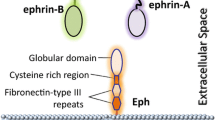
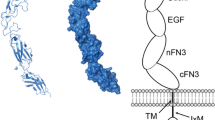
Abstract
The erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular (Eph) receptors comprise the largest family of receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs). Initially regarded as axon-guidance and tissue-patterning molecules, Eph receptors have now been attributed with various functions during development, tissue homeostasis, and disease pathogenesis. Their ligands, ephrins, are synthesized as membrane-associated molecules. At least two properties make this signaling system unique: (1) the signal can be simultaneously transduced in the receptor- and the ligand-expressing cell, (2) the signaling outcome through the same molecules can be opposite depending on cellular context. Moreover, shedding of Eph and ephrin ectodomains as well as ligand-dependent and -independent receptor crosstalk with other RTKs, proteases, and adhesion molecules broadens the repertoire of Eph/ephrin functions. These integrated pathways provide plasticity to cell–microenvironment communication in varying tissue contexts. The complex molecular networks and dynamic cellular outcomes connected to the Eph/ephrin signaling in tumor–host communication and stem cell niche are the main focus of this review.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ADAM:
-
A disintegrin and metalloprotease
- CRC:
-
Colorectal cancer
- CRD:
-
Cysteine-rich domain
- DDR1:
-
Discoidin domain receptor 1
- ECD:
-
Extracellular domain
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- EGF:
-
Epidermal growth factor
- EMT:
-
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
- EPH:
-
Erythropoietin-producing hepatocellular
- FAK:
-
Focal adhesion kinase
- FGF:
-
Fibroblast growth factor
- FN:
-
Fibronectin
- GBM:
-
Glioblastoma multiforme
- GEF:
-
Guanine-nucleotide exchange factor
- GPI:
-
Glycosylphosphatidylinositol
- HGF/SF:
-
Hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor
- JAK:
-
Janus kinase
- LBD:
-
Ligand-binding domain
- MAPK:
-
Mitogen-activated protein kinase
- MDCK:
-
Madin–Darby canine kidney
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase
- MT-MMP:
-
Membrane-type metalloproteinase
- NGF:
-
Nerve growth factor
- PDGF:
-
Platelet-derived growth factor
- PDZ:
-
Postsynaptic density protein PSD95, Drosophila disc large tumor suppressor DlgA, and zonula occludens-1 protein ZO-1
- PI3K:
-
Phosphatidylinositol 3′-kinase
- PTB:
-
Phosphotyrosine binding
- PTPase:
-
Protein tyrosine phosphatases
- RTK:
-
Receptor tyrosine kinase
- SAM:
-
Sterile α motif
- SH2:
-
Src homology 2
- STAT:
-
Signal transducer and activator of transcription
- SVZ:
-
Subventricular zone
- TPC:
-
Tumor-propagating cell
- VEGF:
-
Vascular endothelial growth factor
References
Hirai H, Maru Y, Hagiwara K, Nishida J, Takaku F (1987) A novel putative tyrosine kinase receptor encoded by the eph gene. Science 238:1717–1720
Pasquale EB (2008) Eph-ephrin bidirectional signaling in physiology and disease. Cell 133:38–52
Pasquale EB (2010) Eph receptors and ephrins in cancer: bidirectional signalling and beyond. Nat Rev Cancer 10:165–180
Nievergall E, Lackmann M, Janes PW (2012) Eph-dependent cell–cell adhesion and segregation in development and cancer. Cell Mol Life Sci 69:1813–1842
Wilkinson DG (2001) Multiple roles of EPH receptors and ephrins in neural development. Nat Rev Neurosci 2:155–164
Pitulescu ME, Adams RH (2010) Eph/ephrin molecules—a hub for signaling and endocytosis. Genes Dev 24:2480–2492
Miao H, Wang B (2009) Eph/ephrin signaling in epithelial development and homeostasis. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 41:762–770
Palmer A, Klein R (2003) Multiple roles of ephrins in morphogenesis, neuronal networking, and brain function. Genes Dev 17:1429–1450
Hafner C, Schmitz G, Meyer S, Bataille F, Hau P, Langmann T, Dietmaier W, Landthaler M, Vogt T (2004) Differential gene expression of Eph receptors and ephrins in benign human tissues and cancers. Clin Chem 50:490–499
Binda E, Visioli A, Giani F, Lamorte G, Copetti M, Pitter KL, Huse JT, Cajola L, Zanetti N, DiMeco F, De Filippis L, Mangiola A, Maira G, Anile C, De Bonis P, Reynolds BA, Pasquale EB, Vescovi AL (2012) The EphA2 receptor drives self-renewal and tumorigenicity in stem-like tumor-propagating cells from human glioblastomas. Cancer Cell 22:765–780
Day BW, Stringer BW, Al-Ejeh F, Ting MJ, Wilson J, Ensbey KS, Jamieson PR, Bruce ZC, Lim YC, Offenhauser C, Charmsaz S, Cooper LT, Ellacott JK, Harding A, Leveque L, Inglis P, Allan S, Walker DG, Lackmann M, Osborne G, Khanna KK, Reynolds BA, Lickliter JD, Boyd AW (2013) EphA3 maintains tumorigenicity and is a therapeutic target in glioblastoma multiforme. Cancer Cell 23:238–248
Wykosky J, Palma E, Gibo DM, Ringler S, Turner CP, Debinski W (2008) Soluble monomeric EphrinA1 is released from tumor cells and is a functional ligand for the EphA2 receptor. Oncogene 27:7260–7273
Beauchamp A, Lively MO, Mintz A, Gibo D, Wykosky J, Debinski W (2012) EphrinA1 is released in three forms from cancer cells by matrix metalloproteases. Mol Cell Biol 32:3253–3264
Alford S, Watson-Hurthig A, Scott N, Carette A, Lorimer H, Bazowski J, Howard PL (2010) Soluble ephrin a1 is necessary for the growth of HeLa and SK-BR3 cells. Cancer Cell Int 10:41
Arvanitis D, Davy A (2008) Eph/ephrin signaling: networks. Genes Dev 22:416–429
Pasquale EB (2005) Eph receptor signalling casts a wide net on cell behaviour. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 6:462–475
Shamah SM, Lin MZ, Goldberg JL, Estrach S, Sahin M, Hu L, Bazalakova M, Neve RL, Corfas G, Debant A, Greenberg ME (2001) EphA receptors regulate growth cone dynamics through the novel guanine nucleotide exchange factor ephexin. Cell 105:233–244
Sahin M, Greer PL, Lin MZ, Poucher H, Eberhart J, Schmidt S, Wright TM, Shamah SM, O’Connell S, Cowan CW, Hu L, Goldberg JL, Debant A, Corfas G, Krull CE, Greenberg ME (2005) Eph-dependent tyrosine phosphorylation of ephexin1 modulates growth cone collapse. Neuron 46:191–204
Noren NK, Pasquale EB (2004) Eph receptor-ephrin bidirectional signals that target Ras and Rho proteins. Cell Signal 16:655–666
Marston DJ, Dickinson S, Nobes CD (2003) Rac-dependent trans-endocytosis of ephrinBs regulates Eph-ephrin contact repulsion. Nat Cell Biol 5:879–888
Janes PW, Saha N, Barton WA, Kolev MV, Wimmer-Kleikamp SH, Nievergall E, Blobel CP, Himanen JP, Lackmann M, Nikolov DB (2005) Adam meets Eph: an ADAM substrate recognition module acts as a molecular switch for ephrin cleavage in trans. Cell 123:291–304
Sugiyama N, Gucciardo E, Tatti O, Varjosalo M, Hyytiainen M, Gstaiger M, Lehti K (2013) EphA2 cleavage by MT1-MMP triggers single cancer cell invasion via homotypic cell repulsion. J Cell Biol 201:467–484
Eph Nomenclature Committee (1997) Unified nomenclature for Eph family receptors and their ligands, the ephrins. Cell 90:403–404
Himanen JP, Nikolov DB (2003) Eph signaling: a structural view. Trends Neurosci 26:46–51
Lindberg RA, Hunter T (1990) cDNA cloning and characterization of eck, an epithelial cell receptor protein-tyrosine kinase in the eph/elk family of protein kinases. Mol Cell Biol 10:6316–6324
Binns KL, Taylor PP, Sicheri F, Pawson T, Holland SJ (2000) Phosphorylation of tyrosine residues in the kinase domain and juxtamembrane region regulates the biological and catalytic activities of Eph receptors. Mol Cell Biol 20:4791–4805
