Abstract
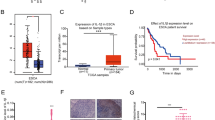
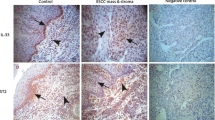
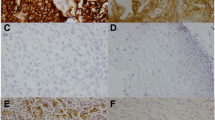
Interleukin (IL)-1 beta has been reported to be a marker of shorter survival in gastric and colorectal adenocarcinoma. In the present study, we examined the potential role and prognostic value of IL-1 beta in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (SCC). Human esophageal SCC cell line, CE81T, was selected for cellular and animal experiments, in which biological changes after experimental manipulation of IL-1 beta signaling were explored, including tumor growth, invasion capacity, and the sensitivity to treatment. Moreover, 147 esophageal SCC samples were analyzed using immunohistochemical staining to correlate the expression of IL-1 beta with clinical outcome. Our data revealed that IL-1 beta was significantly overexpressed both at mRNA and protein levels in cancer specimens compared to nonmalignant tissues. When IL-1 beta signaling was blocked, tumor growth, invasion ability, and treatment resistance were attenuated. Activation of NF-kappa B, increase of E2-EPF ubiquitin carrier protein and subsequent epithelial–mesenchymal transition might be the underlying mechanisms of the more aggressive tumor growth in IL-1 beta-positive esophageal cancer. The immunochemistry findings indicate that positivity staining of IL-1 beta correlated significantly with higher clinical stage, lower response rate to concurrent chemoradiotherapy (CCRT), and higher recurrence rate after curative treatment. Moreover, IL-1 beta was a significant predictor of survival in patients undergoing surgical intervention or definite CCRT. In conclusion, IL-1 beta is significantly linked to poor prognosis for patients with esophageal cancer and may be a promising molecular target for therapeutic intervention for esophageal SCC.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SCC:
-
Squamous cell carcinoma
- UCP:
-
E2-EPF ubiquitin carrier protein
- EMT:
-
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- VHL:
-
Von Hippel–Lindau gene
- HIF-1α:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ (2003) Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med 349:2241–2252
Bedenne L, Michel P, Bouche O, Milan C, Mariette C et al (2007) Chemoradiation followed by surgery compared with chemoradiation alone in squamous cancer of the esophagus: FFCD 9102. J Clin Oncol 25:1160–1168
Siewert JR, Stein HJ, Feith M, Bruecher BL, Bartels H et al (2001) Histologic tumor type is an independent prognostic parameter in esophageal cancer: lessons from more than 1,000 consecutive resections at a single center in the Western world. Ann Surg 234:360–367, discussion 368–369
Rohatgi PR, Swisher SG, Correa AM, Wu TT, Liao Z et al (2006) Histologic subtypes as determinants of outcome in esophageal carcinoma patients with pathologic complete response after preoperative chemoradiotherapy. Cancer 106:552–558
Siewert JR, Ott K (2007) Are squamous and adenocarcinomas of the esophagus the same disease? Semin Radiat Oncol 17:38–44
Wu X, Gu J, Wu TT, Swisher SG, Liao Z et al (2006) Genetic variations in radiation and chemotherapy drug action pathways predict clinical outcomes in esophageal cancer. J Clin Oncol 24:3789–3798
Nozoe T, Saeki H, Sugimachi K (2001) Significance of preoperative elevation of serum C-reactive protein as an indicator of prognosis in esophageal carcinoma. Am J Surg 182:197–201
Forrest LM, McMillan DC, McArdle CS, Angerson WJ, Dunlop DJ (2003) Evaluation of cumulative prognostic scores based on the systemic inflammatory response in patients with inoperable non-small-cell lung cancer. Br J Cancer 89:1028–1030
Gelin J, Moldawer LL, Lonnroth C, Sherry B, Chizzonite R et al (1991) Role of endogenous tumor necrosis factor alpha and interleukin one for experimental tumor growth and the development of cancer cachexia. Cancer Res 51:415–421
Strassmann G, Fong M, Freter CE, Windsor S, D’Alessandro F et al (1993) Suramin interferes with interleukin-6 receptor binding in vitro and inhibits colon-26-mediated experimental cancer cachexia in vivo. J Clin Invest 92:2152–2159
Smyth MJ, Cretney E, Kershaw MH et al (2004) Cytokines in cancer immunity and immunotherapy. Immunol Rev 202:275–293
Abdel-Latif MM, Duggan S, Reynolds JV, Kelleher D (2009) Inflammation and esophageal carcinogenesis. Curr Opin Pharmacol 9:396–404
Weber A, Wasiliew P, Kracht M (2010) Interleukin-1 (IL-1) pathway. Sci Signal 3:cm1
Arlt A, Vorndamm J, Muerkoster S, Yu H, Schmidt WE et al (2002) Autocrine production of interleukin 1beta confers constitutive nuclear factor kappaB activity and chemoresistance in pancreatic carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Res 62:910–916
