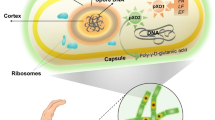
Abstract.
Anthrax has been a major cause of death in grazing animals and an occasional cause of death in humans for thousands of years. Since the late 1800s there has been an exceptional international history of anthrax vaccine development. Due to animal vaccinations, the rate of infection has dropped dramatically. Anthrax vaccines have progressed from uncharacterized whole-cell vaccines in 1881, to pXO2-negative spores in the 1930s, to culture filtrates absorbed to aluminum hydroxide in 1970, and likely to recombinant protective antigen in the near future. Each of these refinements has increased safety without significant loss of efficacy. The threat of genetically engineered, antibiotic and vaccine resistant strains of Bacillus anthracis is fueling hypothesis-driven research and global techniques – including genomics, proteomics and transposon site hybridization – to facilitate the discovery of novel vaccine targets. This review highlights historical achievements and new developments in anthrax vaccine research.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Opinions, interpretations, conclusions, and recommendations are those of the author and are not necessarily endorsed by the U.S. Army.