Fox BP, Kandpal RP (2011) A paradigm shift in EPH receptor interaction: biological relevance of EPHB6 interaction with EPHA2 and EPHB2 in breast carcinoma cell lines. Cancer Genomics Proteomics 8:185–193
Truitt L, Freywald A (2011) Dancing with the dead: Eph receptors and their kinase-null partners. Biochem Cell Biol 89:115–129
Toth J, Cutforth T, Gelinas AD, Bethoney KA, Bard J, Harrison CJ (2001) Crystal structure of an ephrin ectodomain. Dev Cell 1:83–92
Murai KK, Pasquale EB (2003) ‘Eph’ective signaling: forward, reverse and crosstalk. J Cell Sci 116:2823–2832
Vaught D, Brantley-Sieders DM, Chen J (2008) Eph receptors in breast cancer: roles in tumor promotion and tumor suppression. Breast Cancer Res 10:217
Miao H, Li DQ, Mukherjee A, Guo H, Petty A, Cutter J, Basilion JP, Sedor J, Wu J, Danielpour D, Sloan AE, Cohen ML, Wang B (2009) EphA2 mediates ligand-dependent inhibition and ligand-independent promotion of cell migration and invasion via a reciprocal regulatory loop with Akt. Cancer Cell 16:9–20
Himanen JP, Yermekbayeva L, Janes PW, Walker JR, Xu K, Atapattu L, Rajashankar KR, Mensinga A, Lackmann M, Nikolov DB, Dhe-Paganon S (2010) Architecture of Eph receptor clusters. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:10860–10865
Janes PW, Nievergall E, Lackmann M (2012) Concepts and consequences of Eph receptor clustering. Semin Cell Dev Biol 23:43–50
Himanen JP, Goldgur Y, Miao H, Myshkin E, Guo H, Buck M, Nguyen M, Rajashankar KR, Wang B, Nikolov DB (2009) Ligand recognition by A-class Eph receptors: crystal structures of the EphA2 ligand-binding domain and the EphA2/ephrin–A1 complex. EMBO Rep 10:722–728
Himanen JP, Chumley MJ, Lackmann M, Li C, Barton WA, Jeffrey PD, Vearing C, Geleick D, Feldheim DA, Boyd AW, Henkemeyer M, Nikolov DB (2004) Repelling class discrimination: ephrin-A5 binds to and activates EphB2 receptor signaling. Nat Neurosci 7:501–509
Himanen JP, Rajashankar KR, Lackmann M, Cowan CA, Henkemeyer M, Nikolov DB (2001) Crystal structure of an Eph receptor–ephrin complex. Nature 414:933–938
Himanen JP, Saha N, Nikolov DB (2007) Cell–cell signaling via Eph receptors and ephrins. Curr Opin Cell Biol 19:534–542
Lema Tome CM, Palma E, Ferluga S, Lowther WT, Hantgan R, Wykosky J, Debinski W (2012) Structural and functional characterization of monomeric EphrinA1 binding site to EphA2 receptor. J Biol Chem 287:14012–14022
Ferluga S, Hantgan R, Goldgur Y, Himanen JP, Nikolov DB, Debinski W (2013) Biological and structural characterization of glycosylation on ephrin-A1, a preferred ligand for EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase. J Biol Chem 288:18448–18457
Xu K, Tzvetkova-Robev D, Xu Y, Goldgur Y, Chan YP, Himanen JP, Nikolov DB (2013) Insights into Eph receptor tyrosine kinase activation from crystal structures of the EphA4 ectodomain and its complex with ephrin-A5. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 110:14634–14639
Seiradake E, Harlos K, Sutton G, Aricescu AR, Jones EY (2010) An extracellular steric seeding mechanism for Eph-ephrin signaling platform assembly. Nat Struct Mol Biol 17:398–402
Thanos CD, Goodwill KE, Bowie JU (1999) Oligomeric structure of the human EphB2 receptor SAM domain. Science 283:833–836
Smith FM, Vearing C, Lackmann M, Treutlein H, Himanen J, Chen K, Saul A, Nikolov D, Boyd AW (2004) Dissecting the EphA3/Ephrin-A5 interactions using a novel functional mutagenesis screen. J Biol Chem 279:9522–9531
Day B, To C, Himanen JP, Smith FM, Nikolov DB, Boyd AW, Lackmann M (2005) Three distinct molecular surfaces in ephrin-A5 are essential for a functional interaction with EphA3. J Biol Chem 280:26526–26532
Janes PW, Griesshaber B, Atapattu L, Nievergall E, Hii LL, Mensinga A, Chheang C, Day BW, Boyd AW, Bastiaens PI, Jorgensen C, Pawson T, Lackmann M (2011) Eph receptor function is modulated by heterooligomerization of A and B type Eph receptors. J Cell Biol 195:1033–1045
Lai KO, Chen Y, Po HM, Lok KC, Gong K, Ip NY (2004) Identification of the Jak/Stat proteins as novel downstream targets of EphA4 signaling in muscle: implications in the regulation of acetylcholinesterase expression. J Biol Chem 279:13383–13392
Vindis C, Cerretti DP, Daniel TO, Huynh-Do U (2003) EphB1 recruits c-Src and p52Shc to activate MAPK/ERK and promote chemotaxis. J Cell Biol 162:661–671
Xu Z, Lai KO, Zhou HM, Lin SC, Ip NY (2003) Ephrin-B1 reverse signaling activates JNK through a novel mechanism that is independent of tyrosine phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 278:24767–24775
Buchert M, Schneider S, Meskenaite V, Adams MT, Canaani E, Baechi T, Moelling K, Hovens CM (1999) The junction-associated protein AF-6 interacts and clusters with specific Eph receptor tyrosine kinases at specialized sites of cell–cell contact in the brain. J Cell Biol 144:361–371
Hock B, Bohme B, Karn T, Yamamoto T, Kaibuchi K, Holtrich U, Holland S, Pawson T, Rubsamen-Waigmann H, Strebhardt K (1998) PDZ-domain-mediated interaction of the Eph-related receptor tyrosine kinase EphB3 and the ras-binding protein AF6 depends on the kinase activity of the receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:9779–9784
Torres R, Firestein BL, Dong H, Staudinger J, Olson EN, Huganir RL, Bredt DS, Gale NW, Yancopoulos GD (1998) PDZ proteins bind, cluster, and synaptically colocalize with Eph receptors and their ephrin ligands. Neuron 21:1453–1463
Davy A, Gale NW, Murray EW, Klinghoffer RA, Soriano P, Feuerstein C, Robbins SM (1999) Compartmentalized signaling by GPI-anchored ephrin-A5 requires the Fyn tyrosine kinase to regulate cellular adhesion. Genes Dev 13:3125–3135
Gauthier LR, Robbins SM (2003) Ephrin signaling: one raft to rule them all? One raft to sort them? One raft to spread their call and in signaling bind them? Life Sci 74:207–216
Simons K, Toomre D (2000) Lipid rafts and signal transduction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 1:31–39
Lackmann M, Boyd AW (2008) Eph, a protein family coming of age: more confusion, insight, or complexity? Sci Signal 1:re2
Wimmer-Kleikamp SH, Janes PW, Squire A, Bastiaens PI, Lackmann M (2004) Recruitment of Eph receptors into signaling clusters does not require ephrin contact. J Cell Biol 164:661–666
Huynh-Do U, Stein E, Lane AA, Liu H, Cerretti DP, Daniel TO (1999) Surface densities of ephrin-B1 determine EphB1-coupled activation of cell attachment through alphavbeta3 and alpha5beta1 integrins. EMBO J 18:2165–2173
Holmberg J, Frisen J (2002) Ephrins are not only unattractive. Trends Neurosci 25:239–243
Stein E, Lane AA, Cerretti DP, Schoecklmann HO, Schroff AD, Van Etten RL, Daniel TO (1998) Eph receptors discriminate specific ligand oligomers to determine alternative signaling complexes, attachment, and assembly responses. Genes Dev 12:667–678
Macrae M, Neve RM, Rodriguez-Viciana P, Haqq C, Yeh J, Chen C, Gray JW, McCormick F (2005) A conditional feedback loop regulates Ras activity through EphA2. Cancer Cell 8:111–118
Orsulic S, Kemler R (2000) Expression of Eph receptors and ephrins is differentially regulated by E-cadherin. J Cell Sci 113(Pt 10):1793–1802
Zantek ND, Azimi M, Fedor-Chaiken M, Wang B, Brackenbury R, Kinch MS (1999) E-cadherin regulates the function of the EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase. Cell Growth Differ 10:629–638
Poliakov A, Cotrina ML, Pasini A, Wilkinson DG (2008) Regulation of EphB2 activation and cell repulsion by feedback control of the MAPK pathway. J Cell Biol 183:933–947
