Abstract
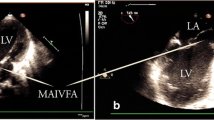
Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral–aortic intervalvular fibrosa (P-MAIVF) is an infrequent but potentially life-threatening condition. Both transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) and transesophageal echocardiography (TEE) can detect P-MAIVF with sensitivity rates of 43 and 90 %, respectively. The typical finding of echocardiography is a pulsatile echo-free sac that expands in systole and collapses in diastole. Our review comprises 166 patients with P-MAIVF, including eight cases in our hospital and 158 cases from the literature. P-MAIVF is often associated with infection or surgical trauma. While it is likely to maintain an asymptomatic course, symptoms of shortness of breath, heart failure, valvular disease, chest pain, endocarditis, and cerebrovascular events are common clinical presentations. The recommended treatment is surgery. However, conservative therapy is an alternative approach for high-risk patients or when surgical treatment is refused. With the increasing incidence of cardiac surgery and infective endocarditis, a likely increment in the new diagnosis of pseudoaneurysm is expected.
Zusammenfassung
Das Pseudoaneurysma der mitral-aortalen intervalvulären Fibrosa (MAIVF, aortomitraler Übergang) ist nicht häufig, aber potenziell lebensbedrohlich. Sowohl mit der transthorakalen Echokardiographie (TTE) als auch mit der transösophagealen Echokardiographie (TEE) kann ein Pseudoaneurysma der MAIVF (P-MAIVF) mit einer Sensitivitätsrate von 43 bzw. 90 % diagnostiziert werden. Typischer Befund bei der Echokardiographie ist ein pulsierender echofreier Sack, der sich in der Systole ausdehnt und in der Diastole zusammenfällt. In die Studie wurden 166 Patienten mit P-MAIVF, darunter 8 Fälle aus der Klinik der Autoren und 158 Fälle aus der Literatur, aufgenommen. Oft geht ein P-MAIVF mit einer Infektion oder einem chirurgischen Trauma einher. Es ist zwar wahrscheinlich, dass der Verlauf asymptomatisch ist, aber Symptome wie Luftnot, Herzinsuffizienz, Herzklappenerkrankungen, Schmerzen in der Brust, Endokarditis und zerebrovaskuläre Ereignisse sind häufige klinische Zeichen. Zumeist wird die chirurgische Behandlung empfohlen. Die konservative Therapie ist jedoch ein alternativer Ansatz für Hochrisikopatienten oder in Fällen, in denen die Operation abgelehnt wird. Mit Zunahme der Häufigkeit von Herzoperationen und infektiöser Endokarditis ist auch von einem Anstieg der neuen Diagnose des Pseudoaneurysmas auszugehen.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LVOT:
-
Left ventricular outflow tract
- MAIVF:
-
Mitral–aortic intervalvular fibrosa
- P-MAIVF:
-
Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral–aortic intervalvular fibrosa
- TEE:
-
Transesophageal echocardiography
- TTE:
-
Transthoracic echocardiography
References
Gin A, Hong H, Rosenblatt A et al (2011) Pseudoaneurysms of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa: survival without reoperation. Am Heart J 161(1):130 e1–e5
Kassim TA, Lowery RC, Nasur A et al (2010) Pseudoaneurysm of mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa: two case reports and review of literature. Eur J Echocardiogr 11(3):E7
Kunavarapu C, Olkovsky Y, Lafferty JC et al (2008) Unusual cardiac complications of Staphylococcus aureus endocarditis. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 21(2):187 e3–e5
Penugonda N, Duncan K, Afonso L (2007) Complex endocarditis in an immunocompromised host: the role of three-dimensional echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 20(11):1314 e9–e11
Ashmeik K, Pai RG (2000) An unusual case of acquired ventricular septal defect as a complication of aortic valve endocarditis: echocardiographic delineation of multiple subvalvular complications in one patient. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 13(7):693–695
Cheong YM, Hamer AW, Johns JA (1997) Mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa pseudoaneurysm complicating aortic valve endocarditis. Aust N Z J Med 27(2):193–194
Bansal RC, Graham BM, Jutzy KR et al (1990) Left ventricular outflow tract to left atrial communication secondary to rupture of mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa in infective endocarditis: diagnosis by transesophageal echocardiography and color flow imaging. J Am Coll Cardiol 15(2):499–504
Sadat K, Joshi D, Sudhakar S et al (2012) Incremental role of three-dimensional transesophageal echocardiography in the assessment of mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa abscess. Echocardiography 29(6):742–744
Schaap J, Brinkman EB, Heijmen RH (2011) Left ventricular outflow tract pseudoaneurysm compromising blood flow through the left main coronary artery after mechanical aortic valve implantation. Eur Heart J 32(12):1508
