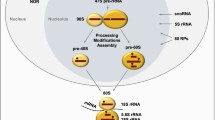
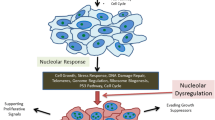
Abstract
Changes in nucleolar morphology and function are tightly associated with cellular activity, such as growth, proliferation, and cell cycle progression. Historically, these relationships have been extensively examined in cancer cells, which frequently exhibit large nucleoli and increased ribosome biogenesis. Recent findings indicate that alteration of nucleolar activity is a key regulator of development and aging. In this review, we have provided evidences that the nucleolus is not just a housekeeping factor but is actively involved in the regulation of cell proliferation, differentiation, and senescence both in vitro and in vivo. In addition, we have discussed how alteration of nucleolar function and nucleolar proteins induces specific physiological effects rather than widespread effects.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Abbreviations
- ES cells:
-
Embryonic stem cells
- pre-rRNA:
-
Precursor ribosomal RNA
- Pol I:
-
RNApolymerase I
- rDNA:
-
Ribosomal DNA
- snoRNPs:
-
Small nucleolar ribonucleoprotein particles
- TIF-IA:
-
Transcription initiation factor IA
- UBF:
-
Upstream binding factor
References
Boulon S, Westman BJ, Hutten S et al (2010) The nucleolus under stress. Mol Cell 40:216–227. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2010.09.024
van Sluis M, McStay B (2014) Ribosome biogenesis: achilles heel of cancer? Genes Cancer 12:710–716. doi:10.1016/j.coph.2012.06.011
Derenzini M, Trere D, Pession A et al (1998) Nucleolar function and size in cancer cells. Am J Pathol 152:1291–1297
Montanaro L, Treré D, Derenzini M (2008) Nucleolus, ribosomes, and cancer. Am J Pathol 173:301–310. doi:10.2353/ajpath.2008.070752
Hein N, Hannan KM, George AJ et al (2013) The nucleolus: an emerging target for cancer therapy. Trends Mol Med 19:643–654. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2013.07.005
Naora H, Takai I, Adachi M et al (1998) Altered cellular responses by varying expression of a ribosomal protein gene: sequential coordination of enhancement and suppression of ribosomal protein S3a gene expression induces apoptosis. J Cell Biol 141:741–753. doi:10.1083/jcb.141.3.741
Kim J-H, You K-R, Kim IH et al (2004) Over-expression of the ribosomal protein L36a gene is associated with cellular proliferation in hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 39:129–138. doi:10.1002/hep.20017
Fichelson P, Moch C, Ivanovitch K et al (2009) Live-imaging of single stem cells within their niche reveals that a U3snoRNP component segregates asymmetrically and is required for self-renewal in Drosophila. Nat Cell Biol 11:685–693. doi:10.1038/ncb1874
Zhang Q, Shalaby NA, Buszczak M (2014) Changes in rRNA transcription influence proliferation and cell fate within a stem cell lineage. Science 343:298–301. doi:10.1126/science.1246384
Hayashi Y, Kuroda T, Kishimoto H et al (2014) Downregulation of rRNA transcription triggers cell differentiation. PLoS ONE 9:e98586. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0098586
Watanabe-Susaki K, Takada H, Enomoto K et al (2014) Biosynthesis of ribosomal RNA in nucleoli regulates pluripotency and differentiation ability of pluripotent stem cells. Stem Cells 32:3099–3111. doi:10.1002/stem.1825
Hansen M, Taubert S, Crawford D et al (2007) Lifespan extension by conditions that inhibit translation in Caenorhabditis elegans. Aging Cell 6:95–110. doi:10.1111/j.1474-9726.2006.00267.x
Steffen KK, MacKay VL, Kerr EO et al (2008) Yeast life span extension by depletion of 60S ribosomal subunits is mediated by Gcn4. Cell 133:292–302. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.037
Kim Y-I, Bandyopadhyay J, Cho I et al (2014) Nucleolar GTPase NOG-1 regulates development, fat storage, and longevity through insulin/IGF signaling in C. elegans. Mol Cells 37:51–58. doi:10.14348/molcells.2014.2251