Miao H, Wei BR, Peehl DM, Li Q, Alexandrou T, Schelling JR, Rhim JS, Sedor JR, Burnett E, Wang B (2001) Activation of EphA receptor tyrosine kinase inhibits the Ras/MAPK pathway. Nat Cell Biol 3:527–530
Menges CW, McCance DJ (2008) Constitutive activation of the Raf–MAPK pathway causes negative feedback inhibition of Ras–PI3K–AKT and cellular arrest through the EphA2 receptor. Oncogene 27:2934–2940
Falivelli G, Lisabeth EM, Rubio de la Torre E, Perez-Tenorio G, Tosato G, Salvucci O, Pasquale EB (2013) Attenuation of eph receptor kinase activation in cancer cells by coexpressed ephrin ligands. PLoS ONE 8:e81445
Janes PW, Wimmer-Kleikamp SH, Frangakis AS, Treble K, Griesshaber B, Sabet O, Grabenbauer M, Ting AY, Saftig P, Bastiaens PI, Lackmann M (2009) Cytoplasmic relaxation of active Eph controls ephrin shedding by ADAM10. PLoS Biol 7:e1000215
Zimmer M, Palmer A, Kohler J, Klein R (2003) EphB-ephrinB bi-directional endocytosis terminates adhesion allowing contact-mediated repulsion. Nat Cell Biol 5:869–878
Bartley TD, Hunt RW, Welcher AA, Boyle WJ, Parker VP, Lindberg RA, Lu HS, Colombero AM, Elliott RL, Guthrie BA, Holst PL, Skrine JD, Toso RJ, Zhang M, Fernandez E, Trail G, Varnum B, Yarden Y, Hunter T, Fox GM (1994) B61 is a ligand for the ECK receptor protein-tyrosine kinase. Nature 368:558–560
Hattori M, Osterfield M, Flanagan JG (2000) Regulated cleavage of a contact-mediated axon repellent. Science 289:1360–1365
Alford SC, Bazowski J, Lorimer H, Elowe S, Howard PL (2007) Tissue transglutaminase clusters soluble A-type ephrins into functionally active high molecular weight oligomers. Exp Cell Res 313:4170–4179
Davis S, Gale NW, Aldrich TH, Maisonpierre PC, Lhotak V, Pawson T, Goldfarb M, Yancopoulos GD (1994) Ligands for EPH-related receptor tyrosine kinases that require membrane attachment or clustering for activity. Science 266:816–819
Noblitt LW, Bangari DS, Shukla S, Knapp DW, Mohammed S, Kinch MS, Mittal SK (2004) Decreased tumorigenic potential of EphA2-overexpressing breast cancer cells following treatment with adenoviral vectors that express EphrinA1. Cancer Gene Ther 11:757–766
Vihanto MM, Vindis C, Djonov V, Cerretti DP, Huynh-Do U (2006) Caveolin-1 is required for signaling and membrane targeting of EphB1 receptor tyrosine kinase. J Cell Sci 119:2299–2309
Parker M, Roberts R, Enriquez M, Zhao X, Takahashi T, Pat Cerretti D, Daniel T, Chen J (2004) Reverse endocytosis of transmembrane ephrin-B ligands via a clathrin-mediated pathway. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 323:17–23
Nievergall E, Janes PW, Stegmayer C, Vail ME, Haj FG, Teng SW, Neel BG, Bastiaens PI, Lackmann M (2010) PTP1B regulates Eph receptor function and trafficking. J Cell Biol 191:1189–1203
Wimmer-Kleikamp SH, Nievergall E, Gegenbauer K, Adikari S, Mansour M, Yeadon T, Boyd AW, Patani NR, Lackmann M (2008) Elevated protein tyrosine phosphatase activity provokes Eph/ephrin-facilitated adhesion of pre-B leukemia cells. Blood 112:721–732
Sharfe N, Freywald A, Toro A, Roifman CM (2003) Ephrin-A1 induces c-Cbl phosphorylation and EphA receptor down-regulation in T cells. J Immunol 170:6024–6032
Fasen K, Cerretti DP, Huynh-Do U (2008) Ligand binding induces Cbl-dependent EphB1 receptor degradation through the lysosomal pathway. Traffic 9:251–266
Walker-Daniels J, Riese DJ 2nd, Kinch MS (2002) c-Cbl-dependent EphA2 protein degradation is induced by ligand binding. Mol Cancer Res 1:79–87
Fang WB, Ireton RC, Zhuang G, Takahashi T, Reynolds A, Chen J (2008) Overexpression of EPHA2 receptor destabilizes adherens junctions via a RhoA-dependent mechanism. J Cell Sci 121:358–368
Hiramoto-Yamaki N, Takeuchi S, Ueda S, Harada K, Fujimoto S, Negishi M, Katoh H (2010) Ephexin4 and EphA2 mediate cell migration through a RhoG-dependent mechanism. J Cell Biol 190:461–477
Hunter SG, Zhuang G, Brantley-Sieders D, Swat W, Cowan CW, Chen J (2006) Essential role of Vav family guanine nucleotide exchange factors in EphA receptor-mediated angiogenesis. Mol Cell Biol 26:4830–4842
Cowan CW, Shao YR, Sahin M, Shamah SM, Lin MZ, Greer PL, Gao S, Griffith EC, Brugge JS, Greenberg ME (2005) Vav family GEFs link activated Ephs to endocytosis and axon guidance. Neuron 46:205–217
Kawai H, Kobayashi M, Hiramoto-Yamaki N, Harada K, Negishi M, Katoh H (2013) Ephexin4-mediated promotion of cell migration and anoikis resistance is regulated by serine 897 phosphorylation of EphA2. FEBS Open Bio 3:78–82
Davy A, Robbins SM (2000) Ephrin-A5 modulates cell adhesion and morphology in an integrin-dependent manner. EMBO J 19:5396–5405
Bruckner K, Pasquale EB, Klein R (1997) Tyrosine phosphorylation of transmembrane ligands for Eph receptors. Science 275:1640–1643
Holland SJ, Gale NW, Mbamalu G, Yancopoulos GD, Henkemeyer M, Pawson T (1996) Bidirectional signalling through the EPH-family receptor Nuk and its transmembrane ligands. Nature 383:722–725
Palmer A, Zimmer M, Erdmann KS, Eulenburg V, Porthin A, Heumann R, Deutsch U, Klein R (2002) EphrinB phosphorylation and reverse signaling: regulation by Src kinases and PTP-BL phosphatase. Mol Cell 9:725–737
Kalo MS, Yu HH, Pasquale EB (2001) In vivo tyrosine phosphorylation sites of activated ephrin-B1 and ephB2 from neural tissue. J Biol Chem 276:38940–38948
Segura I, Essmann CL, Weinges S, Acker-Palmer A (2007) Grb4 and GIT1 transduce ephrinB reverse signals modulating spine morphogenesis and synapse formation. Nat Neurosci 10:301–310
Cowan CA, Henkemeyer M (2001) The SH2/SH3 adaptor Grb4 transduces B-ephrin reverse signals. Nature 413:174–179
Tanaka M, Sasaki K, Kamata R, Sakai R (2007) The C-terminus of ephrin-B1 regulates metalloproteinase secretion and invasion of cancer cells. J Cell Sci 120:2179–2189
Xu NJ, Henkemeyer M (2009) Ephrin-B3 reverse signaling through Grb4 and cytoskeletal regulators mediates axon pruning. Nat Neurosci 12:268–276
Nakada M, Drake KL, Nakada S, Niska JA, Berens ME (2006) Ephrin-B3 ligand promotes glioma invasion through activation of Rac1. Cancer Res 66:8492–8500
Lee HS, Nishanian TG, Mood K, Bong YS, Daar IO (2008) EphrinB1 controls cell–cell junctions through the Par polarity complex. Nat Cell Biol 10:979–986
Bochenek ML, Dickinson S, Astin JW, Adams RH, Nobes CD (2010) Ephrin-B2 regulates endothelial cell morphology and motility independently of Eph-receptor binding. J Cell Sci 123:1235–1246
Foo SS, Turner CJ, Adams S, Compagni A, Aubyn D, Kogata N, Lindblom P, Shani M, Zicha D, Adams RH (2006) Ephrin-B2 controls cell motility and adhesion during blood-vessel-wall assembly. Cell 124:161–173
Brantley-Sieders DM, Zhuang G, Hicks D, Fang WB, Hwang Y, Cates JM, Coffman K, Jackson D, Bruckheimer E, Muraoka-Cook RS, Chen J (2008) The receptor tyrosine kinase EphA2 promotes mammary adenocarcinoma tumorigenesis and metastatic progression in mice by amplifying ErbB2 signaling. J Clin Invest 118:64–78
Miao H, Gale NW, Guo H, Qian J, Petty A, Kaspar J, Murphy AJ, Valenzuela DM, Yancopoulos G, Hambardzumyan D, Lathia JD, Rich JN, Lee J, Wang B (2014) EphA2 promotes infiltrative invasion of glioma stem cells in vivo through cross-talk with Akt and regulates stem cell properties. Oncogene
Zelinski DP, Zantek ND, Stewart JC, Irizarry AR, Kinch MS (2001) EphA2 overexpression causes tumorigenesis of mammary epithelial cells. Cancer Res 61:2301–2306
Larsen AB, Pedersen MW, Stockhausen MT, Grandal MV, van Deurs B, Poulsen HS (2007) Activation of the EGFR gene target EphA2 inhibits epidermal growth factor-induced cancer cell motility. Mol Cancer Res 5:283–293
