons. Pharmacol Res 139:452–459
Rong H, Liang Y, Niu Y (2018) Rosmarinic acid attenuates β-amyloid-induced oxidative stress via Akt/GSK-3β/Fyn-mediated Nrf2 activation in PC12 cells. Free Radic Biol Med 120:114–123
Silva-Palacios A, Ostolga-Chavarría M, Zazueta C, Königsberg M (2018) Nrf2: Molecular and epigenetic regulation during aging. Ageing Res Rev 47:31–40
Chen PC, Vargas MR, Pani AK, Smeyne RJ, Johnson DA, Kan YW, Johnson JA (2009) Nrf2-mediated neuroprotection in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: critical role for the astrocyte. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:2933–2938
Schmidlin CJ, Dodson MB, Madhavan L, Zhang DD (2019) Redox regulation by NRF2 in aging and disease. Free Radic Biol Med 134:702–707
Ran C, Wirdefeldt K, Brodin L, Ramezani M, Westerlund M, Xiang F, Anvret A, Willows T, Sydow O, Johansson A, Galter D, Svenningsson P, Belin AC (2017) Genetic variations and mRNA expression of NRF2 in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsons Dis 2017:4020198
Ramsey CP, Glass CA, Montgomery MB, Lindl KA, Ritson GP, Chia LA, Hamilton RL, Chu CT, Jordan-Sciutto KL (2007) Expression of Nrf2 in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 66:75–85
Kobayashi EH, Suzuki T, Funayama R, Nagashima T, Hayashi M, Sekine H, Tanaka N, Moriguchi T, Motohashi H, Nakayama K, Yamamoto M (2016) Nrf2 suppresses macrophage inflammatory response by blocking proinflammatory cytokine transcription. Nat Commun 7:11624
Nakaso K, Nakamura C, Sato H, Imamura K, Takeshima T, Nakashima K (2006) Novel cytoprotective mechanism of anti-parkinsonian drug deprenyl: PI3K and Nrf2-derived induction of antioxidative proteins. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 339(3):915–922
Gan L, Vargas MR, Johnson DA, Johnson JA (2012) Astrocyte-specific overexpression of Nrf2 delays motor pathology and synuclein aggregation throughout the CNS in the alpha-synuclein mutant (A53T) mouse model. J Neurosci 32:17775–17787
Clements CM, McNally RS, Conti BJ, Mak TW, Ting JP (2006) DJ-1, a cancer- and Parkinson’s disease-associated protein, stabilizes the antioxidant transcriptional master regulator Nrf2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:15091–15096
Skibinski G, Hwang V, Ando DM, Daub A, Lee AK, Ravisankar A, Modan S, Finucane MM, Shaby BA, Finkbeiner S (2017) Nrf2 mitigates LRRK2- and α-synuclein-induced neurodegeneration by modulating proteostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 114:1165–1170
Murata H, Takamatsu H, Liu S, Kataoka K, Huh NH, Sakaguchi M (2015) NRF2 regulates PINK1 expression under oxidative stress conditions. PLoS One 10:e0142438
Cristóvão AC, Guhathakurta S, Bok E, Je G, Yoo SD, Choi DH, Kim YS (2012) NADPH oxidase 1 mediates α-synucleinopathy in Parkinson’s disease. J Neurosci 32:14465–14477
Von Otter M, Landgren S, Nilsson S, Celojevic D, Bergström P, Håkansson A, Nissbrandt H, Drozdzik M, Bialecka M, Kurzawski M, Blennow K, Nilsson M, Hammarsten O, Zetterberg H (2010) Association of Nrf2-encoding NFE2L2 haplotypes with Parkinson’s disease. BMC Med Genet 11:36
Wang L, Yang H, Wang Q, Zhang Q, Wang Z, Zhang Q, Wu S, Li H (2018) Paraquat and MPTP induce alteration in the expression profile of long noncoding RNAs in the substantia nigra of mice: role of the transcription factor Nrf2. Toxicol Lett 291:11–28
