Abstract
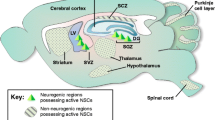
The adult brain most probably reaches its highest degree of plasticity with the lifelong generation and integration of new neurons in the hippocampus and olfactory system. Neural precursor cells (NPCs) residing both in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus and in the subventricular zone of the lateral ventricles continuously generate neurons that populate the dentate gyrus and the olfactory bulb, respectively. The regulation of NPC proliferation in the adult brain has been widely investigated in the past few years. Yet, the intrinsic cell cycle machinery underlying NPC proliferation remains largely unexplored. In this review, we discuss the cell cycle components that are involved in the regulation of NPC proliferation in both neurogenic areas of the adult brain.

Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Ma DK, Bonaguidi MA, Ming GL, Song H (2009) Adult neural stem cells in the mammalian central nervous system. Cell Res 19(6):672–682
Imayoshi I, Sakamoto M, Ohtsuka T, Kageyama R (2009) Continuous neurogenesis in the adult brain. Dev Growth Differ 51(3):379–386
Lindvall O, Kokaia Z (2006) Stem cells for the treatment of neurological disorders. Nature 441(7097):1094–1096
Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH (2008) Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 132(4):645–660
Malumbres M, Barbacid M (2005) Mammalian cyclin-dependent kinases. Trends Biochem Sci 30(11):630–641
Lundberg AS, Weinberg RA (1998) Functional inactivation of the retinoblastoma protein requires sequential modification by at least two distinct cyclin-cdk complexes. Mol Cell Biol 18(2):753–761
Harbour JW, Luo RX, Dei Santi A, Postigo AA, Dean DC (1999) Cdk phosphorylation triggers sequential intramolecular interactions that progressively block Rb functions as cells move through G1. Cell 98(6):859–869
Nigg EA (2001) Mitotic kinases as regulators of cell division and its checkpoints. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 2(1):21–32
Sherr CJ, Roberts JM (1995) Inhibitors of mammalian G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Genes Dev 9(10):1149–1163
Malumbres M, Barbacid M (2009) Cell cycle, CDKs and cancer: a changing paradigm. Nat Rev Cancer 9(3):153–166
Satyanarayana A, Kaldis P (2009) Mammalian cell-cycle regulation: several Cdks, numerous cyclins and diverse compensatory mechanisms. Oncogene 28(33):2925–2939
Malumbres M, Sotillo R, Santamaria D, Galan J, Cerezo A, Ortega S, Dubus P, Barbacid M (2004) Mammalian cells cycle without the D-type cyclin-dependent kinases Cdk4 and Cdk6. Cell 118(4):493–504
Kozar K, Ciemerych MA, Rebel VI, Shigematsu H, Zagozdzon A, Sicinska E, Geng Y, Yu Q, Bhattacharya S, Bronson RT, Akashi K, Sicinski P (2004) Mouse development and cell proliferation in the absence of D-cyclins. Cell 118(4):477–491
Berthet C, Aleem E, Coppola V, Tessarollo L, Kaldis P (2003) Cdk2 knockout mice are viable. Curr Biol 13(20):1775–1785
Pagano M, Jackson PK (2004) Wagging the dogma; tissue-specific cell cycle control in the mouse embryo. Cell 118(5):535–538
Fero ML, Rivkin M, Tasch M, Porter P, Carow CE, Firpo E, Polyak K, Tsai LH, Broudy V, Perlmutter RM, Kaushansky K, Roberts JM (1996) A syndrome of multiorgan hyperplasia with features of gigantism, tumorigenesis, and female sterility in p27(Kip1)-deficient mice. Cell 85(5):733–744
Callaghan DA, Dong L, Callaghan SM, Hou YX, Dagnino L, Slack RS (1999) Neural precursor cells differentiating in the absence of Rb exhibit delayed terminal mitosis and deregulated E2F 1 and 3 activity. Dev Biol 207(2):257–270
