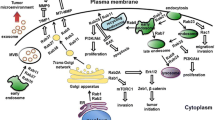
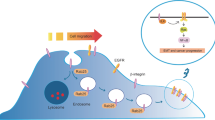
Abstract
Introduction
Oncogenic Ras-related GTP-binding proteins, referred to as Rabs, are characterized by their intricate interactions with upstream, downstream molecules, and notably, extracellular vesicles (EVs). While the expansive family of Rabs and their associated signaling pathways have been exhaustively dissected, Rab22a emerges as an entity of outstanding interest, owing to its potent influence in many biological processes and its conspicuous correlation with cancer metastasis and migration. A burgeoning interest in the interactions between Rab22a and EVs in the field of oncology underscores the necessity for more in-depth reviews and scholarly discourses.
Methods
We performed a review based on published original and review articles related to Rab22a, tumor, microRNA, exosome, microvesicles, EVs, CD147, lysosome, degradation, endosomal recycling, etc. from PubMed, Web of Science and Google Scholar databases.
Results and conclusions
We summarize the regulatory processes governing the expression of Rab22a and the mutants of Rab22a. Notably, the present understanding of complex interactions between Rab22a and EVs are highlighted, encompassing both the impact of Rab22a on the genesis of EVs and the role of EVs that are affected by Rab22a mutants in propelling tumor advancement. The dynamic interaction between Rab22a and EVs plays a significant role in the progression of tumors, and it can provide novel insights into the pathogenesis of cancers and the development of new therapeutic targets.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- Rabs:
-
Ras-related GTP-binding proteins
- EVs:
-
Extracellular vesicles
- ER:
-
Endoplasmic reticulum
- sEVs:
-
Small extracellular vesicles
- MVs:
-
Microvesicles
- DCs:
-
Dendritic cells
- STING:
-
Stimulator of interferon genes
- R-EVs:
-
Rab22a-induced extracellular vesicles
- HIF:
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor
- ARNT:
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor nuclear translocator
- CBP:
-
CREB-binding protein
- Pol II:
-
DNA polymerase II
- HREs:
-
Hypoxia responsive elements
- UTR:
-
Untranslated region
- TNM:
-
Tumor node metastasis
- NSCLC:
-
Non-small cell lung cancer
- BC:
-
Breast cancer
- CC:
-
Colon cancer
- GTP:
-
Guanosine triphosphate
- EEA:
-
Early endosomal antigen
- MMP:
-
Matrix metalloproteinases
- MCT-1:
-
Monocarboxylate transporter-1
- CD44s:
-
CD44 standard splice isoform
- STAT3:
-
Activator of transcription 3
- MVE:
-
Multivesicular endosome
- SmgGDS:
-
Small G protein guanine dissociation stimulator
- ARMs:
-
Armadillo-repeat motifs
- GEF:
-
Guanine exchange factor
- GGTase-I:
-
Geranylgeranyltransferase-I
- PMN:
-
Pre-metastatic niches
- PYK2:
-
Proline-rich tyrosine kinase 2
- ILVs:
-
Intraluminal vesicles
- TAMs:
-
Tumor-associated macrophages
- BMDCs:
-
Bone marrow-derived macrophages
References
Hutagalung AH, Novick PJ. Role of Rab GTPases in membrane traffic and cell physiology. Physiol Rev. 2011;91(1):119–49.
Qi S, Su L, Li J, Zhao P, Zhang Q, Niu X, et al. YIPF2 is a novel Rab-GDF that enhances HCC malignant phenotypes by facilitating CD147 endocytic recycle. Cell Death Dis. 2019;10(6):462.
Gao Y, Zheng X, Chang B, Lin Y, Huang X, Wang W, et al. Intercellular transfer of activated STING triggered by RAB22A-mediated non-canonical autophagy promotes antitumor immunity. Cell Res. 2022;32(12):1086–104.
Wang T, Gilkes DM, Takano N, Xiang L, Luo W, Bishop CJ, et al. Hypoxia-inducible factors and RAB22A mediate formation of microvesicles that stimulate breast cancer invasion and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2014;111(31):E3234–42.
