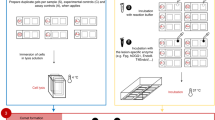
Background and Purpose:
The comet assay offers the opportunity to measure the amount of DNA damage and the effectiveness of DNA repair in single cells. In a first part, experiments are presented comparing three different protocols of the comet assay technique with respect to the analysis of the induction of DNA damage after X-irradiation in isolated human lymphocytes and CHO cells. In a second part, the restriction enzyme AluI, an agent producing DNA double-strand breaks exclusively, was introduced into CHO cells by electroporation and the effects were analyzed using the different comet assay protocols. The experiments were carried out in order to test the assertion that comet assay techniques can measure different types of DNA damages at different pH conditions of lysis and electrophoresis.
Material and Methods:
Three different comet assay protocols were used for the analysis of DNA damage in lymphocytes and CHO cells.
Results:
The results clearly indicate that among the three protocols the modified comet assay technique used by the authors showed the highest sensitivity in the radiotherapy-relevant dose range between 0 and 2 Gy. All three protocols were capable of detecting an effect by AluI. This effect, however, was clearly different from radiation effects. Whereas after radiation exposure all cell nuclei show a dose-dependent increase in DNA content in the comet tail, most of the cell nuclei were unaffected by an AluI uptake. Nevertheless, there was an effect by AluI that could be detected in all three assay versions: between 5% and 15% of the nuclei showed clearly abnormal comet morphologies.
Conclusion:
Neither the strictly alkaline nor the strictly neutral comet assay is applicable in the radiation dose range of about 2 Gy. The restriction enzyme results show that other factors than just DNA strand breaks contribute to DNA migration into the tail of the comets.
Hintergrund und Ziel:
Der „Kometen-Test“ liefert die Möglichkeit, das Ausmaß von DNA-Schäden und DNA-Reparatur in Einzelzellen zu messen. In einem ersten Teil werden Experimente vorgestellt, in denen drei verschiedene Protokolle des Kometen-Tests auf ihre Fähigkeit überprüft wurden, DNA-Schäden nach Röntgenbestrahlung in isolierten menschlichen Lymphozyten und CHO-Zellen zu erfassen. Im zweiten Teil der Experimente wurde das Restriktionsenzym AluI, ein Agens, das ausschließlich DNA-Doppelstrangbrüche hervorruft, durch Elektroporation in CHO-Zellen eingeführt. Die Effekte wurden mit Hilfe der verschiedenen Kometen-Tests analysiert. Die Experimente wurden durchgeführt, um die Behauptung zu testen, dass durch Veränderung der pH-Bedingungen bei der Lyse und der Elektrophorese unterschiedliche DNA-Schadenstypen erfasst werden können.
Material und Methodik:
Es wurden drei verschiedene Kometen-Test-Protokolle (Tabelle 1) zur Analyse von DNA-Schäden in Lymphozyten und CHO-Zellen verwendet.
Ergebnisse:
Die Ergebnisse zeigen eindeutig, dass von den drei Protokollen die von den Autoren verwendete modifizierte Fassung des Kometen-Tests die höchste Empfindlichkeit im für die Strahlentherapie relevanten Dosisbereich von 0–2 Gy aufweist (Abbildungen 1 und 2). Alle drei Protokolle konnten einen Effekt durch AluI erfassen. Allerdings war dieser Effekt deutlich verschieden von Strahleneffekten. Während nach einer Strahlenexposition alle Zellkerne eine dosisabhängige Zunahme an DNA im Kometenschweif aufweisen, blieben die meisten Zellkerne trotz AluI-Aufnahme (Abbildung 5) unbeeinflusst. Dennoch gab es einen AluI-Effekt, der in allen drei Versionen des Tests nachweisbar war: Zwischen 5 und 15% aller Kerne zeigten deutlich anormale Kometenstrukturen (Abbildungen 3 und 4).
Schlussfolgerung:
Weder der strikt alkalische noch der strikt neutrale Kometen-Test ist in einem Strahlendosisbereich von etwa 2 Gy anwendbar. Die Ergebnisse der Restriktionsenzymexperimente zeigen, dass neben DNA-Strangbrüchen noch andere Faktoren das Ausmaß der DNA-Wanderung in den Kometenschweif bestimmen.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Müller, WU., Ciborovius, J., Bauch, T. et al. Analysis of the Action of the Restriction Endonuclease AluI Using Three Different Comet Assay Protocols. Strahlenther Onkol 180, 655–664 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-004-1255-9
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00066-004-1255-9