Huard JM, Forster CC, Carter ML, Sicinski P, Ross ME (1999) Cerebellar histogenesis is disturbed in mice lacking cyclin D2. Development 126(9):1927–1935
Ferguson KL, Callaghan SM, O’Hare MJ, Park DS, Slack RS (2000) The Rb-CDK4/6 signaling pathway is critical in neural precursor cell cycle regulation. J Biol Chem 275(43):33593–33600
Cooper-Kuhn CM, Vroemen M, Brown J, Ye H, Thompson MA, Winkler J, Kuhn HG (2002) Impaired adult neurogenesis in mice lacking the transcription factor E2F1. Mol Cell Neurosci 21(2):312–323
Zhu Y, Jin K, Mao XO, Greenberg DA (2003) Vascular endothelial growth factor promotes proliferation of cortical neuron precursors by regulating E2F expression. FASEB J 17(2):186–193
Lukaszewicz A, Savatier P, Cortay V, Giroud P, Huissoud C, Berland M, Kennedy H, Dehay C (2005) G1 phase regulation, area-specific cell cycle control, and cytoarchitectonics in the primate cortex. Neuron 47(3):353–364
Lange C, Huttner WB, Calegari F (2009) Cdk4/cyclinD1 overexpression in neural stem cells shortens G1, delays neurogenesis, and promotes the generation and expansion of basal progenitors. Cell Stem Cell 5(3):320–331
Pilaz LJ, Patti D, Marcy G, Ollier E, Pfister S, Douglas RJ, Betizeau M, Gautier E, Cortay V, Doerflinger N, Kennedy H, Dehay C (2009) Forced G1-phase reduction alters mode of division, neuron number, and laminar phenotype in the cerebral cortex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(51):21924–21929
Malumbres M, Harlow E, Hunt T, Hunter T, Lahti JM, Manning G, Morgan DO, Tsai LH, Wolgemuth DJ (2009) Cyclin-dependent kinases: a family portrait. Nat Cell Biol 11(11):1275–1276
van den Heuvel S, Harlow E (1993) Distinct roles for cyclin-dependent kinases in cell cycle control. Science 262(5142):2050–2054
Ye X, Zhu C, Harper JW (2001) A premature-termination mutation in the Mus musculus cyclin-dependent kinase 3 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(4):1682–1686
Tsai LH, Delalle I, Caviness VS Jr, Chae T, Harlow E (1994) p35 is a neural-specific regulatory subunit of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Nature 371(6496):419–423
Lew J, Huang QQ, Qi Z, Winkfein RJ, Aebersold R, Hunt T, Wang JH (1994) A brain-specific activator of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Nature 371(6496):423–426
Tang D, Yeung J, Lee KY, Matsushita M, Matsui H, Tomizawa K, Hatase O, Wang JH (1995) An isoform of the neuronal cyclin-dependent kinase 5 (Cdk5) activator. J Biol Chem 270(45):26897–26903
Hellmich MR, Pant HC, Wada E, Battey JF (1992) Neuronal cdc2-like kinase: a cdc2-related protein kinase with predominantly neuronal expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89(22):10867–10871
Santamaria D, Barriere C, Cerqueira A, Hunt S, Tardy C, Newton K, Caceres JF, Dubus P, Malumbres M, Barbacid M (2007) Cdk1 is sufficient to drive the mammalian cell cycle. Nature 448(7155):811–815
Rane SG, Dubus P, Mettus RV, Galbreath EJ, Boden G, Reddy EP, Barbacid M (1999) Loss of Cdk4 expression causes insulin-deficient diabetes and Cdk4 activation results in beta-islet cell hyperplasia. Nat Genet 22(1):44–52
Tsutsui T, Hesabi B, Moons DS, Pandolfi PP, Hansel KS, Koff A, Kiyokawa H (1999) Targeted disruption of CDK4 delays cell cycle entry with enhanced p27(Kip1) activity. Mol Cell Biol 19(10):7011–7019
Ortega S, Prieto I, Odajima J, Martin A, Dubus P, Sotillo R, Barbero JL, Malumbres M, Barbacid M (2003) Cyclin-dependent kinase 2 is essential for meiosis but not for mitotic cell division in mice. Nat Genet 35(1):25–31
Vandenbosch R, Borgs L, Beukelaers P, Foidart A, Nguyen L, Moonen G, Berthet C, Kaldis P, Gallo V, Belachew S, Malgrange B (2007) CDK2 is dispensable for adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Cell Cycle 6(24):3065–3069
