Abstract.
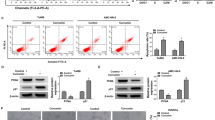
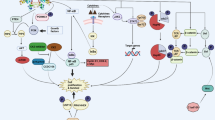
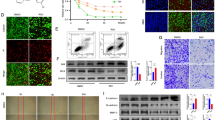
Enhanced cell migration is one of the underlying mechanisms in cancer invasion and metastasis. Therefore, inhibition of cell migration is considered to be an effective strategy for prevention of cancer metastasis. We found that emodin (3-methyl-1,6,8-trihydroxyanthraquinone), an active component from the rhizome of Rheum palmatum, significantly inhibited epidermal growth factor (EGF)- induced migration in various human cancer cell lines. In the search for the underlying molecular mechanisms, we demonstrated that phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) serves as the molecular target for emodin. In addition, emodin markedly suppressed EGF-induced activation of Cdc42 and Rac1 and the corresponding cytoskeleton changes. Moreover, emodin, but not LY294002, was able to block cell migration in cells transfected with constitutively active (CA)-Cdc42 and CA-Rac1 by interference with the formation of Cdc42/Rac1 and the p21-activated kinase complex. Taken together, data from this study suggest that emodin inhibits human cancer cell migration by suppressing the PI3K-Cdc42/Rac1 signaling pathway.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Received 7 February 2005; received after revision 11 March 2005; accepted 18 March 2005
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, Q., Shen, HM. & Ong, CN. Emodin inhibits tumor cell migration through suppression of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Cdc42/Rac1 pathway. CMLS, Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 62, 1167–1175 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5050-2
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-005-5050-2