Koch R, Kapoor A, Spencer KT (2003) Stroke in patient with an intervalvular fibrosa pseudoaneurysm and aortic pseudoaneurysm. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 16(8):894–896
Moaref A, Shahrzad S, Aslani A (2009) Acquired aortoventricular tunnel: a rare complication of infective endocarditis. Echocardiography 26(1):82–83
Berrizbeitia LD, Anderson WA (1997) Ultrafast computed tomography in infectious pseudoaneurysm of the left ventricular outflow tract. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 114(1):138–139
Lastowiecka E, Biederman A, Szajewski T, Rydlewska-Sadowska W (2002) The rupture of periaortic infective aneurysm into the left atrium and the left ventricular outflow tract: preoperative diagnosis by transthoracic echocardiography. Echocardiography 19(3):173–176
Leung DY, Cranney GB, Hopkins AP, Walsh WF (1994) Role of transoesophageal echocardiography in the diagnosis and management of aortic root abscess. Br Heart J 72(2):175–181
Malvindi PG, Ornaghi D, Tarelli G, Raffa GM (2012) Left ventricular pseudoaneurysm following aortic valve prosthesis endocarditis. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 13(7):457–459
Sudhakar S, Sewani A, Agrawal M, Uretsky BF (2010) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa (MAIVF): a comprehensive review. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 23(10):1009–1018
Karalis DG, Bansal RC, Hauck AJ et al (1992) Transesophageal echocardiographic recognition of subaortic complications in aortic valve endocarditis. Clinical and surgical implications. Circulation 86(2):353–362
Dores H, Abecasis J, Ribeiras R et al (2012) Uncommon acquired Gerbode defect following extensive bicuspid aortic valve endocarditis. Cardiovasc Ultrasound 10:7
Takimoto K, Arai F, Kita T, Sasaki S (2010) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa on a native aortic valve following infective endocarditis. J Anesth 24(2):260–263
Tak T (2003) Pseudoaneurysm of mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Clin Med Res 1(1):49–52
Parashara DK, Jacobs LE, Kotler MN et al (1995) Angina caused by systolic compression of the left coronary artery as a result of pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Am Heart J 129(2):417–421
Perelman MJ, Sugimoto J, Arcilla RA, Karp RB (1989) Aortic root replacement for complicated bacterial endocarditis in an infant. J Pediatr Surg 24(11):1121–1123
Frank MW, Mavroudis C, Backer CL, Rocchini AP (1998) Repair of mitral valve and subaortic mycotic aneurysm in a child with endocarditis. Ann Thorac Surg 65(6):1788–1790
Caselli S, Mazzesi G, Tritapepe L et al (2011) 3D echocardiographic delineation of mitral-aortic intervalular fibrosa pseudoaneurysm caused by bicuspid aortic valve endocarditis. Echocardiography 28(1):E1–E4
Layman TE, January LE (1967) Mycotic left ventricular aneurysm involving the fibrous atrioventricular body. Am J Cardiol 20(3):423–427
Sharifkazemi MB, Moarref AR, Rezaian S, Rezaian GR (2013) Brucella endocarditis of pseudoaneurysm of an aortic composite graft. J Cardiovasc Ultrasound 21(4):183–185
Gorselen E van, Nihoyannopoulos P, Verhorst P et al (2011) Severe regurgitation due to perforation of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa 3 years after aortic valve replacement. Eur J Echocardiogr 12(4):E30
Araujo IR, Nunes Mdo C, Gelape CL et al (2012) Challenge in the management of infective endocarditis with multiple valvular involvement. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 45(2):272–274
Grimaldi A, Ho SY, Pozzoli A et al (2011) Pseudoaneurysm of mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 13(2):142–147
Velibey Y, Güngör B, Bolca O (2013) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa and complementary role of 3D transesophageal echocardiographic imaging. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg 13(8):E-44
Muller H, Cikirikcioglu M, Lerch R (2008) Subaortic aneurysm caused by Paecilomyces lilacinus endocarditis. Arch Cardiovasc Dis 101(11–12):803–804
Bansal RC, Moloney PM, Marsa RJ, Jacobson JG (1983) Echocardiographic features of a mycotic aneurysm of the left ventricular outflow tract caused by perforation of mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Circulation 67(4):930–934
Xie M, Li Y, Cheng TO et al (2013) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Int J Cardiol 166(1):2–7
Panneerselvam A, Subbiahnadar P (2011) Ruptured mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa aneurysm with flail aortic valve. BMJ Case Rep
Selcuk H, Selcuk MT, Tufekcioglu O, Arat N (2009) The use of three-dimensional echocardiography in the visualization of pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars 37(5):328–331