Golsteyn RM (2005) Cdk1 and Cdk2 complexes (cyclin dependent kinases) in apoptosis: a role beyond the cell cycle. Cancer Lett 217(2):129–138
Copani A, Condorelli F, Caruso A, Vancheri C, Sala A, Giuffrida Stella AM, Canonico PL, Nicoletti F, Sortino MA (1999) Mitotic signaling by beta-amyloid causes neuronal death. FASEB J 13(15):2225–2234
Rideout HJ, Wang Q, Park DS, Stefanis L (2003) Cyclin-dependent kinase activity is required for apoptotic death but not inclusion formation in cortical neurons after proteasomal inhibition. J Neurosci 23(4):1237–1245
Jablonska B, Aguirre A, Vandenbosch R, Belachew S, Berthet C, Kaldis P, Gallo V (2007) Cdk2 is critical for proliferation and self-renewal of neural progenitor cells in the adult subventricular zone. J Cell Biol 179(6):1231–1245
Beukelaers P, Vandenbosch R, Caron N, Nguyen L, Belachew S, Moonen G, Kiyokawa H, Barbacid M, Santamaria D, Malgrange B (2011) Cdk6-Dependent Regulation of G(1) Length Controls Adult Neurogenesis. Stem Cells 29(4):713–724
Calegari F, Huttner WB (2003) An inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases that lengthens, but does not arrest, neuroepithelial cell cycle induces premature neurogenesis. J Cell Sci 116(Pt 24):4947–4955
Ohshima T, Hirasawa M, Tabata H, Mutoh T, Adachi T, Suzuki H, Saruta K, Iwasato T, Itohara S, Hashimoto M, Nakajima K, Ogawa M, Kulkarni AB, Mikoshiba K (2007) Cdk5 is required for multipolar-to-bipolar transition during radial neuronal migration and proper dendrite development of pyramidal neurons in the cerebral cortex. Development 134(12):2273–2282
Ohshima T, Mikoshiba K (2002) Reelin signaling and Cdk5 in the control of neuronal positioning. Mol Neurobiol 26(2–3):153–166
Hirota Y, Ohshima T, Kaneko N, Ikeda M, Iwasato T, Kulkarni AB, Mikoshiba K, Okano H, Sawamoto K (2007) Cyclin-dependent kinase 5 is required for control of neuroblast migration in the postnatal subventricular zone. J Neurosci 27(47):12829–12838
Jessberger S, Aigner S, Clemenson GD Jr, Toni N, Lie DC, Karalay O, Overall R, Kempermann G, Gage FH (2008) Cdk5 regulates accurate maturation of newborn granule cells in the adult hippocampus. PLoS Biol 6(11):e272
Lagace DC, Benavides DR, Kansy JW, Mapelli M, Greengard P, Bibb JA, Eisch AJ (2008) Cdk5 is essential for adult hippocampal neurogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(47):18567–18571
Fantl V, Stamp G, Andrews A, Rosewell I, Dickson C (1995) Mice lacking cyclin D1 are small and show defects in eye and mammary gland development. Genes Dev 9(19):2364–2372
Sicinski P, Donaher JL, Parker SB, Li T, Fazeli A, Gardner H, Haslam SZ, Bronson RT, Elledge SJ, Weinberg RA (1995) Cyclin D1 provides a link between development and oncogenesis in the retina and breast. Cell 82(4):621–630
Ma C, Papermaster D, Cepko CL (1998) A unique pattern of photoreceptor degeneration in cyclin D1 mutant mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95(17):9938–9943
Sicinski P, Donaher JL, Geng Y, Parker SB, Gardner H, Park MY, Robker RL, Richards JS, McGinnis LK, Biggers JD, Eppig JJ, Bronson RT, Elledge SJ, Weinberg RA (1996) Cyclin D2 is an FSH-responsive gene involved in gonadal cell proliferation and oncogenesis. Nature 384(6608):470–474
Robker RL, Richards JS (1998) Hormone-induced proliferation and differentiation of granulosa cells: a coordinated balance of the cell cycle regulators cyclin D2 and p27Kip1. Mol Endocrinol 12(7):924–940
Sicinska E, Aifantis I, Le Cam L, Swat W, Borowski C, Yu Q, Ferrando AA, Levin SD, Geng Y, von Boehmer H, Sicinski P (2003) Requirement for cyclin D3 in lymphocyte development and T cell leukemias. Cancer Cell 4(6):451–461
