Abstract
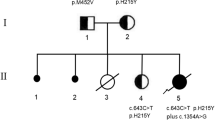
The VARS2 gene encodes a mitochondrial valyl-transfer RNA synthetase which is used in mitochondrial translation. To date, several patients with VARS2 pathogenic variants have been described in the literature. These patients have features of lactic acidosis with encephalomyopathy. We present a case of an infant with lactic acidosis, failure to thrive, and severe primary pulmonary hypertension who was found to be a compound heterozygote for two novel VARS2 variants (c.1940C>T, p.(Thr647Met) and c.2318G>A, p.(Arg773Gln)). The patient was treated with vitamin supplements and a carbohydrate-restricted diet. The lactic acidosis and failure to thrive resolved, and he showed good growth and development. Functional studies and molecular analysis employed a yeast model system and the VAS1 gene (yeast homolog of VARS2). VAS1 genes harboring either one of two mutations corresponding to the two novel variants in the VARS2 gene, exhibited partially reduced function in haploid yeast strains. A combination of both VAS1 variant alleles in a diploid yeast cell exhibited a more significant decrease in oxidative metabolism-dependent growth and in the oxygen consumption rate (reminiscent of the patient who carries two mutant VARS2 alleles). Our results demonstrate the pathogenicity of the biallellic novel VARS2 variants.
Key messages
• A case of an infant who is a compound heterozygote for two novel VARS2 variants.
• This infant displayed lactic acidosis, failure to thrive, and pulmonary hypertension.
• Treatment of the patient with a carbohydrate-restricted diet resulted in good growth and development.
• Studies with the homologous yeast VAS1 gene showed reduced function of corresponding single mutant in haploid yeast strains.
• A combination of both VAS1 variant alleles in diploid yeast exhibited a more significant decrease in function, thereby confirming the pathogenicity of the biallellic novel VARS2 variants.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ben-Menachem R, Pines O (2017) Detection of dual targeting and dual function of mitochondrial proteins in yeast. Methods Mol Biol 2017;1567:179–195. DOI:
Kalderon B, Pines O (2014) Protein folding as a driving force for dual protein targeting in eukaryotes. Front Mol Biosci 1:23
Yogev O, Pines O (2011) Dual targeting of mitochondrial proteins: mechanism, regulation and function. Biochim Biophys Acta 1808(3):1012–1020
Wang CC, Chang KJ, Tang HL, Hsieh CJ, Schimmel P (2003) Mitochondrial form of a tRNA synthetase can be made bifunctional by manipulating its leader peptide. Biochemistry. 42(6):1646–1651
Diodato D, Melchionda L, Haack TB, Dallabona C, Baruffini E, Donnini C, Granata T, Ragona F, Balestri P, Margollicci M et al (2014) VARS2 and TARS2 mutations in patients with mitochondrial encephalomyopathies. Hum Mutat 35(8):983–989
Taylor RW, Pyle A, Griffin H, Blakely EL, Duff J, He L, Smertenko T, Alston CL, Neeve VC, Best A et al (2014) Use of whole-exome sequencing to determine the genetic basis of multiple mitochondrial respiratory chain complex deficiencies. JAMA 312(1):68–77
Pronicka E, Piekutowska-Abramczuk D, Ciara E, Trubicka J, Rokicki D, Karkucinska-Wieckowska A, Pajdowska M, Jurkiewicz E, Halat P, Kosinska J et al (2016) New perspective in diagnostics of mitochondrial disorders: two years’ experience with whole-exome sequencing at a national paediatric centre. J Transl Med 14(1):174
Baertling F, Alhaddad B, Seibt A, Budaeus S, Meitinger T, Strom TM, Mayatepek E, Schaper J, Prokisch H, Haack TB et al (2017) Neonatal encephalocardiomyopathy caused by mutations in VARS2. Metab Brain Dis 32(1):267–270