Ghersin E, Litmanovich D, Agmon Y, Milo S (2005) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa following aortic valve replacement—diagnosis and dynamic evaluation with multidetector CT and transesophageal echocardiography. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 4(6):502–504
Yokoyama Y, Tamaki S, Kato N et al (2003) Pseudoaneurysm from the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa following endocarditis. Jpn J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 51(8):374–377
Griffiths BE, Petch MC, English TA (1982) Echocardiographic detection of subvalvar aortic root aneurysm extending to mitral valve annulus as complication of aortic valve endocarditis. Br Heart J 47(4):392–396
Pai RG, Ortega V, Ferry DR (1995) A case of mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa aneurysm with unique flow patterns and long-term natural survival. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 8(2):211–214
Pirat B, Buergler J, Zoghbi WA (2005) Echocardiographic features of pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic inter-valvular fibrosa. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg 5(4):344–345
Takamiya Y, Miura S, Sako H et al (2007) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa following infective endocarditis in a patient with acute heart failure: a case report. J Cardiol 49(6):353–356
Garneau S, Demers P, Denault AY (2007) Unexpected periaortic cavity during heart surgery. Anesth Analg 104(1):75–76
Hori D, Tanaka M, Yamaguchi A et al (2008) Extracardiac aneurysm of the interleaflet triangle above the aortic-mitral curtain due to infective endocarditis of the bicuspid aortic valve. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 56(8):424–426
Saint-Martin P, Rogers C, Carpenter E et al (2009) Subaortic pseudoaneurysm of the left ventricle complicating staphylococcal endocarditis. J Forensic Sci 54(4):930–932
Sogabe O, Ohya T (2007) A case of tuberculous endocarditis with acute aortic valve insufficiency and annular subvalvular left ventricular aneurysm. Gen Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 55(2):61–64
Afridi I, Apostolidou MA, Saad RM, Zoghbi WA (1995) Pseudoaneurysms of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa: dynamic characterization using transesophageal echocardiographic and Doppler techniques. J Am Coll Cardiol 25(1):137–145
Gelehrter S, Wright G, Gless T et al (2002) Left ventricular outflow tract pseudoaneurysms in congenital heart disease. Am J Cardiol 90(7):806–809
Malcles G, Azarnoush K, Ravan R et al (2011) Pseudo-aneurysm of mitro-aortic continuity: a rare complication after aortic valve replacement. Ann Cardiol Angeiol (Paris) 60(5):296–299
Kahveci G, Keles N, Bayrak F, Mutlu B (2008) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa after aortic valve replacement. Turk Kardiyol Dern Ars 36(7):499
Ivens EL, Thompson CR, Moss RR et al (2008) Images in cardiovascular medicine: prosthetic aortic valve and conduit dehiscence with large periconduit cavity, ascending aortic aneurysm and severe mitral regurgitation. Eur J Echocardiogr 9(1):148–151
Espinosa-Caliani JS, Montijano A, Melero JM, Montiel A (2000) Pseudoaneurysm in the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. A cause of mitral regurgitation. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 17(6):757–759
Tiwari KK, Murzi M, Mariani M, Glauber M (2009) Giant pseudo-aneurysm of the left ventricle outflow tract after aortic root replacement for extensive endocarditis. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 36(2):399
Turiel M, Gottardi B, Muzzupappa S (2001) A case of subannular aortic aneurysm detected by transoesophageal echocardiography. Acta Cardiol 56(6):395–397
Aikat S, Lundergan CF, Adkins MS, Lewis JF (2003) Delayed presentation of left ventricular outflow tract aneurysm after penetrating cardiac trauma. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 16(10):1085–1087
Kruithoff WA, Akl BF, Blacky AR (1995) Surgical repair of an anterior mitral subvalvular aneurysm. Ann Thorac Surg 59(4):1001–1003
Harish A, Hatibu S, Ramkumar SR et al (2009) Aneurysm of mitral aortic intervalvular fibrosa—a case report and review. Indian Heart J 61(4):394–396
Moorthy N, Kumar S, Tewari S et al (2012) Mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa aneurysm with rupture into left atrium: an uncommon cause of acute dyspnea. Heart Views 13(1):13–15
Lurie AO (1960) Left ventricular aneurysm in the African. Br Heart J 22:181–188
Acioli Pereira L, Fontes Gontijo P, Alcantara Farran J et al (2013) Giant pseudoaneurysm of the left ventricular outflow tract: a rare disease. Rev Port Cardiol 32(6):541–544