Fukai J, Yokote H, Yamanaka R, Arao T, Nishio K, Itakura T (2008) EphA4 promotes cell proliferation and migration through a novel EphA4-FGFR1 signaling pathway in the human glioma U251 cell line. Mol Cancer Ther 7:2768–2778
Kumar SR, Singh J, Xia G, Krasnoperov V, Hassanieh L, Ley EJ, Scehnet J, Kumar NG, Hawes D, Press MF, Weaver FA, Gill PS (2006) Receptor tyrosine kinase EphB4 is a survival factor in breast cancer. Am J Pathol 169:279–293
Genander M, Halford MM, Xu NJ, Eriksson M, Yu Z, Qiu Z, Martling A, Greicius G, Thakar S, Catchpole T, Chumley MJ, Zdunek S, Wang C, Holm T, Goff SP, Pettersson S, Pestell RG, Henkemeyer M, Frisen J (2009) Dissociation of EphB2 signaling pathways mediating progenitor cell proliferation and tumor suppression. Cell 139:679–692
Tawadros T, Brown MD, Hart CA, Clarke NW (2012) Ligand-independent activation of EphA2 by arachidonic acid induces metastasis-like behaviour in prostate cancer cells. Br J Cancer 107:1737–1744
Taddei ML, Parri M, Angelucci A, Onnis B, Bianchini F, Giannoni E, Raugei G, Calorini L, Rucci N, Teti A, Bologna M, Chiarugi P (2009) Kinase-dependent and -independent roles of EphA2 in the regulation of prostate cancer invasion and metastasis. Am J Pathol 174:1492–1503
Parri M, Taddei ML, Bianchini F, Calorini L, Chiarugi P (2009) EphA2 reexpression prompts invasion of melanoma cells shifting from mesenchymal to amoeboid-like motility style. Cancer Res 69:2072–2081
Bromann PA, Korkaya H, Courtneidge SA (2004) The interplay between Src family kinases and receptor tyrosine kinases. Oncogene 23:7957–7968
Amanchy R, Zhong J, Hong R, Kim JH, Gucek M, Cole RN, Molina H, Pandey A (2009) Identification of c-Src tyrosine kinase substrates in platelet-derived growth factor receptor signaling. Mol Oncol 3:439–450
Liu J, Huang C, Zhan X (1999) Src is required for cell migration and shape changes induced by fibroblast growth factor 1. Oncogene 18:6700–6706
Zou W, Kitaura H, Reeve J, Long F, Tybulewicz VL, Shattil SJ, Ginsberg MH, Ross FP, Teitelbaum SL (2007) Syk, c-Src, the alphavbeta3 integrin, and ITAM immunoreceptors, in concert, regulate osteoclastic bone resorption. J Cell Biol 176:877–888
Yang NY, Pasquale EB, Owen LB, Ethell IM (2006) The EphB4 receptor-tyrosine kinase promotes the migration of melanoma cells through Rho-mediated actin cytoskeleton reorganization. J Biol Chem 281:32574–32586
Meng W, Numazaki M, Takeuchi K, Uchibori Y, Ando-Akatsuka Y, Tominaga M, Tominaga T (2004) DIP (mDia interacting protein) is a key molecule regulating Rho and Rac in a Src-dependent manner. EMBO J 23:760–771
Faoro L, Singleton PA, Cervantes GM, Lennon FE, Choong NW, Kanteti R, Ferguson BD, Husain AN, Tretiakova MS, Ramnath N, Vokes EE, Salgia R (2010) EphA2 mutation in lung squamous cell carcinoma promotes increased cell survival, cell invasion, focal adhesions, and mammalian target of rapamycin activation. J Biol Chem 285:18575–18585
Taddei ML, Parri M, Angelucci A, Bianchini F, Marconi C, Giannoni E, Raugei G, Bologna M, Calorini L, Chiarugi P (2011) EphA2 induces metastatic growth regulating amoeboid motility and clonogenic potential in prostate carcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Res 9:149–160
Sugiyama N, Gucciardo E, Lehti K (2013) EphA2 bears plasticity to tumor invasion. Cell Cycle 12:2927–2928
Leroy C, Fialin C, Sirvent A, Simon V, Urbach S, Poncet J, Robert B, Jouin P, Roche S (2009) Quantitative phosphoproteomics reveals a cluster of tyrosine kinases that mediates SRC invasive activity in advanced colon carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 69:2279–2286
Moro L, Dolce L, Cabodi S, Bergatto E, Boeri Erba E, Smeriglio M, Turco E, Retta SF, Giuffrida MG, Venturino M, Godovac-Zimmermann J, Conti A, Schaefer E, Beguinot L, Tacchetti C, Gaggini P, Silengo L, Tarone G, Defilippi P (2002) Integrin-induced epidermal growth factor (EGF) receptor activation requires c-Src and p130Cas and leads to phosphorylation of specific EGF receptor tyrosines. J Biol Chem 277:9405–9414
Ireton RC, Chen J (2005) EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase as a promising target for cancer therapeutics. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 5:149–157
Hafner C, Becker B, Landthaler M, Vogt T (2006) Expression profile of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands in human skin and downregulation of EphA1 in nonmelanoma skin cancer. Mod Pathol 19:1369–1377
Easty DJ, Hill SP, Hsu MY, Fallowfield ME, Florenes VA, Herlyn M, Bennett DC (1999) Up-regulation of ephrin-A1 during melanoma progression. Int J Cancer 84:494–501
Udayakumar D, Zhang G, Ji Z, Njauw CN, Mroz P, Tsao H (2011) EphA2 is a critical oncogene in melanoma. Oncogene 30:4921–4929
Fox BP, Kandpal RP (2004) Invasiveness of breast carcinoma cells and transcript profile: Eph receptors and ephrin ligands as molecular markers of potential diagnostic and prognostic application. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 318:882–892
Ogawa K, Pasqualini R, Lindberg RA, Kain R, Freeman AL, Pasquale EB (2000) The ephrin-A1 ligand and its receptor, EphA2, are expressed during tumor neovascularization. Oncogene 19:6043–6052
Wu Q, Suo Z, Risberg B, Karlsson MG, Villman K, Nesland JM (2004) Expression of Ephb2 and Ephb4 in breast carcinoma. Pathol Oncol Res 10:26–33
Fox BP, Tabone CJ, Kandpal RP (2006) Potential clinical relevance of Eph receptors and ephrin ligands expressed in prostate carcinoma cell lines. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 342:1263–1272
Wang LF, Fokas E, Juricko J, You A, Rose F, Pagenstecher A, Engenhart-Cabillic R, An HX (2008) Increased expression of EphA7 correlates with adverse outcome in primary and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme patients. BMC Cancer 8:79
Zeng G, Hu Z, Kinch MS, Pan CX, Flockhart DA, Kao C, Gardner TA, Zhang S, Li L, Baldridge LA, Koch MO, Ulbright TM, Eble JN, Cheng L (2003) High-level expression of EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase in prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia. Am J Pathol 163:2271–2276
Guo DL, Zhang J, Yuen ST, Tsui WY, Chan AS, Ho C, Ji J, Leung SY, Chen X (2006) Reduced expression of EphB2 that parallels invasion and metastasis in colorectal tumours. Carcinogenesis 27:454–464
Cheng N, Brantley D, Fang WB, Liu H, Fanslow W, Cerretti DP, Bussell KN, Reith A, Jackson D, Chen J (2003) Inhibition of VEGF-dependent multistage carcinogenesis by soluble EphA receptors. Neoplasia 5:445–456
Lahtela J, Corson LB, Hemmes A, Brauer MJ, Koopal S, Lee J, Hunsaker TL, Jackson PK, Verschuren EW (2013) A high-content cellular senescence screen identifies candidate tumor suppressors, including EPHA3. Cell Cycle 12:625–634
Kullander K, Klein R (2002) Mechanisms and functions of Eph and ephrin signalling. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 3:475–486
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2011) Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell 144:646–674
Friedl P, Locker J, Sahai E, Segall JE (2012) Classifying collective cancer cell invasion. Nat Cell Biol 14:777–783
Brantley-Sieders DM, Fang WB, Hicks DJ, Zhuang G, Shyr Y, Chen J (2005) Impaired tumor microenvironment in EphA2-deficient mice inhibits tumor angiogenesis and metastatic progression. FASEB J 19:1884–1886
Meyer S, Hafner C, Guba M, Flegel S, Geissler EK, Becker B, Koehl GE, Orso E, Landthaler M, Vogt T (2005) Ephrin-B2 overexpression enhances integrin-mediated ECM-attachment and migration of B16 melanoma cells. Int J Oncol 27:1197–1206
