Abstract
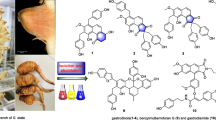
Phytochemical investigation on the fruits of Gleditsia aquatica resulted in the isolation and identification of two new bisdesmosidic triterpenoidal saponins, aquaticasaponin A (1) and aquaticasaponin B (2) acylated with two and one monoterpenic acids, respectively, and one known cytokinin, aquaticine C (3). The structural elucidation of isolated metabolites was established on the basis of 1D, 2D NMR, and MS spectral analyses. The antimicrobial activity of the isolated compounds [1–3] was evaluated. Compound 1 exhibited the highest degree of activity against Syncephalastrum racemosum with an MIC value of 9.2 μM, whereas compound 2 exhibited the highest degree of activity against Escherichia coli with an MIC value of 67.3 μM. The isolated compounds also exhibited good cytotoxic activity against human breast cancer (MCF-7) and human colon cancer (HCT-116) cell lines with values of IC50 from 0.5 to 1.0 μM. Compound 1 was found to be the most active against colon cancer HCT-116 cell line with IC50 value of 0.5 μM.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akai E, Takeda T, Kobayashi Y, Ogihara Y (1985) Sulfated triterpenoid saponins from the leaves of Bupleurum rotundfolium L. Chem Pharm Bull 33:3715–3723
Gorin PAJ, Mazurek M (1975) Further studies on the assignment of signals in 13C magnetic resonance spectra of aldoses and derived methyl glycosides. Can J Chem 53:1212–1223
Hosny M, Ragab EA, Mohammed AI, Shaheen UY (2009) Isolation and structure identification of new cytokinins from Gleditsia caspia. Arkivoc xiv:109–117
Maillard M, Adewunmi CO, Hostettmann K (1992) A triterpene glycoside from the fruits of Tetrapleura tetraptera. Phytochemistry 31:1321–1323
Mosmann T (1983) Rapid colorimetric assay for cellular growth and survival: application to proliferation and cytotoxicity assays. J Immunol Methods 65:55–63
Okada Y, Koyama K, Takahashi K, Okuyama T, Shibata S (1980) Structures of monoterpene moieties of gleditsia saponin C. Planta Med 40:185–192
Overend WG (1972) Glycosides. In: Pigman W, Horton D (eds) The carbohydrates-chemistry and biochemistry, Academic Press, New York, pp 308–309
Ragab EA, Hosny M, Kadry HA, Ammar HA (2010) Acylated triterpenoidal saponins and cytokinins from Gleditsia aquatica. JPP 2:24–33
Rajbhandari M, Schopke T (1999) Antimicrobial activity of some Nepalese medicinal plants. Pharmazie 54:232–233
Scott AC (1989) Laboratory control of antimicrobial therapy. In: Collee JG, Duguid JP, Fraser AG, Marmion BP (eds) Practical medical microbiology, 13th edn. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 161–181
Woodson RR (1987) Statistical methods for the analysis of biochemical data. Series in probability and mathematical statistics. Wiley, New York, pp 315–316
Zang Z, Koike K, Jia Z, Nikaido T, Guo D, Zheng J (1999a) Four new triterpenoidal saponins acylated with one monoterpenic acid from Gleditsia sinensis. J Nat Prod 62:740–745
Zang Z, Koike K, Jia Z, Nikaido T, Guo D, Zheng J (1999b) Triterpenoidal saponins acylated with two monoterpenic acids from Gleditsia sinensis. Chem Pharm Bull 47:388–393
Zang Z, Koike K, Jia Z, Nikaido T, Guo D, Zheng J (1999c) Gleditsiosides N–Q, new triterpenoid saponins from Gleditsia sinensis. J Nat Prod 62:877–881
Zang Z, Koike K, Jia Z, Nikaido T, Guo D, Zheng J (1999d) Triterpenoidal saponins from Gleditsia sinensis. Phytochemistry 52:715–722
Zhong Y, Dian DC (1977) Jiangsu New Medical College. Shanghai People’s Public Health Publishing House: Shanghai 1144–1147, 2198
Acknowledgments
Many thanks are due to Dr. Mohammed Hosny, Professor of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt and Dr. Ehab M. Mostafa, Lecturer of Pharmacognosy, Faculty of Pharmacy, Al-Azhar University, Cairo, Egypt, for 2D NMR and Ms Facilities.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ragab, E.A. New antimicrobial and cytotoxic acylated triterpenoidal saponins from Gleditsia aquatica . Med Chem Res 24, 2916–2925 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-015-1345-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-015-1345-5