Ao X, Zou L, Wu Y. Regulation of autophagy by the Rab GTPase network. Cell Death Differ. 2014;21(3):348–58.
van Niel G, D’Angelo G, Raposo G. Shedding light on the cell biology of extracellular vesicles. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(4):213–28.
Wu P, Zhang B, Ocansey DKW, Xu W, Qian H. Extracellular vesicles: a bright star of nanomedicine. Biomaterials. 2021;269: 120467.
Huang T, Song C, Zheng L, Xia L, Li Y, Zhou Y. The roles of extracellular vesicles in gastric cancer development, microenvironment, anti-cancer drug resistance, and therapy. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):62.
Bai Y, Huang W, Ma L-T, Jiang J-L, Chen Z-N. Importance of N-glycosylation on CD147 for its biological functions. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15(4):6356–77.
Xunian Z, Kalluri R. Biology and therapeutic potential of mesenchymal stem cell-derived exosomes. Cancer Sci. 2020;111(9):3100–10.
Alia Moosavian S, Hashemi M, Etemad L, Daneshmand S, Salmasi Z. Melanoma-derived exosomes: versatile extracellular vesicles for diagnosis, metastasis, immune modulation, and treatment of melanoma. Int Immunopharmacol. 2022;113(Pt A): 109320.
Bobrie A, Krumeich S, Reyal F, Recchi C, Moita LF, Seabra MC, et al. Rab27a supports exosome-dependent and -independent mechanisms that modify the tumor microenvironment and can promote tumor progression. Cancer Res. 2012;72(19):4920–30.
Grismayer B, Sölch S, Seubert B, Kirchner T, Schäfer S, Baretton G, et al. Rab31 expression levels modulate tumor-relevant characteristics of breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 2012;11:62.
Sun L, He M, Xu N, Xu D-H, Ben-David Y, Yang Z-Y, et al. Regulation of RAB22A by mir-193b inhibits breast cancer growth and metastasis mediated by exosomes. Int J Oncol. 2018;53(6):2705–14.
Yin Y, Zhang B, Wang W, Fei B, Quan C, Zhang J, et al. miR-204-5p inhibits proliferation and invasion and enhances chemotherapeutic sensitivity of colorectal cancer cells by downregulating RAB22A. Clin Cancer Res. 2014;20(23):6187–99.
Huang LE, Gu J, Schau M, Bunn HF. Regulation of hypoxia-inducible factor 1alpha is mediated by an O2-dependent degradation domain via the ubiquitin-proteasome pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1998;95(14):7987–92.
Yamashita K, Discher DJ, Hu J, Bishopric NH, Webster KA. Molecular regulation of the endothelin-1 gene by hypoxia. Contributions of hypoxia-inducible factor-1, activator protein-1, GATA-2, AND p300/CBP. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(16):12645–53.
Semenza GL. HIF-1 and mechanisms of hypoxia sensing. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001;13(2):167–71.
Zhang B, Yin Y, Hu Y, Zhang J, Bian Z, Song M, et al. MicroRNA-204-5p inhibits gastric cancer cell proliferation by downregulating USP47 and RAB22A. Med Oncol. 2015;32(1):331.
Bian Z, Jin L, Zhang J, Yin Y, Quan C, Hu Y, et al. LncRNA-UCA1 enhances cell proliferation and 5-fluorouracil resistance in colorectal cancer by inhibiting miR-204-5p. Sci Rep. 2016;6:23892.
Zhang L, Yu S. Role of miR-520b in non-small cell lung cancer. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(5):3987–95.
Zhou J, Gao F, Zhang H, Xing M, Xu Z, Zhang R. MiR-520b inhibits proliferation, migration and invasion in gallbladder carcinoma by targeting RAB22A. Arch Med Sci. 2021;17(2):481–91.