Nakada M, Niska JA, Tran NL, McDonough WS, Berens ME (2005) EphB2/R-Ras signaling regulates glioma cell adhesion, growth, and invasion. Am J Pathol 167:565–576
Brantley-Sieders DM, Jiang A, Sarma K, Badu-Nkansah A, Walter DL, Shyr Y, Chen J (2011) Eph/ephrin profiling in human breast cancer reveals significant associations between expression level and clinical outcome. PLoS ONE 6:e24426
Castano J, Davalos V, Schwartz S Jr, Arango D (2008) EPH receptors in cancer. Histol Histopathol 23:1011–1023
Wang XD, Reeves K, Luo FR, Xu LA, Lee F, Clark E, Huang F (2007) Identification of candidate predictive and surrogate molecular markers for dasatinib in prostate cancer: rationale for patient selection and efficacy monitoring. Genome Biol 8:R255
Herath NI, Doecke J, Spanevello MD, Leggett BA, Boyd AW (2009) Epigenetic silencing of EphA1 expression in colorectal cancer is correlated with poor survival. Br J Cancer 100:1095–1102
Kuang SQ, Bai H, Fang ZH, Lopez G, Yang H, Tong W, Wang ZZ, Garcia-Manero G (2010) Aberrant DNA methylation and epigenetic inactivation of Eph receptor tyrosine kinases and ephrin ligands in acute lymphoblastic leukemia. Blood 115:2412–2419
Fu DY, Wang ZM, Wang BL, Chen L, Yang WT, Shen ZZ, Huang W, Shao ZM (2010) Frequent epigenetic inactivation of the receptor tyrosine kinase EphA5 by promoter methylation in human breast cancer. Hum Pathol 41:48–58
Astin JW, Batson J, Kadir S, Charlet J, Persad RA, Gillatt D, Oxley JD, Nobes CD (2010) Competition amongst Eph receptors regulates contact inhibition of locomotion and invasiveness in prostate cancer cells. Nat Cell Biol 12:1194–1204
Heroult M, Schaffner F, Augustin HG (2006) Eph receptor and ephrin ligand-mediated interactions during angiogenesis and tumor progression. Exp Cell Res 312:642–650
Luo H, Yu G, Tremblay J, Wu J (2004) EphB6-null mutation results in compromised T cell function. J Clin Invest 114:1762–1773
Sharfe N, Nikolic M, Cimpeon L, Van De Kratts A, Freywald A, Roifman CM (2008) EphA and ephrin-A proteins regulate integrin-mediated T lymphocyte interactions. Mol Immunol 45:1208–1220
Lee M, Vasioukhin V (2008) Cell polarity and cancer—cell and tissue polarity as a non-canonical tumor suppressor. J Cell Sci 121:1141–1150
Royer C, Lu X (2011) Epithelial cell polarity: a major gatekeeper against cancer? Cell Death Differ 18:1470–1477
Muthuswamy SK, Xue B (2012) Cell polarity as a regulator of cancer cell behavior plasticity. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 28:599–625
Winning RS, Wyman TL, Walker GK (2001) EphA4 activity causes cell shape change and a loss of cell polarity in Xenopus laevis embryos. Differentiation 68:126–132
Miao H, Nickel CH, Cantley LG, Bruggeman LA, Bennardo LN, Wang B (2003) EphA kinase activation regulates HGF-induced epithelial branching morphogenesis. J Cell Biol 162:1281–1292
Cortina C, Palomo-Ponce S, Iglesias M, Fernandez-Masip JL, Vivancos A, Whissell G, Huma M, Peiro N, Gallego L, Jonkheer S, Davy A, Lloreta J, Sancho E, Batlle E (2007) EphB–ephrin-B interactions suppress colorectal cancer progression by compartmentalizing tumor cells. Nat Genet 39:1376–1383
Rosenberg IM, Goke M, Kanai M, Reinecker HC, Podolsky DK (1997) Epithelial cell kinase-B61: an autocrine loop modulating intestinal epithelial migration and barrier function. Am J Physiol 273:G824–G832
Miura K, Nam JM, Kojima C, Mochizuki N, Sabe H (2009) EphA2 engages Git1 to suppress Arf6 activity modulating epithelial cell–cell contacts. Mol Biol Cell 20:1949–1959
Tanaka M, Kamata R, Sakai R (2005) EphA2 phosphorylates the cytoplasmic tail of Claudin-4 and mediates paracellular permeability. J Biol Chem 280:42375–42382
Batlle E, Henderson JT, Beghtel H, van den Born MM, Sancho E, Huls G, Meeldijk J, Robertson J, van de Wetering M, Pawson T, Clevers H (2002) Beta-catenin and TCF mediate cell positioning in the intestinal epithelium by controlling the expression of EphB/ephrinB. Cell 111:251–263
Etienne-Manneville S (2008) Polarity proteins in migration and invasion. Oncogene 27:6970–6980
Thiery JP (2002) Epithelial–mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer 2:442–454
Parri M, Chiarugi P (2010) Rac and Rho GTPases in cancer cell motility control. Cell Commun Signal 8:23
Fang WB, Brantley-Sieders DM, Parker MA, Reith AD, Chen J (2005) A kinase-dependent role for EphA2 receptor in promoting tumor growth and metastasis. Oncogene 24:7859–7868
Friedl P, Alexander S (2011) Cancer invasion and the microenvironment: plasticity and reciprocity. Cell 147:992–1009
Campbell TN, Attwell S, Arcellana-Panlilio M, Robbins SM (2006) Ephrin A5 expression promotes invasion and transformation of murine fibroblasts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 350:623–628
Nakada M, Niska JA, Miyamori H, McDonough WS, Wu J, Sato H, Berens ME (2004) The phosphorylation of EphB2 receptor regulates migration and invasion of human glioma cells. Cancer Res 64:3179–3185
Wang B (2011) Cancer cells exploit the Eph-ephrin system to promote invasion and metastasis: tales of unwitting partners. Sci Signal 4:pe28
Chiu ST, Chang KJ, Ting CH, Shen HC, Li H, Hsieh FJ (2009) Over-expression of EphB3 enhances cell–cell contacts and suppresses tumor growth in HT-29 human colon cancer cells. Carcinogenesis 30:1475–1486
Noren NK, Foos G, Hauser CA, Pasquale EB (2006) The EphB4 receptor suppresses breast cancer cell tumorigenicity through an Abl–Crk pathway. Nat Cell Biol 8:815–825
Zou JX, Wang B, Kalo MS, Zisch AH, Pasquale EB, Ruoslahti E (1999) An Eph receptor regulates integrin activity through R-Ras. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13813–13818
Miao H, Burnett E, Kinch M, Simon E, Wang B (2000) Activation of EphA2 kinase suppresses integrin function and causes focal-adhesion-kinase dephosphorylation. Nat Cell Biol 2:62–69
Parri M, Buricchi F, Giannoni E, Grimaldi G, Mello T, Raugei G, Ramponi G, Chiarugi P (2007) EphrinA1 activates a Src/focal adhesion kinase-mediated motility response leading to rho-dependent actino/myosin contractility. J Biol Chem 282:19619–19628
Ivaska J, Heino J (2011) Cooperation between integrins and growth factor receptors in signaling and endocytosis. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 27:291–320
Guo W, Giancotti FG (2004) Integrin signalling during tumour progression. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 5:816–826
Prevost N, Woulfe DS, Jiang H, Stalker TJ, Marchese P, Ruggeri ZM, Brass LF (2005) Eph kinases and ephrins support thrombus growth and stability by regulating integrin outside-in signaling in platelets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:9820–9825
Nagashima K, Endo A, Ogita H, Kawana A, Yamagishi A, Kitabatake A, Matsuda M, Mochizuki N (2002) Adaptor protein Crk is required for ephrin-B1-induced membrane ruffling and focal complex assembly of human aortic endothelial cells. Mol Biol Cell 13:4231–4242
Carter N, Nakamoto T, Hirai H, Hunter T (2002) EphrinA1-induced cytoskeletal re-organization requires FAK and p130(cas). Nat Cell Biol 4:565–573
Miao H, Strebhardt K, Pasquale EB, Shen TL, Guan JL, Wang B (2005) Inhibition of integrin-mediated cell adhesion but not directional cell migration requires catalytic activity of EphB3 receptor tyrosine kinase. Role of Rho family small GTPases. J Biol Chem 280:923–932