Murakami S, Miyazaki I, Asanuma M (2018) Neuroprotective effect of fermented papaya preparation by activation of Nrf2 pathway in astrocytes. Nutr Neurosci 21:176–184
Barone MC, Sykiotis GP, Bohmann D (2011) Genetic activation of Nrf2 signaling is sufficient to ameliorate neurodegenerative phenotypes in a Drosophila model of Parkinson’s disease. Dis Model Mech 4:701–707
Zhang D, Teng J (2016) Nrf2 knockout: the effect on neurological dysfunction and the activation of glial cells of mice after brain injury. Pak J Pharm Sci 29:1365–1369
Enomoto A, Itoh K, Nagayoshi E, Haruta J, Kimura T, O’Connor T, Harada T, Yamamoto M (2001) High sensitivity of Nrf2 knockout mice to acetaminophen hepatotoxicity associated with decreased expression of ARE-regulated drug metabolizing enzymes and antioxidant genes. Toxicol Sci 59:169–177
Kaidery NA, Banerjee R, Yang L, Smirnova NA, Hushpulian DM, Liby KT, Williams CR, Yamamoto M, Kensler TW, Ratan RR, Sporn MB, Beal MF, Gazaryan IG, Thomas B (2013) Targeting Nrf2-mediated gene transcription by extremely potent synthetic triterpenoids attenuate dopaminergic neurotoxicity in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 18:139–157
Dinkova-Kostova AT, Holtzclaw WD, Cole RN, Itoh K, Wakabayashi N, Katoh Y, Yamamoto M, Talalay P (2002) Direct evidence that sulfhydryl groups of Keap1 are the sensors regulating induction of phase 2 enzymes that protect against carcinogens and oxidants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:11908–11913
Ohkoshi A, Suzuki T, Ono M, Kobayashi T, Yamamoto M (2013) Roles of Keap1-Nrf2 system in upper aerodigestive tract carcinogenesis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila) 6:149–159
Cui Q, Li X, Zhu H (2016) Curcumin ameliorates dopaminergic neuronal oxidative damage via activation of the Akt/Nrf2 pathway. Mol Med Rep 13:1381–1388
Wu J, Liu X, Fan J, Chen W, Wang J, Zeng Y, Feng X, Yu X, Yang X (2014) Bardoxolone methyl (BARD) ameliorates aristolochic acid (AA)-induced acute kidney injury through Nrf2 pathway. Toxicology 318:22–31
Singh N, Vijayanti S, Saha L (2018) Targeting crosstalk between Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 and nuclear factor kappa beta pathway by Nrf2 activator dimethyl fumarate in epileptogenesis. Int J Neurosci 128:987–994
Yao W, Zhang JC, Ishima T, Ren Q, Yang C, Dong C, Ma M, Saito A, Honda T, Hashimoto K (2016) Antidepressant effects of TBE-31 and MCE-1, the novel Nrf2 activators, in an inflammation model of depression. Eur J Pharmacol 793:21–27
Bao B, Zhang MQ, Chen ZY, Wu XB, Xia ZB, Chai JY, Yin XP (2019) Sulforaphane prevents PC12 cells from oxidative damage via the Nrf2 pathway. Mol Med Rep 19:4890–4896
Sun W, Liu X, Zhang H, Song Y, Li T, Liu X, Liu Y, Guo L, Wang F, Yang T, Guo W, Wu J, Jin H, Wu H (2017) Epigallocatechin gallate upregulates NRF2 to prevent diabetic nephropathy via disabling KEAP1. Free Radic Biol Med 108:840–857
Na HK, Kim EH, Jung JH, Lee HH, Hyun JW, Surh YJ (2008) (-)-Epigallocatechin gallate induces Nrf2-mediated antioxidant enzyme expression via activation of PI3K and ERK in human mammary epithelial cells. Arch Biochem Biophys 476:171–177
Kim J, Oh J, Averilla JN, Kim HJ, Kim JS, Kim JS (2019) Grape Peel extract and resveratrol inhibit wrinkle formation in mice model through activation of Nrf2/HO-1 signaling pathway. J Food Sci 84:1600–1608
Miltonprabu S, Sumedha NC, Senthilraja P (2017) Diallyl trisulfide, a garlic polysulfide protects against As-induced renal oxidative nephrotoxicity, apoptosis and inflammation in rats by activating the Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol 50:107–120