Dai M-S, Lu H (2008) Crosstalk between c-Myc and ribosome in ribosomal biogenesis and cancer. J Cell Biochem 105:670–677. doi:10.1002/jcb.21895
Gomez-Roman N, Grandori C, Eisenman RN, White RJ (2003) Direct activation of RNA polymerase III transcription by c-Myc. Nature 421:290–294. doi:10.1038/nature01327
Hannan KM, Sanij E, Hein N et al (2011) Signaling to the ribosome in cancer-It is more than just mTORC1. IUBMB Life 63:79–85. doi:10.1002/iub.428
Mayer C, Grummt I (2006) Ribosome biogenesis and cell growth: mTOR coordinates transcription by all three classes of nuclear RNA polymerases. Oncogene 25:6384–6391. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1209883
Zhai W, Comai L (2000) Repression of RNA polymerase I transcription by the tumor suppressor p53. Mol Cell Biol 20:5930–5938. doi:10.1128/MCB.20.16.5930-5938.2000
Voit R, Schäfer K, Grummt I (1997) Mechanism of repression of RNA polymerase I transcription by the retinoblastoma protein. Mol Cell Biol 17:4230–4237
Ghoshal K (2003) Role of human ribosomal RNA (rRNA) promoter methylation and of methyl-CpG-binding protein MBD2 in the suppression of rRNA gene expression. J Biol Chem 279:6783–6793. doi:10.1074/jbc.M309393200
Henry JL, Coggin DL, King CR (1993) High-level expression of the ribosomal protein L19 in human breast tumors that overexpress erbB-2. Cancer Res 53:1403–1408
Vaarala MH, Porvari KS, Kyllönen AP et al (1998) Several genes encoding ribosomal proteins are over-expressed in prostate-cancer cell lines: confirmation of L7a and L37 over-expression in prostate-cancer tissue samples. Int J Cancer 78:27–32. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-0215(19980925)78:1<27:AID-IJC6>3.0.CO;2-Z
Wang Q, Yang C, Zhou J et al (2001) Cloning and characterization of full-length human ribosomal protein L15 cDNA which was overexpressed in esophageal cancer. Gene 263:205–209. doi:10.1016/S0378-1119(00)00570-9
Choesmel V, Bacqueville D, Rouquette J et al (2006) Impaired ribosome biogenesis in Diamond-Blackfan anemia. Blood 109:1275–1283. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-07-038372
Shenoy N, Kessel R, Bhagat TD et al (2012) Alterations in the ribosomal machinery in cancer and hematologic disorders. J Hematol Oncol 5:32. doi:10.1186/1756-8722-5-32
Ebert BL, Pretz J, Bosco J et al (2008) Identification of RPS14 as a 5q- syndrome gene by RNA interference screen. Nature 451:335–339. doi:10.1038/nature06494
Knight SW, Heiss NS, Vulliamy TJ et al (1999) X-linked dyskeratosis congenita is predominantly caused by missense mutations in the DKC1 gene. Am J Hum Genet 65:50–58. doi:10.1086/302446
He J, Navarrete S, Jasinski M et al (2002) Targeted disruption of Dkc1, the gene mutated in X-linked dyskeratosis congenita, causes embryonic lethality in mice. Oncogene 21:7740–7744. doi:10.1038/sj.onc
Ridanpää M, van Eenennaam H, Pelin K, Chadwick R (2001) Mutations in the RNA component of RNase MRP cause a pleiotropic human disease, cartilage-hair hypoplasia. Cell 104:195–203. doi:10.1016/S0092-8674(01)00205-7
Zhang Y, Lu H (2009) Signaling to p53: ribosomal proteins find their way. Cancer Cell 16:369–377. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.09.024
Mayer C, Grummt I (2014) Cellular stress and nucleolar function. Cell Cycle 4:1036–1038. doi:10.4161/cc.4.8.1925
Hein N, Ganley A, Sanij E, et al. (2012) The nucleolus and ribosomal genes in aging and senescence. InTech. doi:10.5772/34581. ISBN: 978-935051-0144-4
Lim MJ, Wang XW (2006) Nucleophosmin and human cancer. Cancer Detect Prev 30:481–490. doi:10.1016/j.cdp.2006.10.008
Di Fiore PP (2008) Playing both sides: nucleophosmin between tumor suppression and oncogenesis. J Cell Biol 182:7–9. doi:10.1083/jcb.200806069
Falini B, Mecucci C, Tiacci E et al (2005) Cytoplasmic nucleophosmin in acute myelogenous leukemia with a normal karyotype. N Engl J Med 352:254–266. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa041974