Yang Z, He M, Wang K, Sun G, Tang L, Xu Z. Tumor suppressive microRNA-193b promotes breast cancer progression via targeting DNAJC13 and RAB22A. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2014;7(11):7563–70.
Fang Z, Li C, Li S. MicroRNA-193b acts as a tumor suppressor in colon cancer progression via targeting RAB22A. Exp Ther Med. 2019;17(5):3921–8.
Tanaka T, Arai M, Wu S, Kanda T, Miyauchi H, Imazeki F, et al. Epigenetic silencing of microRNA-373 plays an important role in regulating cell proliferation in colon cancer. Oncol Rep. 2011;26(5):1329–35.
Ngalame NNO, Tokar EJ, Person RJ, Xu Y, Waalkes MP. Aberrant microRNA expression likely controls RAS oncogene activation during malignant transformation of human prostate epithelial and stem cells by arsenic. Toxicol Sci. 2014;138(2):268–77.
Zheng S, Jiang F, Ge D, Tang J, Chen H, Yang J, et al. LncRNA SNHG3/miRNA-151a-3p/RAB22A axis regulates invasion and migration of osteosarcoma. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019;112:108695.
Yu H, Yang W. MiR-211 is epigenetically regulated by DNMT1 mediated methylation and inhibits EMT of melanoma cells by targeting RAB22A. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2016;476(4):400–5.
Mesa R, Salomón C, Roggero M, Stahl PD, Mayorga LS. Rab22a affects the morphology and function of the endocytic pathway. J Cell Sci. 2001;114(Pt 22):4041–9.
Liao D, Zhong L, Yin J, Zeng C, Wang X, Huang X, et al. Chromosomal translocation-derived aberrant Rab22a drives metastasis of osteosarcoma. Nat Cell Biol. 2020;22(7):868–81.
Barral DC, Cavallari M, McCormick PJ, Garg S, Magee AI, Bonifacino JS, et al. CD1a and MHC class I follow a similar endocytic recycling pathway. Traffic. 2008;9(9):1446–57.
Radhakrishna H, Donaldson JG. ADP-ribosylation factor 6 regulates a novel plasma membrane recycling pathway. J Cell Biol. 1997;139(1):49–61.
Naslavsky N, Weigert R, Donaldson JG. Convergence of non-clathrin- and clathrin-derived endosomes involves Arf6 inactivation and changes in phosphoinositides. Mol Biol Cell. 2003;14(2):417–31.
Naslavsky N, Weigert R, Donaldson JG. Characterization of a nonclathrin endocytic pathway: membrane cargo and lipid requirements. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15(8):3542–52.
Mayorga LS, Cebrian I. Rab22a: A novel regulator of immune functions. Mol Immunol. 2019;113:87–92.
Eyster CA, Cole NB, Petersen S, Viswanathan K, Früh K, Donaldson JG. MARCH ubiquitin ligases alter the itinerary of clathrin-independent cargo from recycling to degradation. Mol Biol Cell. 2011;22(17):3218–30.
Maldonado-Báez L, Cole NB, Krämer H, Donaldson JG. Microtubule-dependent endosomal sorting of clathrin-independent cargo by Hook1. J Cell Biol. 2013;201(2):233–47.
Shakya S, Sharma P, Bhatt AM, Jani RA, Delevoye C, Setty SR. Rab22A recruits BLOC-1 and BLOC-2 to promote the biogenesis of recycling endosomes. EMBO Rep. 2018;19(12):e45918.
Thankachan JM, Setty SRG. KIF13A-A Key regulator of recycling endosome dynamics. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022;10: 877532.
Kong L, Huang S, Bao Y, Chen Y, Hua C, Gao S. Crucial roles of Rab22a in endosomal cargo recycling. Traffic. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1111/tra.12907.
Zhou Y, Wu B, Li J-H, Nan G, Jiang J-L, Chen Z-N. Rab22a enhances CD147 recycling and is required for lung cancer cell migration and invasion. Exp Cell Res. 2017;357(1):9–16.
Tang W, Chang SB, Hemler ME. Links between CD147 function, glycosylation, and caveolin-1. Mol Biol Cell. 2004;15(9):4043–50.