Parakh N, Yadav N, Kathuria S et al (2013) Pseudo-aneurysm of mitral aortic intervalvular fibrosa: two case reports. Indian Heart J 65(1):100–103
Hasin T, Reisner SA, Agmon Y (2011) Large pseudoaneurysms of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa: long-term natural history without surgery in two patients. Eur J Echocardiogr 12(3):E24
Kim HW, Chung CH (2010) Mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa pseudoaneurysm resulting in the displacement of the left main coronary artery after aortic valve replacement. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 139(2):e18–e20
Rodrigues Borges AG, Suresh K, Mirza H et al (2002) False aneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa after uncomplicated aortic valve replacement. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 15(7):743–745
Antonellis J, Kostopoulos K, Routoulas T et al (1997) Aneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa as a rare cause of angina pectoris: angiographic demonstration. Cathet Cardiovasc Diagn 42(4):423–426
Romaguera R, Slack MC, Waksman R et al (2010) IMAGE CARDIO MED: Percutaneous closure of a left ventricular outflow tract pseudoaneurysm causing extrinsic left coronary artery compression by transseptal approach. Circulation 121(4):e20–e22
Turkvatan A, Demirkan B, Guray Y (2011) Multidetector computed tomographic angiography diagnosis of a giant pseudoaneurysm of the left ventricular outflow tract. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg 39(3):e30
Almeida J, Pinho P, Torres JP et al (2002) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic fibrosa: myocardial ischemia secondary to left coronary compression. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 15(1):96–98
Aoyagi S, Fukunaga S, Otsuka H et al (2004) Left ventricular outflow tract pseudoaneurysm after aortic valve replacement: case report. J Heart Valve Dis 13(1):145–148
Linhartova K, Veselka J, Adla T (2007) Left ventricular pseudoaneurysm as a late complication of mitral annuloplasty. Eur Heart J 28(19):2360
Jaggers J, Fullerton DA, Campbell DN, Clarke DR (1996) LVOT pseudoaneurysm: a late complication of extended aortic root replacement. Ann Thorac Surg 62(4):1198–1199
Tsai IC, Hsieh SR, Chern MS et al (2009) Pseudoaneurysm in the left ventricular outflow tract after prosthetic aortic valve implantation: evaluation upon multidetector-row computed tomography. Tex Heart Inst J 36(5):428–432
Joshi SS, Jagadeesh AM, Furtado A, Bhat S (2013) Transesophageal echocardiography in surgical management of pseudoaneurysm of mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa with aneurysms of right sinus of Valsalva and left main coronary artery. Ann Card Anaesth 16(1):40–43
Tsai IC, Fu YC, Lin PC et al (2009) MDCT evaluation of congenital mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa aneurysm: implications for the aetiology and differential diagnosis. Pediatr Radiol 39(1):80–83
Tufekcioglu O, Ozlu MF, Cay S et al (2008) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa in a patient with Takayasu’s arteritis. Can J Cardiol 24(9):718
Gupta R, Jammula P, Huang MH et al (2006) An unusual complication after aortic valve replacement. J Clin Ultrasound 34(7):361–364
Yamamoto S, Tedoriya T, Masuda Z et al (2006) Mitral-aortic intervalvular pseudoaneurysm with ventricular septal defect. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann 14(2):e35–e37
Jimenez Valero S, Garcia E, Gonzalez Pinto A, Delcan JL (2005) Percutaneous closure of pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Rev Esp Cardiol 58(12):1473–1475
Gungor B, Altay S, Dayi SU, Bolca O (2012) 3D echocardiographic evaluation of ruptured pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg 12(8):E42–E43
Normann SJ (1991) Annular subaortic aneurysm resulting in sudden death. Clin Cardiol 14(1):68–72
Dogan M, Vural MG, Turkvatan A, Yeter E (2012) Incidentally diagnosed pseudoaneurysm of mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Anadolu Kardiyol Derg 12(8):E41–E42
Barranhas AD, Dias MC, Dos Santos AA et al (2012) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa presenting after chest trauma and diagnosed by cardiac magnetic resonance: a case report. J Med Case Rep 6(1):357
Spampinato RA, Borger MA, Strotdrees E, Mohr FW (2013) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa as a complication after minimally invasive mitral valve repair. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 16(3):396–398
Choh NA, Shaheen F, Rather H, Aslam K (2013) Pseudoaneurysm of mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa in a child: Demonstration by MDCT and MRI. Ann Pediatr Cardiol 6(1):80–82