Bai J, Yu XJ, Liu KL, Wang FF, Jing GX, Li HB, Zhang Y, Huo CJ, Li X, Gao HL, Qi J, Kang YM (2017) Central administration of tert-butylhydroquinone attenuates hypertension via regulating Nrf2 signaling in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus of hypertensive rats. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 333:100–109
Polat EC, Besiroglu H, Ozcan L, Otunctemur A, Eruyar AT, Somay A, Ozbay N, Cekmen M, Eraldemir C, Ozbek E (2018) Beneficial effects of Oltipraz, nuclear factor - erythroid - 2 - related factor 2 (Nrf2), on renal damage in unilateral ureteral obstruction rat model. Int Braz J Urol 44:1243–1251
Lin J, Xia J, Zhao HS, Hou R, Talukder M, Yu L, Guo JY, Li JL (2018) Lycopene Triggers Nrf2-AMPK Cross Talk to Alleviate Atrazine-Induced Nephrotoxicity in Mice. J Agric Food Chem 66:12385–12394
Hu X, Li L, Yan S, Li Z (2019) Arsenic trioxide suppresses acute graft-versus-host disease by activating the Nrf2/HO-1 pathway in mice. Br J Haematol 186:e145–e148
Terazawa R, Garud DR, Hamada N, Fujita Y, Itoh T, Nozawa Y, Nakane K, Deguchi T, Koketsu M, Ito M (2010) Identification of organoselenium compounds that possess chemopreventive properties in human prostate cancer LNCaP cells. Bioorg Med Chem 18:7001–7008
Tocmo R, Parkin K (2019) S-1-propenylmercaptocysteine protects murine hepatocytes against oxidative stress via persulfidation of Keap1 and activation of Nrf2. Free Radic Biol Med 143:164–175
Qu KC, Wang ZY, Tang KK, Zhu YS, Fan RF (2019) Trehalose suppresses cadmium-activated Nrf2 signaling pathway to protect against spleen injury. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 181:224–230
Cuadrado A, Manda G, Hassan A, Alcaraz MJ, Barbas C, Daiber A, Ghezzi P, León R, López MG, Oliva B, Pajares M, Rojo AI, Robledinos-Antón N, Valverde AM, Guney E, Schmidt HHHW (2018) Transcription factor NRF2 as a therapeutic target for chronic diseases: a systems medicine approach. Pharmacol Rev 70:348–383
Miyazaki I, Asanuma M (2017) Therapeutic strategy of targeting astrocytes for neuroprotection in Parkinson’s disease. Curr Pharm Des 23:4936–4947
Campolo M, Casili G, Biundo F, Crupi R, Cordaro M, Cuzzocrea S, Esposito E (2017) The neuroprotective effect of dimethyl fumarate in an MPTP-mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: involvement of reactive oxygen species/nuclear factor-κB/nuclear transcription factor related to NF-E2. Antioxid Redox Signal 27:453–471
Lastres-Becker I, García-Yagüe AJ, Scannevin RH, Casarejos MJ, Kügler S, Rábano A, Cuadrado A (2016) Repurposing the NRF2 activator dimethyl fumarate as therapy against synucleinopathy in Parkinson’s disease. Antioxid Redox Signal 25:61–77
Yang L, Calingasan NY, Thomas B, Chaturvedi RK, Kiaei M, Wille EJ, Liby KT, Williams C, Royce D, Risingsong R, Musiek ES, Morrow JD, Sporn M, Beal MF (2009) Neuroprotective effects of the triterpenoid, CDDO methyl amide, a potent inducer of Nrf2-mediated transcription. PLoS One 4(6):e5757
Abdel-Wahab MH (2005) Potential neuroprotective effect of t-butylhydroquinone against neurotoxicity-induced by 1-methyl-4-(2'-methylphenyl)-1,2,3,6- tetrahydropyridine (2'-methyl-MPTP) in mice. J Biochem Mol Toxicol 19:32–41