Colombo E (2006) Delocalization and destabilization of the Arf tumor suppressor by the leukemia-associated NPM mutant. Cancer Res 66:3044–3050. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-2378
Grisendi S, Bernardi R, Rossi M et al (2005) Role of nucleophosmin in embryonic development and tumorigenesis. Nature 437:147–153. doi:10.1038/nature03915
Bertwistle D, Sugimoto M, Sherr CJ (2004) Physical and functional interactions of the Arf tumor suppressor protein with nucleophosmin/B23. Mol Cell Biol 24:985–996. doi:10.1128/MCB.24.3.985-996.2004
Kondo T, Minamino N, Nagamura-Inoue T et al (1997) Identification and characterization of nucleophosmin/B23/numatrin which binds the anti-oncogenic transcription factor IRF-1 and manifests oncogenic activity. Oncogene 15:1275–1281. doi:10.1038/sj.onc.1201286
Pederson T, Tsai RYL (2009) In search of nonribosomal nucleolar protein function and regulation. J Cell Biol 184:771–776. doi:10.1083/jcb.200812014
Okamoto N, Yasukawa M, Nguyen C et al (2011) Maintenance of tumor initiating cells of defined genetic composition by nucleostemin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:20388–20393. doi:10.1073/pnas.1015171108
Meshorer E, Misteli T (2006) Chromatin in pluripotent embryonic stem cells and differentiation. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 7:540–546. doi:10.1038/nrm1938
Baker NE (2013) Developmental regulation of nucleolus size during Drosophila eye differentiation. PLoS ONE 8:e58266. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0058266
Poortinga G, Wall M, Sanij E et al (2011) c-MYC coordinately regulates ribosomal gene chromatin remodeling and Pol I availability during granulocyte differentiation. Nucleic Acids Res 39:3267–3281. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq1205
Ali SA, Zaidi SK, Dacwag CS et al (2008) Phenotypic transcription factors epigenetically mediate cell growth control. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:6632–6637. doi:10.1073/pnas.0800970105
Yang A, Shi G, Zhou C et al (2011) Nucleolin maintains embryonic stem cell self-renewal by suppression of p53 protein-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 286:43370–43382. doi:10.1074/jbc.M111.225185
Qu J, Bishop JM (2012) Nucleostemin maintains self-renewal of embryonic stem cells and promotes reprogramming of somatic cells to pluripotency. J Cell Biol 197:731–745. doi:10.1083/jcb.201103071
Rosby R, Cui Z, Rogers E, Robinson VL (2009) Knockdown of the Drosophila GTPase nucleostemin 1 impairs large ribosomal subunit biogenesis, cell growth, and midgut precursor cell maintenance. Mol Biol Cell 20:4424–4434. doi:10.1091/mbc.E08
McCain J, Danzy L, Hamdi A et al (2005) Tracking nucleolar dynamics with GFP-Nopp140 during Drosophila oogenesis and embryogenesis. Cell Tissue Res 323:105–115. doi:10.1007/s00441-005-0044-9
James A, Cindass R Jr, Mayer D et al (2014) Nucleolar stress in Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleus 4:123–133. doi:10.4161/nucl.23944
Qin W, Chen Z, Zhang Y et al (2014) Nom1 mediates pancreas development by regulating ribosome biogenesis in zebrafish. PLoS One 9:e100796. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0100796
Grewal SS, Li L, Orian A et al (2005) Myc-dependent regulation of ribosomal RNA synthesis during Drosophila development. Nat Cell Biol 7:295–302. doi:10.1038/ncb1223
Demontis F, Perrimon N (2009) Integration of insulin receptor/Foxo signaling and dMyc activity during muscle growth regulates body size in Drosophila. Development 136:983–993. doi:10.1242/dev.027466
Grewal SS, Evans JR, Edgar BA (2007) Drosophila TIF-IA is required for ribosome synthesis and cell growth and is regulated by the TOR pathway. J Cell Biol 179:1105–1113. doi:10.1083/jcb.200709044
Guarente L (1997) Link between aging and the nucleolus. Genes Dev 11:2449–2455. doi:10.1101/gad.11.19.2449