Agirbasli M, Fadel BM (1999) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa: a long-term complication of infective endocarditis. Echocardiography 16(3):253–257
Matthews RV, French WJ, Criley JM (1989) Chest trauma and subvalvular left ventricular aneurysms. Chest 95(2):474–476
Sousa L, Branco L, Abreu J et al (1999) A pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosis after aortic valve replacement. Rey Port Cardiol 18(2):177–178
Da Col U, Ramoni E, Di Bella I, Ragni T (2009) An unusual left ventricular outflow pseudoaneurysm: usefulness of echocardiography and multidetector computed tomography for surgical repair. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32(1):188–191
Entrikin DW, Shroff GS, Kon ND, Carr JJ (2011) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa: a delayed complication of aortic root replacement. J Cardiovasc Comput Tomogr 5(5):333–335
Winkler ML, Higgins CB (1986) MRI of perivalvular infectious pseudoaneurysms. AJR Am J Roentgenol 147(2):253–256
Robles P, Sonlleva A (2007) Aneurysm of the intervalvular mitroaortic fibrosa after aortic valve replacement diagnosed by cardiovascular magnetic resonance imaging. Intern Med 46(21):1825
Bolcal C, Baysan O, Doganci S et al (2007) A mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa false aneurysm in a patient without overt heart disease. Can J Cardiol 23(5):389–390
Goldfarb B, Rovner M, Goldbraich N (1997) Pseudoaneurysm of the left ventricular outflow tract with reentry into the ascending aorta: an iatrogenic left ventricular ascending aortic fistula. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 10(8):866–868
Ueno T, Sakata R, Iguro Y, Yamamoto H (2008) Intervalvular fibrosa pseudoaneurysm with projectile shunt flow to left atrium. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg 7(4):727–729
Strauch JT, Wippermann J, Krep H, Wahlers T (2008) Subannular perforation after long-lasting aortic valve replacement mimicking mitral insufficiency. Ann Thorac Surg 85(1):311–313
Economopoulos G (2007) Delayed pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Ann Thorac Surg 83(6):2233
Han J, He Y, Li Z et al (2009) Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa in a patient after radio frequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. J Ultrasound Med 28(2):249–251
Pongratz G, Pohlmann M, Gehling G, Bachmann K (1997) Images in cardiovascular medicine. Pseudoaneurysm in the intervalvular mitral-aortic region after endocarditis and prosthetic aortic valve replacement. Circulation 96(9):3241–3242
Dawson D, Pessotto R, Neary P (2009) Inter-valvular fibrosa pseudo-aneurysm as a late complication after aortic valve surgery. Eur J Echocardiogr 10(1):169–170
Salerno D, Donati G, Forconi S, Gori T (2008) Giant pseudoaneurysm of the mitro-aortic intervalvular fibrosa: incidental diagnosis. Intern Emerg Med 3(3):279–282
Frary G, Hasselman T, Patel P (2012) Atypical left ventricular outflow tract aneurysm diagnosed by three-dimensional echocardiography. Cardiol Young 22(4):478–480
Kahveci G, Yilmaz F, Mutlu B (2008) Bicuspid aortic valve endocarditis complicated with aortic valve aneurysm and pseudoaneurysm of the mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Echocardiography 25(7):799–801
Ekici F, Kocabas A, Aktas D et al (2014) Native aortic valve endocarditis complicated by pseudoaneurysm of mitral-aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Echocardiography 31(2):60–63
Silbiger JJ, Krasner A, Chikwe J et al (2013) Pseudoaneurysm formation in infective endocarditis. Echocardiography 30(10):319–321
Chandra S, Ameta D, Kharwar RB et al (2013) Three-dimensional echocardiographic delineation of an acquired aorto-left atrial fistula complicating native aortic valve endocarditis—”advantage of three dimensions”. Echocardiography 30(10):326–330
Compliance with ethical guidelines
Conflict of interest. E. Şahan, M. Gül, S. Şahan, E. Sokmen, Y.A. Guray, and O. Tufekçioglu state that there are no conflicts of interest. The accompanying manuscript does not include studies on humans or animals.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Additional material online: This article includes an additional Table. You will find this supplemental at dx.doi.org/10.1007/s00059-014-4185-z.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şahan, E., Gül, M., Şahan, S. et al. Pseudoaneurysm of the mitral–aortic intervalvular fibrosa. Herz 40 (Suppl 2), 182–189 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00059-014-4185-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00059-014-4185-z
Keywords
- Pseudoaneurysm
- Mitral–aortic intervalvular fibrosa
- Transthoracic echocardiography
- Transesophageal echocardiography
- Therapy