Maihöfner C, Charalambous MP, Bhambra U et al (2003) Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 parallels expression of interleukin-1beta, interleukin-6 and NF-kappaB in human colorectal cancer. Carcinogenesis 24:665–671
Wolf JS, Chen Z, Dong G et al (2001) IL (interleukin)-1alpha promotes nuclear factor-kappaB and AP-1-induced IL-8 expression, cell survival, and proliferation in head and neck squamous cell carcinomas. Clin Cancer Res 7:1812–1820
Mukhopadhyay P, Ali MA, Nandi A et al (2006) The cyclin-dependent kinase two inhibitor down-regulates nterleukin-1beta-mediated induction of cyclooxygenase-2 expression in human lung carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 66:1758–1766
Ito H, Kaneko K, Makino R, Konishi K, Kurahashi T et al (2007) Interleukin-1beta gene in esophageal, gastric and colorectal carcinomas. Oncol Rep 18:473–481
Deans DA, Wigmore SJ, Gilmour H, Paterson-Brown S, Ross JA et al (2006) Elevated tumour interleukin-1beta is associated with systemic inflammation: a marker of reduced survival in gastro-oesophageal cancer. Br J Cancer 95:1568–1575
Wu IC, Lu CY, Kuo FC, Tsai SM, Lee KW et al (2006) Interaction between cigarette, alcohol and betel nut use on esophageal cancer risk in Taiwan. Eur J Clin Invest 36:236–241
Hu CP, Hsieh HG, Chien KY, Wang PY, Wang CI et al (1984) Biologic properties of three newly established human esophageal carcinoma cell lines. J Natl Cancer Inst 72:577–583
Chen MF, Lee KD, Lu MS, Chen CC, Hsieh MJ et al (2009) The predictive role of E2-EPF ubiquitin carrier protein in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Mol Med 87:307–320
Baeuerle PA, Henkel T (1994) Function and activation of NF-kappa B in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 12:141–179
Karin M, Cao Y, Greten FR, Li ZW (2002) NF-kappaB in cancer: from innocent bystander to major culprit. Nat Rev Cancer 2:301–310
Wu CS, Chen MF, Lee IL, Tung SY (2007) Predictive role of nuclear factor-kappaB activity in gastric cancer: a promising adjuvant approach with caffeic acid phenethyl ester. J Clin Gastroenterol 41:894–900
Yamanaka N, Morisaki T, Nakashima H et al (2004) Interleukin 1beta enhances invasive ability of gastric carcinoma through nuclear factor-kappaB activation. Clin Cancer Res 10:1853–1859
Karin M, Lin A (2002) NF-kappaB at the crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol 3:221–227
Michaluart P, Masferrer JL, Carothers AM, Subbaramaiah K, Zweifel BS et al (1999) Inhibitory effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on the activity and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 in human oral epithelial cells and in a rat model of inflammation. Cancer Res 59:2347–2352
Natarajan K, Singh S, Burke TR Jr, Grunberger D, Aggarwal BB (1996) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester is a potent and specific inhibitor of activation of nuclear transcription factor NF-kappa B. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 93:9090–9095
Chiao C, Carothers AM, Grunberger D, Solomon G, Preston GA et al (1995) Apoptosis and altered redox state induced by caffeic acid phenethyl ester (CAPE) in transformed rat fibroblast cells. Cancer Res 55:3576–3583
Chen MF, Keng PC, Lin PY, Yang CT, Liao SK et al (2005) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester decreases acute pneumonitis after irradiation in vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer 5:158
Kim MK, Cho KJ, Kwon GY, Park SI, Kim YH et al (2008) ERCC1 predicting chemoradiation resistance and poor outcome in oesophageal cancer. Eur J Cancer 44:54–60
Chen MF, Fang FM, Lu CH, Lu MS, Chen WC et al (2008) Significance of nuclear accumulation of Foxo3a in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 71:1220–1229
Brown JM, Attardi LD (2005) The role of apoptosis in cancer development and treatment response. Nat Rev Cancer 5:231–237
Olive PL, Banath JP (2004) Phosphorylation of histone H2AX as a measure of radiosensitivity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 58:331–335
Acknowledgments
The grant was supported by the National Science Council, Taiwan grant 98-2314-B-182-038-MY2.
Competing interests
There is no conflict of interest that could be perceived as prejudicing the impartiality of the research reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary materials
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
ESM 1
DOC 271 kb
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, MF., Lu, MS., Chen, PT. et al. Role of interleukin 1 beta in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. J Mol Med 90, 89–100 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0809-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-011-0809-4