Jaholkowski P, Kiryk A, Jedynak P, Ben Abdallah NM, Knapska E, Kowalczyk A, Piechal A, Blecharz-Klin K, Figiel I, Lioudyno V, Widy-Tyszkiewicz E, Wilczynski GM, Lipp HP, Kaczmarek L, Filipkowski RK (2009) New hippocampal neurons are not obligatory for memory formation; cyclin D2 knockout mice with no adult brain neurogenesis show learning. Learn Mem 16(7):439–451
Kowalczyk A, Filipkowski RK, Rylski M, Wilczynski GM, Konopacki FA, Jaworski J, Ciemerych MA, Sicinski P, Kaczmarek L (2004) The critical role of cyclin D2 in adult neurogenesis. J Cell Biol 167(2):209–213
Kempermann G, Kuhn HG, Gage FH (1997) More hippocampal neurons in adult mice living in an enriched environment. Nature 386(6624):493–495
Steiner B, Zurborg S, Horster H, Fabel K, Kempermann G (2008) Differential 24 h responsiveness of Prox1-expressing precursor cells in adult hippocampal neurogenesis to physical activity, environmental enrichment, and kainic acid-induced seizures. Neuroscience 154(2):521–529
van Praag H, Kempermann G, Gage FH (2000) Neural consequences of environmental enrichment. Nat Rev Neurosci 1(3):191–198
Assoian RK, Zhu X (1997) Cell anchorage and the cytoskeleton as partners in growth factor dependent cell cycle progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol 9(1):93–98
Matsushime H, Roussel MF, Ashmun RA, Sherr CJ (1991) Colony-stimulating factor 1 regulates novel cyclins during the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cell 65(4):701–713
Glickstein SB, Moore H, Slowinska B, Racchumi J, Suh M, Chuhma N, Ross ME (2007) Selective cortical interneuron and GABA deficits in cyclin D2-null mice. Development 134(22):4083–4093
Muramatsu R, Ikegaya Y, Matsuki N, Koyama R (2007) Neonatally born granule cells numerically dominate adult mice dentate gyrus. Neuroscience 148(3):593–598
Mathews EA, Morgenstern NA, Piatti VC, Zhao C, Jessberger S, Schinder AF, Gage FH (2010) A distinctive layering pattern of mouse dentate granule cells is generated by developmental and adult neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol 518(22):4479–4490
Imayoshi I, Sakamoto M, Ohtsuka T, Takao K, Miyakawa T, Yamaguchi M, Mori K, Ikeda T, Itohara S, Kageyama R (2008) Roles of continuous neurogenesis in the structural and functional integrity of the adult forebrain. Nat Neurosci 11(10):1153–1161
Krishnamurthy J, Torrice C, Ramsey MR, Kovalev GI, Al-Regaiey K, Su L, Sharpless NE (2004) Ink4a/Arf expression is a biomarker of aging. J Clin Invest 114(9):1299–1307
Zindy F, Quelle DE, Roussel MF, Sherr CJ (1997) Expression of the p16INK4a tumor suppressor versus other INK4 family members during mouse development and aging. Oncogene 15(2):203–211
Molofsky AV, Slutsky SG, Joseph NM, He S, Pardal R, Krishnamurthy J, Sharpless NE, Morrison SJ (2006) Increasing p16INK4a expression decreases forebrain progenitors and neurogenesis during ageing. Nature 443(7110):448–452
Kuhn HG, Dickinson-Anson H, Gage FH (1996) Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. J Neurosci 16(6):2027–2033
Olariu A, Cleaver KM, Cameron HA (2007) Decreased neurogenesis in aged rats results from loss of granule cell precursors without lengthening of the cell cycle. J Comp Neurol 501(4):659–667
Hattiangady B, Shetty AK (2008) Aging does not alter the number or phenotype of putative stem/progenitor cells in the neurogenic region of the hippocampus. Neurobiol Aging 29(1):129–147
Molofsky AV, He S, Bydon M, Morrison SJ, Pardal R (2005) Bmi-1 promotes neural stem cell self-renewal and neural development but not mouse growth and survival by repressing the p16Ink4a and p19Arf senescence pathways. Genes Dev 19(12):1432–1437