Jorgensen C, Sherman A, Chen GI, Pasculescu A, Poliakov A, Hsiung M, Larsen B, Wilkinson DG, Linding R, Pawson T (2009) Cell-specific information processing in segregating populations of Eph receptor ephrin-expressing cells. Science 326:1502–1509
Sieg DJ, Hauck CR, Ilic D, Klingbeil CK, Schaefer E, Damsky CH, Schlaepfer DD (2000) FAK integrates growth-factor and integrin signals to promote cell migration. Nat Cell Biol 2:249–256
Berrier AL, Mastrangelo AM, Downward J, Ginsberg M, LaFlamme SE (2000) Activated R-ras, Rac1, PI 3-kinase and PKCepsilon can each restore cell spreading inhibited by isolated integrin beta1 cytoplasmic domains. J Cell Biol 151:1549–1560
Raftopoulou M, Hall A (2004) Cell migration: Rho GTPases lead the way. Dev Biol 265:23–32
Hwang YS, Hodge JC, Sivapurapu N, Lindholm PF (2006) Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates PC-3 prostate cancer cell Matrigel invasion through activation of RhoA and NF-kappaB activity. Mol Carcinog 45:518–529
Irie F, Yamaguchi Y (2002) EphB receptors regulate dendritic spine development via intersectin, Cdc42 and N-WASP. Nat Neurosci 5:1117–1118
Lawrenson ID, Wimmer-Kleikamp SH, Lock P, Schoenwaelder SM, Down M, Boyd AW, Alewood PF, Lackmann M (2002) Ephrin-A5 induces rounding, blebbing and de-adhesion of EphA3-expressing 293T and melanoma cells by CrkII and Rho-mediated signalling. J Cell Sci 115:1059–1072
Barbolina MV, Stack MS (2008) Membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase: substrate diversity in pericellular proteolysis. Semin Cell Dev Biol 19:24–33
Kryczka J, Stasiak M, Dziki L, Mik M, Dziki A, Cierniewski C (2012) Matrix metalloproteinase-2 cleavage of the beta1 integrin ectodomain facilitates colon cancer cell motility. J Biol Chem 287:36556–36566
Ieguchi K, Tomita T, Omori T, Komatsu A, Deguchi A, Masuda J, Duffy SL, Coulthard MG, Boyd A, Maru Y (2013) ADAM12-cleaved ephrin-A1 contributes to lung metastasis. Oncogene
Lehti K, Allen E, Birkedal-Hansen H, Holmbeck K, Miyake Y, Chun TH, Weiss SJ (2005) An MT1-MMP–PDGF receptor-beta axis regulates mural cell investment of the microvasculature. Genes Dev 19:979–991
Sugiyama N, Varjosalo M, Meller P, Lohi J, Chan KM, Zhou Z, Alitalo K, Taipale J, Keski-Oja J, Lehti K (2010) FGF receptor-4 (FGFR4) polymorphism acts as an activity switch of a membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase-FGFR4 complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 107:15786–15791
Sugiyama N, Varjosalo M, Meller P, Lohi J, Hyytiainen M, Kilpinen S, Kallioniemi O, Ingvarsen S, Engelholm LH, Taipale J, Alitalo K, Keski-Oja J, Lehti K (2010) Fibroblast growth factor receptor 4 regulates tumor invasion by coupling fibroblast growth factor signaling to extracellular matrix degradation. Cancer Res 70:7851–7861
Chan KM, Wong HL, Jin G, Liu B, Cao R, Cao Y, Lehti K, Tryggvason K, Zhou Z (2012) MT1-MMP inactivates ADAM9 to regulate FGFR2 signaling and calvarial osteogenesis. Dev Cell 22:1176–1190
Eisenach PA, Roghi C, Fogarasi M, Murphy G, English WR (2010) MT1-MMP regulates VEGF-A expression through a complex with VEGFR-2 and Src. J Cell Sci 123:4182–4193
Fu HL, Sohail A, Valiathan RR, Wasinski BD, Kumarasiri M, Mahasenan KV, Bernardo MM, Tokmina-Roszyk D, Fields GB, Mobashery S, Fridman R (2013) Shedding of discoidin domain receptor 1 by membrane-type matrix metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem 288:12114–12129
Niiya M, Endo M, Shang D, Zoltick PW, Muvarak NE, Cao W, Jin SY, Skipwith CG, Motto DG, Flake AW, Zheng XL (2009) Correction of ADAMTS13 deficiency by in utero gene transfer of lentiviral vector encoding ADAMTS13 genes. Mol Ther 17:34–41
Wong HL, Cao R, Jin G, Chan KM, Cao Y, Zhou Z (2012) When MT1-MMP meets ADAMs. Cell Cycle 11:2793–2798
Salaita K, Nair PM, Petit RS, Neve RM, Das D, Gray JW, Groves JT (2010) Restriction of receptor movement alters cellular response: physical force sensing by EphA2. Science 327:1380–1385
Nyalendo C, Michaud M, Beaulieu E, Roghi C, Murphy G, Gingras D, Beliveau R (2007) Src-dependent phosphorylation of membrane type I matrix metalloproteinase on cytoplasmic tyrosine 573: role in endothelial and tumor cell migration. J Biol Chem 282:15690–15699
Tatti O, Arjama M, Ranki A, Weiss SJ, Keski-Oja J, Lehti K (2011) Membrane-type-3 matrix metalloproteinase (MT3-MMP) functions as a matrix composition-dependent effector of melanoma cell invasion. PLoS ONE 6:e28325
Rowe RG, Weiss SJ (2009) Navigating ECM barriers at the invasive front: the cancer cell–stroma interface. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 25:567–595
Sabeh F, Ota I, Holmbeck K, Birkedal-Hansen H, Soloway P, Balbin M, Lopez-Otin C, Shapiro S, Inada M, Krane S, Allen E, Chung D, Weiss SJ (2004) Tumor cell traffic through the extracellular matrix is controlled by the membrane-anchored collagenase MT1-MMP. J Cell Biol 167:769–781
Tam EM, Morrison CJ, Wu YI, Stack MS, Overall CM (2004) Membrane protease proteomics: isotope-coded affinity tag MS identification of undescribed MT1-matrix metalloproteinase substrates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:6917–6922
Hwang YS, Park KK, Chung WY (2012) Invadopodia formation in oral squamous cell carcinoma: the role of epidermal growth factor receptor signalling. Arch Oral Biol 57:335–343
Steinle JJ, Meininger CJ, Forough R, Wu G, Wu MH, Granger HJ (2002) Eph B4 receptor signaling mediates endothelial cell migration and proliferation via the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase pathway. J Biol Chem 277:43830–43835
Lin KT, Sloniowski S, Ethell DW, Ethell IM (2008) Ephrin-B2-induced cleavage of EphB2 receptor is mediated by matrix metalloproteinases to trigger cell repulsion. J Biol Chem 283:28969–28979
Inoue E, Deguchi-Tawarada M, Togawa A, Matsui C, Arita K, Katahira-Tayama S, Sato T, Yamauchi E, Oda Y, Takai Y (2009) Synaptic activity prompts gamma-secretase-mediated cleavage of EphA4 and dendritic spine formation. J Cell Biol 185:551–564
Tomita T, Tanaka S, Morohashi Y, Iwatsubo T (2006) Presenilin-dependent intramembrane cleavage of ephrin-B1. Mol Neurodegener 1:2
Georgakopoulos A, Litterst C, Ghersi E, Baki L, Xu C, Serban G, Robakis NK (2006) Metalloproteinase/Presenilin1 processing of ephrinB regulates EphB-induced Src phosphorylation and signaling. EMBO J 25:1242–1252
Litterst C, Georgakopoulos A, Shioi J, Ghersi E, Wisniewski T, Wang R, Ludwig A, Robakis NK (2007) Ligand binding and calcium influx induce distinct ectodomain/gamma-secretase-processing pathways of EphB2 receptor. J Biol Chem 282:16155–16163
Wykosky J, Debinski W (2008) The EphA2 receptor and ephrinA1 ligand in solid tumors: function and therapeutic targeting. Mol Cancer Res 6:1795–1806
Teng L, Nakada M, Furuyama N, Sabit H, Furuta T, Hayashi Y, Takino T, Dong Y, Sato H, Sai Y, Miyamoto K, Berens ME, Zhao SG, Hamada J (2013) Ligand-dependent EphB1 signaling suppresses glioma invasion and correlates with patient survival. Neuro Oncol 15:1710–1720
Wykosky J, Gibo DM, Stanton C, Debinski W (2005) EphA2 as a novel molecular marker and target in glioblastoma multiforme. Mol Cancer Res 3:541–551
Liu DP, Wang Y, Koeffler HP, Xie D (2007) Ephrin-A1 is a negative regulator in glioma through down-regulation of EphA2 and FAK. Int J Oncol 30:865–871
Parri M, Buricchi F, Taddei ML, Giannoni E, Raugei G, Ramponi G, Chiarugi P (2005) EphrinA1 repulsive response is regulated by an EphA2 tyrosine phosphatase. J Biol Chem 280:34008–34018
Guo H, Miao H, Gerber L, Singh J, Denning MF, Gilliam AC, Wang B (2006) Disruption of EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase leads to increased susceptibility to carcinogenesis in mouse skin. Cancer Res 66:7050–7058