Xu LL, Wu YF, Yan F, Li CC, Dai Z, You QD, Jiang ZY, Di B (2019) 5-(3,4-Difluorophenyl)-3-(6-methylpyridin-3-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazole (DDO-7263), a novel Nrf2 activator targeting brain tissue, protects against MPTP-induced subacute Parkinson’s disease in mice by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome and protects PC12 cells against oxidative stress. Free Radic Biol Med 134:288–303
Jung UJ, Kim SR (2018) Beneficial effects of flavonoids against Parkinson’s disease. J Med Food 21:421–432
Baluchnejadmojarad T, Rabiee N, Zabihnejad S, Roghani M (2017) Ellagic acid exerts protective effect in intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson’s disease: possible involvement of ERβ/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Brain Res 1662:23–30
Dos Santos Nunes RG, Pereira PS, Elekofehinti OO, Fidelis KR, da Silva CS, Ibrahim M, Barros LM, da Cunha FAB, Lukong KE, de Menezes IRA, Tsopmo A, Duarte AE, Kamdem JP (2019) Possible involvement of transcriptional activation of nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) in the protective effect of caffeic acid on paraquat-induced oxidative damage in Drosophila melanogaster. Pestic Biochem Physiol 157:161–168
Zhou ZD, Xie SP, Saw WT, Ho PGH, Wang H, Lei Z, Yi Z, Tan EK (2019) The therapeutic implications of tea polyphenols against dopamine (DA) neuron degeneration in Parkinson’s Disease (PD). Cells 8:911
Guo C, Zhu J, Wang J, Duan J, Ma S, Yin Y, Quan W, Zhang W, Guan Y, Ding Y, Wen A, Zhang Y (2019) Neuroprotective effects of protocatechuic aldehyde through PLK2/p-GSK3β/Nrf2 signaling pathway in both in vivo and in vitro models of Parkinson’s disease. Aging (Albany NY) 11:9424–9441
Gaballah HH, Zakaria SS, Elbatsh MM, Tahoon NM (2016) Modulatory effects of resveratrol on endoplasmic reticulum stress-associated apoptosis and oxido-inflammatory markers in a rat model of rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease. Chem Biol Interact 251:10–16
Morroni F, Sita G, Djemil A, D’Amico M, Pruccoli L, Cantelli-Forti G, Hrelia P, Tarozzi A (2018) Comparison of adaptive neuroprotective mechanisms of sulforaphane and its interconversion product erucin in in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson’s disease. J Agric Food Chem 66:856–865
Yang C, Mo Y, Xu E, Wen H, Wei R, Li S, Zheng J, Li W, Le B, Chen Y, Pan H, Huang S, Wang S, Wang Q (2019) Astragaloside IV ameliorates motor deficits and dopaminergic neuron degeneration via inhibiting neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in a Parkinson’s disease mouse model. Int Immunopharmacol 75:105651
Chen JH, Ou HP, Lin CY, Lin FJ, Wu CR, Chang SW, Tsai CW (2012) Carnosic acid prevents 6-hydroxydopamine-induced cell death in SH-SY5Y cells via mediation of glutathione synthesis. Chem Res Toxicol 25:1893–1901
Bae J, Lee D, Kim YK, Gil M, Lee JY, Lee KJ (2013) Berberine protects 6-hydroxydopamine-induced human dopaminergic neuronal cell death through the induction of heme oxygenase-1. Mol Cells 35:151–157
Zhang Z, Cui W, Li G, Yuan S, Xu D, Hoi MP, Lin Z, Dou J, Han Y, Lee SM (2012) Baicalein protects against 6-OHDA-induced neurotoxicity through activation of Keap1/Nrf2/HO-1 and involving PKCalpha and PI3K/AKT signaling pathways. J Agric Food Chem 60:8171–8182
Du X, Xu H, Jiang H, Xie J (2013) Akt/Nrf2 activated upregulation of heme oxygenase-1 involves in the role of Rg1 against ferrous iron-induced neurotoxicity in SK-N-SH cells. Neurotox Res 24:71–79