Molofsky AV, Pardal R, Iwashita T, Park IK, Clarke MF, Morrison SJ (2003) Bmi-1 dependence distinguishes neural stem cell self-renewal from progenitor proliferation. Nature 425(6961):962–967
Bruggeman SW, Valk-Lingbeek ME, van der Stoop PP, Jacobs JJ, Kieboom K, Tanger E, Hulsman D, Leung C, Arsenijevic Y, Marino S, van Lohuizen M (2005) Ink4a and Arf differentially affect cell proliferation and neural stem cell self-renewal in Bmi1-deficient mice. Genes Dev 19(12):1438–1443
Lee MH, Reynisdottir I, Massague J (1995) Cloning of p57KIP2, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor with unique domain structure and tissue distribution. Genes Dev 9(6):639–649
Harper JW, Elledge SJ, Keyomarsi K, Dynlacht B, Tsai LH, Zhang P, Dobrowolski S, Bai C, Connell-Crowley L, Swindell E et al (1995) Inhibition of cyclin-dependent kinases by p21. Mol Biol Cell 6(4):387–400
Polyak K, Lee MH, Erdjument-Bromage H, Koff A, Roberts JM, Tempst P, Massague J (1994) Cloning of p27Kip1, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor and a potential mediator of extracellular antimitogenic signals. Cell 78(1):59–66
Carnero A, Hannon GJ (1998) The INK4 family of CDK inhibitors. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol 227:43–55
Vidal A, Koff A (2000) Cell-cycle inhibitors: three families united by a common cause. Gene 247(1–2):1–15
Kippin TE, Martens DJ, van der Kooy D (2005) p21 loss compromises the relative quiescence of forebrain stem cell proliferation leading to exhaustion of their proliferation capacity. Genes Dev 19(6):756–767
Qiu J, Takagi Y, Harada J, Rodrigues N, Moskowitz MA, Scadden DT, Cheng T (2004) Regenerative response in ischemic brain restricted by p21cip1/waf1. J Exp Med 199(7):937–945
Morshead CM, Reynolds BA, Craig CG, McBurney MW, Staines WA, Morassutti D, Weiss S, van der Kooy D (1994) Neural stem cells in the adult mammalian forebrain: a relatively quiescent subpopulation of subependymal cells. Neuron 13(5):1071–1082
Seaberg RM, van der Kooy D (2002) Adult rodent neurogenic regions: the ventricular subependyma contains neural stem cells, but the dentate gyrus contains restricted progenitors. J Neurosci 22(5):1784–1793
Cheng T, Rodrigues N, Shen H, Yang Y, Dombkowski D, Sykes M, Scadden DT (2000) Hematopoietic stem cell quiescence maintained by p21cip1/waf1. Science 287(5459):1804–1808
Pechnick RN, Zonis S, Wawrowsky K, Pourmorady J, Chesnokova V (2008) p21Cip1 restricts neuronal proliferation in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105(4):1358–1363
Doetsch F, Verdugo JM, Caille I, Alvarez-Buylla A, Chao MV, Casaccia-Bonnefil P (2002) Lack of the cell-cycle inhibitor p27Kip1 results in selective increase of transit-amplifying cells for adult neurogenesis. J Neurosci 22(6):2255–2264
Durand B, Gao FB, Raff M (1997) Accumulation of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27/Kip1 and the timing of oligodendrocyte differentiation. EMBO J 16(2):306–317
Casaccia-Bonnefil P, Hardy RJ, Teng KK, Levine JM, Koff A, Chao MV (1999) Loss of p27Kip1 function results in increased proliferative capacity of oligodendrocyte progenitors but unaltered timing of differentiation. Development 126(18):4027–4037
Casaccia-Bonnefil P, Tikoo R, Kiyokawa H, Friedrich V Jr, Chao MV, Koff A (1997) Oligodendrocyte precursor differentiation is perturbed in the absence of the cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor p27Kip1. Genes Dev 11(18):2335–2346
Cheng T, Rodrigues N, Dombkowski D, Stier S, Scadden DT (2000) Stem cell repopulation efficiency but not pool size is governed by p27(kip1). Nat Med 6(11):1235–1240
Qiu J, Takagi Y, Harada J, Topalkara K, Wang Y, Sims JR, Zheng G, Huang P, Ling Y, Scadden DT, Moskowitz MA, Cheng T (2009) p27Kip1 constrains proliferation of neural progenitor cells in adult brain under homeostatic and ischemic conditions. Stem Cells 27(4):920–927