Pratt RL, Kinch MS (2002) Activation of the EphA2 tyrosine kinase stimulates the MAP/ERK kinase signaling cascade. Oncogene 21:7690–7699
Nasreen N, Mohammed KA, Lai Y, Antony VB (2007) Receptor EphA2 activation with ephrinA1 suppresses growth of malignant mesothelioma (MM). Cancer Lett 258:215–222
Liu F, Park PJ, Lai W, Maher E, Chakravarti A, Durso L, Jiang X, Yu Y, Brosius A, Thomas M, Chin L, Brennan C, DePinho RA, Kohane I, Carroll RS, Black PM, Johnson MD (2006) A genome-wide screen reveals functional gene clusters in the cancer genome and identifies EphA2 as a mitogen in glioblastoma. Cancer Res 66:10815–10823
Margaryan NV, Strizzi L, Abbott DE, Seftor EA, Rao MS, Hendrix MJ, Hess AR (2009) EphA2 as a promoter of melanoma tumorigenicity. Cancer Biol Ther 8:279–288
Dodelet VC, Pasquale EB (2000) Eph receptors and ephrin ligands: embryogenesis to tumorigenesis. Oncogene 19:5614–5619
Wang LF, Fokas E, Bieker M, Rose F, Rexin P, Zhu Y, Pagenstecher A, Engenhart-Cabillic R, An HX (2008) Increased expression of EphA2 correlates with adverse outcome in primary and recurrent glioblastoma multiforme patients. Oncol Rep 19:151–156
Goparaju C, Donington JS, Hsu T, Harrington R, Hirsch N, Pass HI (2013) Overexpression of EPH receptor B2 in malignant mesothelioma correlates with oncogenic behavior. J Thorac Oncol 8:1203–1211
Batlle E, Bacani J, Begthel H, Jonkheer S, Gregorieff A, van de Born M, Malats N, Sancho E, Boon E, Pawson T, Gallinger S, Pals S, Clevers H (2005) EphB receptor activity suppresses colorectal cancer progression. Nature 435:1126–1130
Xiao Z, Carrasco R, Kinneer K, Sabol D, Jallal B, Coats S, Tice DA (2012) EphB4 promotes or suppresses Ras/MEK/ERK pathway in a context-dependent manner: implications for EphB4 as a cancer target. Cancer Biol Ther 13:630–637
Shin D, Garcia-Cardena G, Hayashi S, Gerety S, Asahara T, Stavrakis G, Isner J, Folkman J, Gimbrone MA Jr, Anderson DJ (2001) Expression of ephrinB2 identifies a stable genetic difference between arterial and venous vascular smooth muscle as well as endothelial cells, and marks subsets of microvessels at sites of adult neovascularization. Dev Biol 230:139–150
Noren NK, Lu M, Freeman AL, Koolpe M, Pasquale EB (2004) Interplay between EphB4 on tumor cells and vascular ephrin-B2 regulates tumor growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:5583–5588
Sawai Y, Tamura S, Fukui K, Ito N, Imanaka K, Saeki A, Sakuda S, Kiso S, Matsuzawa Y (2003) Expression of ephrin-B1 in hepatocellular carcinoma: possible involvement in neovascularization. J Hepatol 39:991–996
Adams RH, Wilkinson GA, Weiss C, Diella F, Gale NW, Deutsch U, Risau W, Klein R (1999) Roles of ephrinB ligands and EphB receptors in cardiovascular development: demarcation of arterial/venous domains, vascular morphogenesis, and sprouting angiogenesis. Genes Dev 13:295–306
Gerety SS, Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ (1999) Symmetrical mutant phenotypes of the receptor EphB4 and its specific transmembrane ligand ephrin-B2 in cardiovascular development. Mol Cell 4:403–414
Wang HU, Chen ZF, Anderson DJ (1998) Molecular distinction and angiogenic interaction between embryonic arteries and veins revealed by ephrin-B2 and its receptor Eph-B4. Cell 93:741–753
Chen J, Hicks D, Brantley-Sieders D, Cheng N, McCollum GW, Qi-Werdich X, Penn J (2006) Inhibition of retinal neovascularization by soluble EphA2 receptor. Exp Eye Res 82:664–673
Erber R, Eichelsbacher U, Powajbo V, Korn T, Djonov V, Lin J, Hammes HP, Grobholz R, Ullrich A, Vajkoczy P (2006) EphB4 controls blood vascular morphogenesis during postnatal angiogenesis. EMBO J 25:628–641
Gale NW, Baluk P, Pan L, Kwan M, Holash J, DeChiara TM, McDonald DM, Yancopoulos GD (2001) Ephrin-B2 selectively marks arterial vessels and neovascularization sites in the adult, with expression in both endothelial and smooth-muscle cells. Dev Biol 230:151–160
Makinen T, Adams RH, Bailey J, Lu Q, Ziemiecki A, Alitalo K, Klein R, Wilkinson GA (2005) PDZ interaction site in ephrinB2 is required for the remodeling of lymphatic vasculature. Genes Dev 19:397–410
Sawamiphak S, Seidel S, Essmann CL, Wilkinson GA, Pitulescu ME, Acker T, Acker-Palmer A (2010) Ephrin-B2 regulates VEGFR2 function in developmental and tumour angiogenesis. Nature 465:487–491
Wang Y, Nakayama M, Pitulescu ME, Schmidt TS, Bochenek ML, Sakakibara A, Adams S, Davy A, Deutsch U, Luthi U, Barberis A, Benjamin LE, Makinen T, Nobes CD, Adams RH (2010) Ephrin-B2 controls VEGF-induced angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Nature 465:483–486
Cheng N, Brantley DM, Chen J (2002) The ephrins and Eph receptors in angiogenesis. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 13:75–85
Sullivan DC, Bicknell R (2003) New molecular pathways in angiogenesis. Br J Cancer 89:228–231
Brantley DM, Cheng N, Thompson EJ, Lin Q, Brekken RA, Thorpe PE, Muraoka RS, Cerretti DP, Pozzi A, Jackson D, Lin C, Chen J (2002) Soluble Eph A receptors inhibit tumor angiogenesis and progression in vivo. Oncogene 21:7011–7026
Cheng N, Brantley DM, Liu H, Lin Q, Enriquez M, Gale N, Yancopoulos G, Cerretti DP, Daniel TO, Chen J (2002) Blockade of EphA receptor tyrosine kinase activation inhibits vascular endothelial cell growth factor-induced angiogenesis. Mol Cancer Res 1:2–11
Dobrzanski P, Hunter K, Jones-Bolin S, Chang H, Robinson C, Pritchard S, Zhao H, Ruggeri B (2004) Antiangiogenic and antitumor efficacy of EphA2 receptor antagonist. Cancer Res 64:910–919
Brantley-Sieders DM, Caughron J, Hicks D, Pozzi A, Ruiz JC, Chen J (2004) EphA2 receptor tyrosine kinase regulates endothelial cell migration and vascular assembly through phosphoinositide 3-kinase-mediated Rac1 GTPase activation. J Cell Sci 117:2037–2049
Maniotis AJ, Folberg R, Hess A, Seftor EA, Gardner LM, Pe’er J, Trent JM, Meltzer PS, Hendrix MJ (1999) Vascular channel formation by human melanoma cells in vivo and in vitro: vasculogenic mimicry. Am J Pathol 155:739–752
Hendrix MJ, Seftor EA, Hess AR, Seftor RE (2003) Vasculogenic mimicry and tumour-cell plasticity: lessons from melanoma. Nat Rev Cancer 3:411–421
Hess AR, Seftor EA, Gardner LM, Carles-Kinch K, Schneider GB, Seftor RE, Kinch MS, Hendrix MJ (2001) Molecular regulation of tumor cell vasculogenic mimicry by tyrosine phosphorylation: role of epithelial cell kinase (Eck/EphA2). Cancer Res 61:3250–3255
Hess AR, Margaryan NV, Seftor EA, Hendrix MJ (2007) Deciphering the signaling events that promote melanoma tumor cell vasculogenic mimicry and their link to embryonic vasculogenesis: role of the Eph receptors. Dev Dyn 236:3283–3296
Hess AR, Seftor EA, Seftor RE, Hendrix MJ (2003) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase regulates membrane Type 1-matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) and MMP-2 activity during melanoma cell vasculogenic mimicry. Cancer Res 63:4757–4762
Seftor RE, Seftor EA, Koshikawa N, Meltzer PS, Gardner LM, Bilban M, Stetler-Stevenson WG, Quaranta V, Hendrix MJ (2001) Cooperative interactions of laminin 5 gamma2 chain, matrix metalloproteinase-2, and membrane type-1-matrix/metalloproteinase are required for mimicry of embryonic vasculogenesis by aggressive melanoma. Cancer Res 61:6322–6327
Nomura T, Goritz C, Catchpole T, Henkemeyer M, Frisen J (2010) EphB signaling controls lineage plasticity of adult neural stem cell niche cells. Cell Stem Cell 7:730–743