Bruni F, Meo ID, Bellacchio E, Webb BD, McFarland R, Chrzanowska-Lightowlers ZMA, He L, Skorupa E, Moroni I, Ardissone A et al (2018) Clinical, biochemical and genetic features associated with VARS2-related mitochondrial disease. Hum Mutat. https://doi.org/10.1002/humu.23398
Pereira S, Adrião M, Sampaio M, Basto MA, Rodrigues E, Vilarinho L, Teles EL, Alonso I, Leão M (2018) Mitochondrial encephalopathy: first Portuguese report of a VARS2 causative variant. JIMD Rep 42:113–119
Ma K, Xie M, He X, Liu G, Lu X, Peng Q, Zhong B, Li N (2018) A novel compound heterozygous mutation in VARS2 in a newborn with mitochondrial cardiomyopathy: a case report of a Chinese family. BMC Med Genet 19:202
Siekierska A, Stamberger H, Deconinck T, Oprescu SN, Partoens M, Zhang Y, Sourbron J, Adriaenssens E, Mullen P, Wiencek P et al (2019) Biallelic VARS variants cause developmental encephalopathy with microcephaly that is recapitulated in vars knockout zebrafish. Nat Commun 10(1):708
Fukai S, Nureki O, Sekine S, Shimada A, Tao J, Vassylyev DG, Yokoyama S (2000) Structural basis for double-sieve discrimination of L-valine from L-isoleucine and L-threonine by the complex of tRNA(Val) and valyl-tRNA synthetase. Cell 103(5):793–803
Baruffini E, Ferrero I, Foury F (2010) In vivo analysis of mtDNA replication defects in yeast. Methods. 51(4):426–436
Nunnari J, Suomalainen A (2012) Mitochondria: in sickness and in health. Cell 148(6):1145–1159
Fukai S, Nureki O, Sekine S, Shimada A, Vassylyev DG, Yokoyama S (2003) Mechanism of molecular interactions for tRNA(Val) recognition by valyl-tRNA synthetase. RNA Jan 9(1):100–111
Kaiser C, Michaelis S, Mitchell A (1994) Methods in yeast genetics: a laboratory course manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, ColdSpring Harbor
Peleg Y, Rokem JS, Goldberg I, Pines O (1990) Inducible overexpression of the FUM1 gene in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: localization of fumarase and efficient fumaric acid bioconversion to L-malic acid. Appl Environ Microbiol 56(9):2777–2783
Gietz RD, Schiestl RH (2007) Quick and easy yeast transformation using the LiAc/SS carrier DNA/PEG method. Nat Protoc 2(1):35–37
Ho SN, Hunt HD, Horton RM, Pullen JK, Pease LR (1989) Site-directed mutagenesis by overlap extension using the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 77(1):51–59
Del Dotto V, Fogazza M, Musiani F, Maresca A, Aleo SJ, Caporali L, La Morgia C, Nolli C, Lodi T, Goffrini P et al (2018) Deciphering OPA1 mutations pathogenicity by combined analysis of human, mouse and yeast cell models. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis 1864(10):3496–3514
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank the patient and his family for allowing us to discuss their case.
Funding
This study was supported, in part, by a MMID-2 SHARE grant, CREATE, National Research Foundation (NRF) of Singapore to OP, HLC, and CKH; Telethon GGP15041 to CD and EB and DIP; ISF, Pakula family grants to OP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Informed consent from the patient’s parents was obtained. The requirement for ethics approval was waived as functional testing was not done on patient samples. The patient’s growth chart was plotted on charts developed by the National Center for Health Statistics in collaboration with the National Center for Chronic Disease Prevention and Health Promotion (2000). http://www.cdc.gov.sg/growthcharts.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chin, HL., Goh, D.LM., Wang, F.S. et al. A combination of two novel VARS2 variants causes a mitochondrial disorder associated with failure to thrive and pulmonary hypertension. J Mol Med 97, 1557–1566 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-019-01834-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-019-01834-5