Shin I, Yakes FM, Rojo F, Shin NY, Bakin AV, Baselga J, Arteaga CL (2002) PKB/Akt mediates cell-cycle progression by phosphorylation of p27(Kip1) at threonine 157 and modulation of its cellular localization. Nat Med 8(10):1145–1152
Liang J, Zubovitz J, Petrocelli T, Kotchetkov R, Connor MK, Han K, Lee JH, Ciarallo S, Catzavelos C, Beniston R, Franssen E, Slingerland JM (2002) PKB/Akt phosphorylates p27, impairs nuclear import of p27 and opposes p27-mediated G1 arrest. Nat Med 8(10):1153–1160
Mudo G, Belluardo N, Mauro A, Fuxe K (2007) Acute intermittent nicotine treatment induces fibroblast growth factor-2 in the subventricular zone of the adult rat brain and enhances neuronal precursor cell proliferation. Neuroscience 145(2):470–483
Nguyen L, Besson A, Heng JI, Schuurmans C, Teboul L, Parras C, Philpott A, Roberts JM, Guillemot F (2006) p27kip1 independently promotes neuronal differentiation and migration in the cerebral cortex. Genes Dev 20(11):1511–1524
Li X, Tang X, Jablonska B, Aguirre A, Gallo V, Luskin MB (2009) p27(KIP1) regulates neurogenesis in the rostral migratory stream and olfactory bulb of the postnatal mouse. J Neurosci 29(9):2902–2914
Burkhart DL, Sage J (2008) Cellular mechanisms of tumour suppression by the retinoblastoma gene. Nat Rev Cancer 8(9):671–682
Clarke AR, Maandag ER, van Roon M, van der Lugt NM, van der Valk M, Hooper ML, Berns A, te Riele H (1992) Requirement for a functional Rb-1 gene in murine development. Nature 359(6393):328–330
Jacks T, Fazeli A, Schmitt EM, Bronson RT, Goodell MA, Weinberg RA (1992) Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature 359(6393):295–300
Lee EY, Chang CY, Hu N, Wang YC, Lai CC, Herrup K, Lee WH, Bradley A (1992) Mice deficient for Rb are nonviable and show defects in neurogenesis and haematopoiesis. Nature 359(6393):288–294
Ferguson KL, Vanderluit JL, Hebert JM, McIntosh WC, Tibbo E, MacLaurin JG, Park DS, Wallace VA, Vooijs M, McConnell SK, Slack RS (2002) Telencephalon-specific Rb knockouts reveal enhanced neurogenesis, survival and abnormal cortical development. EMBO J 21(13):3337–3346
MacPherson D, Sage J, Crowley D, Trumpp A, Bronson RT, Jacks T (2003) Conditional mutation of Rb causes cell cycle defects without apoptosis in the central nervous system. Mol Cell Biol 23(3):1044–1053
Cobrinik D, Lee MH, Hannon G, Mulligan G, Bronson RT, Dyson N, Harlow E, Beach D, Weinberg RA, Jacks T (1996) Shared role of the pRB-related p130 and p107 proteins in limb development. Genes Dev 10(13):1633–1644
Lee MH, Williams BO, Mulligan G, Mukai S, Bronson RT, Dyson N, Harlow E, Jacks T (1996) Targeted disruption of p107: functional overlap between p107 and Rb. Genes Dev 10(13):1621–1632
Vanderluit JL, Ferguson KL, Nikoletopoulou V, Parker M, Ruzhynsky V, Alexson T, McNamara SM, Park DS, Rudnicki M, Slack RS (2004) p107 regulates neural precursor cells in the mammalian brain. J Cell Biol 166(6):853–863
Hitoshi S, Alexson T, Tropepe V, Donoviel D, Elia AJ, Nye JS, Conlon RA, Mak TW, Bernstein A, van der Kooy D (2002) Notch pathway molecules are essential for the maintenance, but not the generation, of mammalian neural stem cells. Genes Dev 16(7):846–858
Vanderluit JL, Wylie CA, McClellan KA, Ghanem N, Fortin A, Callaghan S, MacLaurin JG, Park DS, Slack RS (2007) The Retinoblastoma family member p107 regulates the rate of progenitor commitment to a neuronal fate. J Cell Biol 178(1):129–139
McClellan KA, Slack RS (2007) Specific in vivo roles for E2Fs in differentiation and development. Cell Cycle 6(23):2917–2927