Thakur A, Qiu G, Xu C, Han X, Yang T, Ng SP, et al. Label-free sensing of exosomal MCT1 and CD147 for tracking metabolic reprogramming and malignant progression in glioma. Sci Adv. 2020;6(26):eaaz6119.
Li L, Tang W, Wu X, Karnak D, Meng X, Thompson R, et al. HAb18G/CD147 promotes pSTAT3-mediated pancreatic cancer development via CD44s. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19(24):6703–15.
Dorayappan KDP, Wanner R, Wallbillich JJ, Saini U, Zingarelli R, Suarez AA, et al. Hypoxia-induced exosomes contribute to a more aggressive and chemoresistant ovarian cancer phenotype: a novel mechanism linking STAT3/Rab proteins. Oncogene. 2018;37(28):3806–21.
Jordens I, Fernandez-Borja M, Marsman M, Dusseljee S, Janssen L, Calafat J, et al. The Rab7 effector protein RILP controls lysosomal transport by inducing the recruitment of dynein-dynactin motors. Curr Biol. 2001;11(21):1680–5.
Roberts EA, Chua J, Kyei GB, Deretic V. Higher order Rab programming in phagolysosome biogenesis. J Cell Biol. 2006;174(7):923–9.
Zhong L, Liao D, Li J, Liu W, Wang J, Zeng C, et al. Rab22a-NeoF1 fusion protein promotes osteosarcoma lung metastasis through its secretion into exosomes. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2021;6(1):59.
Brahimi-Horn MC, Chiche J, Pouysségur J. Hypoxia and cancer. J Mol Med (Berl). 2007;85(12):1301–7.
Gillies RJ, Gatenby RA. Hypoxia and adaptive landscapes in the evolution of carcinogenesis. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26(2):311–7.
King HW, Michael MZ, Gleadle JM. Hypoxic enhancement of exosome release by breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 2012;12:421.
Hsu YL, Hung JY, Chang WA, Lin YS, Pan YC, Tsai PH, et al. Hypoxic lung cancer-secreted exosomal miR-23a increased angiogenesis and vascular permeability by targeting prolyl hydroxylase and tight junction protein ZO-1. Oncogene. 2017;36(34):4929–42.
Kaelin WG. Proline hydroxylation and gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 2005;74:115–28.
Kumar A, Deep G. Hypoxia in tumor microenvironment regulates exosome biogenesis: molecular mechanisms and translational opportunities. Cancer Lett. 2020;479:23–30.
Kortylewski M, Kujawski M, Wang T, Wei S, Zhang S, Pilon-Thomas S, et al. Inhibiting Stat3 signaling in the hematopoietic system elicits multicomponent antitumor immunity. Nat Med. 2005;11(12):1314–21.
Yan D, Wang HW, Bowman RL, Joyce JA. STAT3 and STAT6 signaling pathways synergize to promote cathepsin secretion from macrophages via IRE1alpha activation. Cell Rep. 2016;16(11):2914–27.
Wortzel I, Dror S, Kenific CM, Lyden D. Exosome-mediated metastasis: communication from a distance. Dev Cell. 2019;49(3):347–60.
Acknowledgements
We thank all the subjects who participated in this study.
Funding
This work was supported by the Science and Technology Plan Project of Wenzhou (Grant Nos. Y20220389, Y20220045), Zhejiang Province Natural Science Foundation (Grant No. LTGY23H100001), and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81901660).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Writing, review, and editing, SHH, YXB; writing the first draft, SHH, YXB; final editing and proof reading, LJK, SG, CYH. All the authors have read and agreed to the published version of the article.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Ethical approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable as no patient’s or individual data have been used.
Additional information
Responsible Editor: John Di Battista.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Huang, S., Bao, Y., Kong, L. et al. Insights into the complex interactions between Rab22a and extracellular vesicles in cancers. Inflamm. Res. 73, 99–110 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-023-01821-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00011-023-01821-0