Smith JS, Brachmann CB, Pillus L, Boeke JD (1998) Distribution of a limited Sir2 protein pool regulates the strength of yeast rDNA silencing and is modulated by Sir4p. Genetics 149:1205–1219
Machín F, Paschos K, Jarmuz A et al (2004) Condensin regulates rDNA silencing by modulating nucleolar Sir2p. Curr Biol 14:125–130. doi:10.1016/j.cub.2004.01.001
Guarente L (1999) Diverse and dynamic functions of the Sir silencing complex. Nat Genet 23:281–285. doi:10.1038/15458
Murayama A, Ohmori K, Fujimura A et al (2008) Epigenetic control of rDNA loci in response to intracellular energy status. Cell 133:627–639. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2008.03.030
Yang L, Song T, Chen L et al (2013) Regulation of SirT1-nucleomethylin binding by rRNA coordinates ribosome biogenesis with nutrient availability. Mol Cell Biol 33:3835–3848. doi:10.1128/MCB.00476-13
Evans DS, Kapahi P, Hsueh W-C, Kockel L (2011) TOR signaling never gets old: aging, longevity and TORC1 activity. Ageing Res Rev 10:225–237. doi:10.1016/j.arr.2010.04.001
Martin DE, Powers T, Hall MN (2006) Regulation of ribosome biogenesis: where is TOR? Cell Metab 4:259–260. doi:10.1016/j.cmet.2006.09.002
Demontis F, Patel VK, Swindell WR, Perrimon N (2014) Intertissue control of the nucleolus via a myokine-dependent longevity pathway. Cell Rep 7:1481–1494. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2014.05.001
Matheu A, Maraver A, Klatt P et al (2007) Delayed ageing through damage protection by the Arf/p53 pathway. Nature 448:375–379. doi:10.1038/nature05949
Hulbert AJ, Pamplona R, Buffenstein R, Buttemer WA (2007) Life and death: metabolic rate, membrane composition, and life span of animals. Physiol Rev 87:1175–1213. doi:10.1152/physrev.00047.2006
Ping Tang Y, Wade J (2006) Sexually dimorphic expression of the genes encoding ribosomal proteins L17 and L37 in the song control nuclei of juvenile zebra finches. Brain Res 1126:102–108. doi:10.1016/j.brainres.2006.08.002
Wu S, De Croos JNA, Storey KB (2008) Cold acclimation-induced up-regulation of the ribosomal protein L7 gene in the freeze tolerant wood frog, Rana sylvatica. Gene 424:48–55. doi:10.1016/j.gene.2008.07.023
Twiss JL, Smith DS, Chang B, Shooter EM (2000) Translational control of ribosomal protein L4 mRNA is required for rapid neurite regeneration. Neurobiol Dis 7:416–428. doi:10.1006/nbdi.2000.0293
Uechi T, Nakajima Y, Nakao A et al (2006) Ribosomal protein gene knockdown causes developmental defects in zebrafish. PLoS ONE 1:e37. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000037
Zhang Y, Duc A-CE, Rao S et al (2013) Control of hematopoietic stem cell emergence by antagonistic functions of ribosomal protein paralogs. Dev Cell 24:411–425. doi:10.1016/j.devcel.2013.01.018
Komili S, Farny NG, Roth FP, Silver PA (2007) Functional specificity among ribosomal proteins regulates gene expression. Cell 131:557–571. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2007.08.037
Kondrashov N, Pusic A, Stumpf CR et al (2011) Ribosome-mediated specificity in Hox mRNA translation and vertebrate tissue patterning. Cell 145:383–397. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.02
Xue S, Tian S, Fujii K et al (2015) RNA regulons in Hox 5′ UTRs confer ribosome specificity to gene regulation. Nature 517:33–38. doi:10.1038/nature14010
Le Bouteiller M, Souilhol C, Beck-Cormier S et al (2013) Notchless-dependent ribosome synthesis is required for the maintenance of adult hematopoietic stem cells. J Exp Med 210:2351–2369. doi:10.1084/jem.20122019
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Takada, H., Kurisaki, A. Emerging roles of nucleolar and ribosomal proteins in cancer, development, and aging. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 72, 4015–4025 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-1984-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-1984-1