Conover JC, Doetsch F, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Gale NW, Yancopoulos GD, Alvarez-Buylla A (2000) Disruption of Eph/ephrin signaling affects migration and proliferation in the adult subventricular zone. Nat Neurosci 3:1091–1097
Furne C, Ricard J, Cabrera JR, Pays L, Bethea JR, Mehlen P, Liebl DJ (2009) EphrinB3 is an anti-apoptotic ligand that inhibits the dependence receptor functions of EphA4 receptors during adult neurogenesis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1793:231–238
Lickliter JD, Smith FM, Olsson JE, Mackwell KL, Boyd AW (1996) Embryonic stem cells express multiple Eph-subfamily receptor tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:145–150
van de Wetering M, Sancho E, Verweij C, de Lau W, Oving I, Hurlstone A, van der Horn K, Batlle E, Coudreuse D, Haramis AP, Tjon-Pon-Fong M, Moerer P, van den Born M, Soete G, Pals S, Eilers M, Medema R, Clevers H (2002) The beta-catenin/TCF-4 complex imposes a crypt progenitor phenotype on colorectal cancer cells. Cell 111:241–250
Holmberg J, Genander M, Halford MM, Anneren C, Sondell M, Chumley MJ, Silvany RE, Henkemeyer M, Frisen J (2006) EphB receptors coordinate migration and proliferation in the intestinal stem cell niche. Cell 125:1151–1163
Ming GL, Song H (2011) Adult neurogenesis in the mammalian brain: significant answers and significant questions. Neuron 70:687–702
Doetsch F, Garcia-Verdugo JM, Alvarez-Buylla A (1997) Cellular composition and three-dimensional organization of the subventricular germinal zone in the adult mammalian brain. J Neurosci 17:5046–5061
Carlen M, Meletis K, Goritz C, Darsalia V, Evergren E, Tanigaki K, Amendola M, Barnabe-Heider F, Yeung MS, Naldini L, Honjo T, Kokaia Z, Shupliakov O, Cassidy RM, Lindvall O, Frisen J (2009) Forebrain ependymal cells are Notch-dependent and generate neuroblasts and astrocytes after stroke. Nat Neurosci 12:259–267
Qiu R, Wang X, Davy A, Wu C, Murai K, Zhang H, Flanagan JG, Soriano P, Lu Q (2008) Regulation of neural progenitor cell state by ephrin-B. J Cell Biol 181:973–983
Aoki M, Yamashita T, Tohyama M (2004) EphA receptors direct the differentiation of mammalian neural precursor cells through a mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent pathway. J Biol Chem 279:32643–32650
Ivanova NB, Dimos JT, Schaniel C, Hackney JA, Moore KA, Lemischka IR (2002) A stem cell molecular signature. Science 298:601–604
Steidl U, Bork S, Schaub S, Selbach O, Seres J, Aivado M, Schroeder T, Rohr UP, Fenk R, Kliszewski S, Maercker C, Neubert P, Bornstein SR, Haas HL, Kobbe G, Tenen DG, Haas R, Kronenwett R (2004) Primary human CD34+ hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells express functionally active receptors of neuromediators. Blood 104:81–88
Lazarova P, Wu Q, Kvalheim G, Suo Z, Haakenstad KW, Metodiev K, Nesland JM (2006) Growth factor receptors in hematopoietic stem cells: EPH family expression in CD34+ and CD133+ cell populations from mobilized peripheral blood. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 19:49–56
Inada T, Iwama A, Sakano S, Ohno M, Sawada K, Suda T (1997) Selective expression of the receptor tyrosine kinase, HTK, on human erythroid progenitor cells. Blood 89:2757–2765
Wang Z, Cohen K, Shao Y, Mole P, Dombkowski D, Scadden DT (2004) Ephrin receptor, EphB4, regulates ES cell differentiation of primitive mammalian hemangioblasts, blood, cardiomyocytes, and blood vessels. Blood 103:100–109
Suenobu S, Takakura N, Inada T, Yamada Y, Yuasa H, Zhang XQ, Sakano S, Oike Y, Suda T (2002) A role of EphB4 receptor and its ligand, ephrin-B2, in erythropoiesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 293:1124–1131
Nguyen TM, Arthur A, Hayball JD, Gronthos S (2013) EphB and Ephrin-B interactions mediate human mesenchymal stem cell suppression of activated T-cells. Stem Cells Dev 22:2751–2764
Irie N, Takada Y, Watanabe Y, Matsuzaki Y, Naruse C, Asano M, Iwakura Y, Suda T, Matsuo K (2009) Bidirectional signaling through ephrinA2–EphA2 enhances osteoclastogenesis and suppresses osteoblastogenesis. J Biol Chem 284:14637–14644
Zhao C, Irie N, Takada Y, Shimoda K, Miyamoto T, Nishiwaki T, Suda T, Matsuo K (2006) Bidirectional ephrinB2–EphB4 signaling controls bone homeostasis. Cell Metab 4:111–121
Cheng HJ, Nakamoto M, Bergemann AD, Flanagan JG (1995) Complementary gradients in expression and binding of ELF-1 and Mek4 in development of the topographic retinotectal projection map. Cell 82:371–381
Sefton M, Araujo M, Nieto MA (1997) Novel expression gradients of Eph-like receptor tyrosine kinases in the developing chick retina. Dev Biol 188:363–368
Brittis PA, Lu Q, Flanagan JG (2002) Axonal protein synthesis provides a mechanism for localized regulation at an intermediate target. Cell 110:223–235
Tanaka M, Ohashi R, Nakamura R, Shinmura K, Kamo T, Sakai R, Sugimura H (2004) Tiam1 mediates neurite outgrowth induced by ephrin-B1 and EphA2. EMBO J 23:1075–1088
Gopal U, Bohonowych JE, Lema-Tome C, Liu A, Garrett-Mayer E, Wang B, Isaacs JS (2011) A novel extracellular Hsp90-mediated co-receptor function for LRP1 regulates EphA2-dependent glioblastoma cell invasion. PLoS ONE 6:e17649
Miao H, Wang B (2012) EphA receptor signaling—complexity and emerging themes. Semin Cell Dev Biol 23:16–25
Marshall CJ (1995) Specificity of receptor tyrosine kinase signaling: transient versus sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase activation. Cell 80:179–185
Chen JY, Lin JR, Cimprich KA, Meyer T (2012) A two-dimensional ERK-AKT signaling code for an NGF-triggered cell-fate decision. Mol Cell 45:196–209
Santos SD, Verveer PJ, Bastiaens PI (2007) Growth factor-induced MAPK network topology shapes Erk response determining PC-12 cell fate. Nat Cell Biol 9:324–330
Sasagawa S, Ozaki Y, Fujita K, Kuroda S (2005) Prediction and validation of the distinct dynamics of transient and sustained ERK activation. Nat Cell Biol 7:365–373
Huang F, Reeves K, Han X, Fairchild C, Platero S, Wong TW, Lee F, Shaw P, Clark E (2007) Identification of candidate molecular markers predicting sensitivity in solid tumors to dasatinib: rationale for patient selection. Cancer Res 67:2226–2238
Conway A, Vazin T, Spelke DP, Rode NA, Healy KE, Kane RS, Schaffer DV (2013) Multivalent ligands control stem cell behaviour in vitro and in vivo. Nat Nanotechnol 8:831–838
Chen J, Li Y, Yu TS, McKay RM, Burns DK, Kernie SG, Parada LF (2012) A restricted cell population propagates glioblastoma growth after chemotherapy. Nature 488:522–526
Xi HQ, Wu XS, Wei B, Chen L (2012) Eph receptors and ephrins as targets for cancer therapy. J Cell Mol Med 16:2894–2909
Tandon M, Vemula SV, Mittal SK (2011) Emerging strategies for EphA2 receptor targeting for cancer therapeutics. Expert Opin Ther Targets 15:31–51
Wykosky J, Gibo DM, Debinski W (2007) A novel, potent, and specific ephrinA1-based cytotoxin against EphA2 receptor expressing tumor cells. Mol Cancer Ther 6:3208–3218
Friedl P, Wolf K (2010) Plasticity of cell migration: a multiscale tuning model. J Cell Biol 188:11–19
Harunaga JS, Yamada KM (2011) Cell–matrix adhesions in 3D. Matrix Biol 30:363–368
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gucciardo, E., Sugiyama, N. & Lehti, K. Eph- and ephrin-dependent mechanisms in tumor and stem cell dynamics. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 71, 3685–3710 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1633-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-014-1633-0