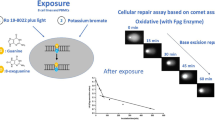
Background:
The “comet assay” has become an interesting and a very useful tool for the analysis of the induction and amount of DNA damage in single cells thus offering the opportunity to measure the effectiveness of DNA repair. On the basis of the Östling and Johanson protocol we have developed a modified method with increased sensitivity and high reproducibility.
Material and Methods: Human tumor cells or isolated human peripheral blood lymphocytes were analyzed in the experiments. The amount of DNA damage and the effectiveness of DNA repair was measured after X-irradiation using the “comet assay” technique.
Results: In this presentation the influences of different methodological factors like agarose concentration, buffer pH, electrophoresis time, electric field strength on the applicability of the “comet assay” are described in detail and optimum conditions for “comet assay” experiments have been evaluated. Additionally the authors will show a comparison of different fluorescent DNA dyes pointing out their advantages or disadvantages for “comet” analysis. The usefulness of this technique and its capabilities are exemplified by showing DNA repair kinetics of human lymphocytes of different healthy or radiosensitive donors after in-vitro irradiation with 2 Gy X-rays.
Conclusions: This paper presents data on the optimization and standardization of the original “comet assay” leading to an extremely fast and practicable protocol in the field of single cell gel electrophoresis. After irradiation with 0.1 Gy an increase in the amount of DNA damage can be measured with high statistical significance and the DNA repair capacitiy of individual cells after X-ray doses of 2 Gy can be analyzed with high reproducibility. The results comparing DNA repair capacities of different donors point out that the “comet assay” may have the potential for the estimation of individual radiosensitivity.
Hintergrund:
Der “Comet Assay” hat sich in Hinsicht auf die Analyse eines induzierten DNS-Schadens in Einzelzellen zu einer interessanten Technik entwickelt. Zudem wird die Möglichkeit geboten, die Effektivität der DNS-Reparatur zu messen. Basierend auf dem Östling-und-Johanson-Protokoll, haben wir einen modifizierten “Comet Assay” mit sehr hoher Empfindlichkeit und guter Reproduzierbarkeit entwickelt.
Material und Methoden: Humane Tumorzellen oder isolierte menschliche Lymphozyten wurden in den Experimenten untersucht. Der DNS-Schaden und die Effektivität der DNS-Reparatur nach Röntgenbestrahlung wurden mit Hilfe des “Comet Assay”, bestimmt.
Ergebnisse: Die Einflüsse unterschiedlicher methodischer Faktoren wie Agarosekonzentration, pH-Werte der Pufferlösungen, Elektrophoresezeit, Stärke des elektrischen Feldes auf die Anwendung des “Comet Assay” werden zusammengefaßt und detailliert beschrieben. Zusätzlich zeigen die Autoren einen Vergleich unterschiedlicher fluoreszierender DNS-Farbstoffe hinsichtlich ihrer Vor- und Nachteile für die Analyse der “Kometen”. Die Anwendbarkeit dieser Technik wird verdeutlicht durch die Darstellung der DNS-Reparaturkinetik menschlicher Lymphozyten unterschiedlicher gesunder und strahlenempfindlicher Spender nach einer In-vitro-Bestrahlung mit 2-Gy-Röntgenstrahlen.
Schlußfolgerungen: Mit den hier präsentierten Daten soll die Optimierung und Standardisierung des originalen “Comet Assay”-Protokolls gezeigt werden. Mit dieser extrem schnellen und praktikablen Version der Einzelzell-Gelelektrophorese sind DNS-Schäden nach Röntgenbestrahlung mit 0,1 Gy und DNS-Reparaturuntersuchungen nach 2 Gy meßbar mit hoher Reproduzierbarkeit. Vergleichende Untersuchungen von DNS-Reparaturkapazitäten unterschiedlicher Spender deuten an, daß der “Comet Assay” eine Einschätzung der individuellen Strahlenempfindlichkeit ermöglichen könnte.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Submitted: 18 Jan 1999 / Accepted: 22 Apr 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bauch, T., Böcker, W., Mallek, U. et al. Optimization and Standardization of the “Comet Assay” for Analyzing the Repair of DNA Damage in Cells. Strahlenther Onkol 175, 333–340 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000660050020
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000660050020