Lammens T, Li J, Leone G, De Veylder L (2009) Atypical E2Fs: new players in the E2F transcription factor family. Trends Cell Biol 19(3):111–118
Field SJ, Tsai FY, Kuo F, Zubiaga AM, Kaelin WG Jr, Livingston DM, Orkin SH, Greenberg ME (1996) E2F–1 functions in mice to promote apoptosis and suppress proliferation. Cell 85(4):549–561
Yamasaki L, Jacks T, Bronson R, Goillot E, Harlow E, Dyson NJ (1996) Tumor induction and tissue atrophy in mice lacking E2F–1. Cell 85(4):537–548
Tevosian SG, Paulson KE, Bronson R, Yee AS (1996) Expression of the E2F–1/DP-1 transcription factor in murine development. Cell Growth Differ 7(1):43–52
Dagnino L, Fry CJ, Bartley SM, Farnham P, Gallie BL, Phillips RA (1997) Expression patterns of the E2F family of transcription factors during mouse nervous system development. Mech Dev 66(1–2):13–25
Orford KW, Scadden DT (2008) Deconstructing stem cell self-renewal: genetic insights into cell-cycle regulation. Nat Rev Genet 9(2):115–128
Mira H, Andreu Z, Suh H, Lie DC, Jessberger S, Consiglio A, San Emeterio J, Hortiguela R, Marques-Torrejon MA, Nakashima K, Colak D, Gotz M, Farinas I, Gage FH (2010) Signaling through BMPR-IA regulates quiescence and long-term activity of neural stem cells in the adult hippocampus. Cell Stem Cell 7(1):78–89
He S, Iwashita T, Buchstaller J, Molofsky AV, Thomas D, Morrison SJ (2009) Bmi-1 over-expression in neural stem/progenitor cells increases proliferation and neurogenesis in culture but has little effect on these functions in vivo. Dev Biol 328(2):257–272
Meletis K, Wirta V, Hede SM, Nister M, Lundeberg J, Frisen J (2006) p53 suppresses the self-renewal of adult neural stem cells. Development 133(2):363–369
Medrano S, Scrable H (2005) Maintaining appearances–the role of p53 in adult neurogenesis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 331(3):828–833
Gregorian C, Nakashima J, Le Belle J, Ohab J, Kim R, Liu A, Smith KB, Groszer M, Garcia AD, Sofroniew MV, Carmichael ST, Kornblum HI, Liu X, Wu H (2009) Pten deletion in adult neural stem/progenitor cells enhances constitutive neurogenesis. J Neurosci 29(6):1874–1886
Paik JH, Ding Z, Narurkar R, Ramkissoon S, Muller F, Kamoun WS, Chae SS, Zheng H, Ying H, Mahoney J, Hiller D, Jiang S, Protopopov A, Wong WH, Chin L, Ligon KL, DePinho RA (2009) FoxOs cooperatively regulate diverse pathways governing neural stem cell homeostasis. Cell Stem Cell 5(5):540–553
Renault VM, Rafalski VA, Morgan AA, Salih DA, Brett JO, Webb AE, Villeda SA, Thekkat PU, Guillerey C, Denko NC, Palmer TD, Butte AJ, Brunet A (2009) FoxO3 regulates neural stem cell homeostasis. Cell Stem Cell 5(5):527–539
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Fonds Léon Frédéricq (FLF) and the Fondation Médicale Reine Elisabeth. PB was supported by the FLF and a concerted action of the French Community of Belgium (Convention no. 04/09-322). RV is supported by a postdoctoral fellowship from the Alzheimer Society of Canada. NC is a research fellow of the Fonds pour la formation à la Recherche dans l’Industrie et dans l’Agriculture (FRIA). LN and BM are respectively research associate and research director of the Belgian Fonds National de la Recherche Scientifique (FNRS).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
P. Beukelaers and R. Vandenbosch contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Beukelaers, P., Vandenbosch, R., Caron, N. et al. Cycling or not cycling: cell cycle regulatory molecules and adult neurogenesis. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 69, 1493–1503 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0880-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-011-0880-6
Keywords
Profiles
- Brigitte Malgrange View author profile