Zhang L, Hao J, Zheng Y, Su R, Liao Y, Gong X, Liu L, Wang X (2018) Fucoidan Protects Dopaminergic Neurons by Enhancing the mitochondrial function in a rotenone-induced rat model of Parkinson’s disease. Aging Dis 9:590–604
Anis E, Zafeer MF, Firdaus F, Islam SN, Khan AA, Hossain MM (2020) Perillyl alcohol mitigates behavioural changes and limits cell death and mitochondrial changes in unilateral 6-OHDA lesion model of Parkinson’s disease through alleviation of oxidative stress. Neurotox Res 38:461–477
Michel HE, Tadros MG, Esmat A, Khalifa AE, Abdel-Tawab AM (2017) Tetramethylpyrazine ameliorates rotenone-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats: involvement of its anti-inflammatory and anti-apoptotic actions. Mol Neurobiol 54:4866–4878
Li X, Zhang J, Zhang X, Dong M (2020) Puerarin suppresses MPP(+)/MPTP-induced oxidative stress through an Nrf2-dependent mechanism. Food Chem Toxicol 144:111644
Li X, Zhang J, Rong H, Zhang X, Dong M (2020) Ferulic acid ameliorates MPP(+)/MPTP-induced oxidative stress via ERK1/2-dependent Nrf2 activation: translational implications for Parkinson disease treatment. Mol Neurobiol 57:2981–2995
Zou Y, Wang R, Guo H, Dong M (2015) Phytoestrogen beta-ecdysterone protects PC12 cells against MPP+-induced neurotoxicity in vitro: involvement of PI3K-Nrf2-regulated pathway. Toxicol Sci 147:28–38
Wang XL, Xing GH, Hong B, Li XM, Zou Y, Zhang XJ, Dong MX (2014) Gastrodin prevents motor deficits and oxidative stress in the MPTP mouse model of Parkinson’s disease: involvement of ERK1/2-Nrf2 signaling pathway. Life Sci 114:77–85
Tu W, Wang H, Li S, Liu Q, Sha H (2019) The anti-inflammatory and anti-oxidant mechanisms of the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE signaling pathway in chronic diseases. Aging Dis 10:637–651
Imaizumi Y, Okada Y, Akamatsu W, Koike M, Kuzumaki N, Hayakawa H, Nihira T, Kobayashi T, Ohyama M, Sato S, Takanashi M, Funayama M, Hirayama A, Soga T, Hishiki T, Suematsu M, Yagi T, Ito D, Kosakai A, Hayashi K, Shouji M, Nakanishi A, Suzuki N, Mizuno Y, Mizushima N, Amagai M, Uchiyama Y, Mochizuki H, Hattori N, Okano H (2012) Mitochondrial dysfunction associated with increased oxidative stress and α-synuclein accumulation in PARK2 iPSC-derived neurons and postmortem brain tissue. Mol Brain 5:35
Bresciani A, Missineo A, Gallo M, Cerretani M, Fezzardi P, Tomei L, Cicero DO, Altamura S, Santoprete A, Ingenito R, Bianchi E, Pacifici R, Dominguez C, Munoz-Sanjuan I, Harper S, Toledo-Sherman L, Park LC (2017) Nuclear factor (erythroid-derived 2)-like 2 (NRF2) drug discovery: Biochemical toolbox to develop NRF2 activators by reversible binding of Kelch-like ECH-associated protein 1 (KEAP1). Arch Biochem Biophys 631:31–41
Funding
This work is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grants No. 81873133, 81373629, 81241107, and 81073080 to Dong M; grants No. 81673686, 81473407, 81273640, 81141117, 30973925, and 30873396 to Niu Y).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Miaoxian Dong had the idea for the article, Yingcai Niu drafted and critically revised the work, and Jing Zhang performed the literature search.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Niu, Y., Zhang, J. & Dong, M. Nrf2 as a potential target for Parkinson’s disease therapy. J Mol Med 99, 917–931 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-021-02071-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-021-02071-5