Abstract
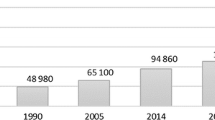
Economic analyses of geriatric syndromes are seldom performed. However, demographic and epidemiological imperatives have led to significant interest in the evaluation of AD-related costs. Over 300 papers devoted to economic considerations of Alzheimer’s disease have been published in peer-reviewed journals, within the last five years. In these papers, the chosen perspective (costs to society or to specific payers) is important. Analytical methods are still evolving and remain complex. Unresolved methodological issues will need to be addressed to further our understanding of long-term economic consequences. At present, it is clear that diagnostic and drug costs are low compared to the major cost of institutionalization. Thus, directing efforts at early diagnosis and delaying nursing home placement are two key cost-containment interventions. In this respect, the need to support informal care should not be underestimated.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Souetre E.J., Qing W., Vigoureux I.: Economic analysis of Alzheimer’s disease in outpatients: impact of symptom severity. In: Giacobini E., Becker R. (Eds.), Alzheimer’s disease: therapeutic strategies. Birkhauser, Boston, 1994, pp. 470–480.
Kalache A.: Ageing world-wide. In: Ebrahim S., Kalache A. (Eds.), Epidemiology in old age. British Medical Society Publishing Group, London, 1996, pp. 22–31.
Khatchaturian Z.S., Radebaugh T.S.: Alzheimer Disease: Where are we now? Where are we going? Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 12 (Suppl. 3): S24–S28, 1998.
Ritchie K., Kildea D.: Is senile dementia “age related” or “aging related”? Evidence from a meta-analysis of dementia prevalence in the oldest old. Lancet 346: 931–934, 1995.
Herrmann F.: Prevalence of Dementia in Switzerland (Unpublished data).
Murray C.J., Lopez A.D.: Summary: the global burden of disease. Cambridge Mass., Harvard University Press, 1997, p. 43.
Henderson A.S., Jorm A.F.: Definition, and epidemiology of dementia. In: Maj M., Sartorius N. (Eds.), Dementia. John Willey & Sons LTD, Chichester, 2000, pp. 1–33.
Whitehouse P.J.: Pharmacoeconomics of dementia. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 11 (Suppl. 5): S22–S33, 1997.
Winblad B., Hill S., Beermann B., Post S.G., Wimo A.: Issues in the economic evaluation of treatment for dementia. Position paper from the International Working Group on Harmonization of Dementia Drug Guidelines. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 11 (Suppl. 3): 39–45, 1997.
Wimo A., Ljunggren G., Winblad B.: Costs of dementia and dementia care: a review. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 12: 841–856, 1997.
Volz A., Monsch A.U., Zahno A., Wettstein A., Staehelin H.B.: Was kostete die Schweiz die Alzheimer-Krankheit 1998?: Eine praliminare. Analyse Praxis 89: 803–811, 2000.
Meerding W.J., Bonneux L., Polder J.J., Koopmanschap M.A., van der Mass P.J.: Demographic and epidemiological determinants of healthcare costs in the Netherlands: cost of illness study. BMJ 317: 111–115, 1998.
Ernst R.L., Hay J.W.: The U.S. economic and social cost of Alzheimer’s Disease revisited. Am. J. Public Health 84: 1261–1264, 1994.
Menzin J., Lang K., Friedman M., Neumann P., Cummings J.L.: The economic cost of Alzheimer’s Disease and related dementia to the California Medicaid Program (“Medi-Cal”) in 1995. Am. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 7: 300–308, 1999.
Neumann P., Kuntz K.M., Leon J.L., Araki S.S., Hermann R.C., Hsu M.A., Weinstein M.C.: Health utilities in Alzheimer’s Disease: a cross sectional study of patients and caregivers. Med. Care 37: 27–32, 1999.
Drummond M., Stoddart G.L., Torrance G.E.W.: Methods for the economic evaluation of health care programmes. Oxford University Press, Oxford, 1987.
Nagaratnam N., Lewis-Jones M., Scott D., Palazzi L.: Behavioral and psychiatric manifestations in dementia patients in a community: caregiver burden and outcome. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 12: 330–334, 1998.
Cavallo M.C., Fattore G.: The economic and social burden of Alzheimer Disease on families in the Lombardy region of Italy. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 11: 184–190, 1997.
Wimo A., Karlson G., Jonsson B., Winblad B.: The Health Economics of dementia. John Wiley & Son, London, UK, 1998.
Fox P.J.: Service use and cost outcomes for persons with Alzheimer Disease. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 11 (Suppl. 6): 125–134, 1997.
Albert S.M., Sano M., Bell K., Merchant C., Small S., Stern Y.: Hourly care received by people with Alzheimer’s Disease: results from an urban community survey. Gerontologist 38: 704–714, 1998.
Knapp M., Wilkinson D., Wigglesworth R.: The economic consequences of Alzheimer’s disease in the context of new drug developments. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 13: 531–543, 1998.
Trabucchi M., Govoni S., Bianchetti A.: Socio-economic aspects of Alzheimer’s disease treatment. In: Giacobini E., Becker R. (Eds.), Alzheimer’s disease: therapeutic strategies. Birkhauser, Boston, 1994, pp. 459–463.
Trabucchi M., Ghisla K.M., Bianchetti A.: CODEM: a longitudinal study on Alzheimer disease costs. In: Becker R., Giacobini E. (Eds.), Alzheimer’s disease: From molecular biology to therapy. Birkhauser, Boston, 1996, pp. 561–565.
Hux M.J., O’Brien B.J., Iskedjian M., Goeree R., Gagnon M., Gauthier S.: Relation between severity of Alzheimer’s disease and costs of caring. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 159: 457–465, 1998.
US Congress General Accounting Office: Alzheimer’s disease: estimates of prevalence in the United States [GAO pub. No.HEHS-98-16]. Washington, DC, US Government Printing Office, 1998.
Souetre E., Thwaites R.M., Yeardley H.L.: Economic impact of Alzheimer’s disease in the United Kingdom. Cost of care and disease severity for non-institutionalised patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Br. J. Psychiatry 174: 1–5, 1999.
Neumann P.J., Hermann R.C., Berenbaum P.A., Weinstein M.C.: Methods of cost-effectiveness analysis in the assessment of new drugs for Alzheimer’s Disease. Psychiatr. Serv. 48: 1440–1444, 1997.
Busschbach J.J., Brouwer W.B., van der Donk A., Passchier J., Rutten F.F: An outline for a cost-effectiveness analysis of a drug for patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Pharmacoeconomics 13: 21–34, 1998.
Torrance G.W.: Utility approach to measuring health related quality of life. J. Chronic Dis. 40: 593–603, 1987.
Albert S.M., Del Castillo-Castaneda C., Sano M., Jacobs D.M., Marder K., Bell K., Bylsma F., Lafleche G., Brandt J., Albert M., Stern Y.: Quality of life in patients with Alzheimer’s Disease as reported by patients proxies. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 44: 1342–1347, 1996.
Bootman J.L., Townsend R.J., McGhan W.F.: Principles of pharmacoeconomics, ed. 2. Harvey Whitney Books, Cincinnati, 1996.
Spilker B.: Adopting higher standards for quality of life trials. Quality of life and pharmacoeconomics in clinical trials, ed. 2. Lippincott-Raven, Philadelphia, 1996.
Withehouse P.J.: Pharmacoeconomics of dementia. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 11 (Suppl. 5): S22–S33, 1997.
Ernst R.L., Hay J.W.: Economic research on Alzheimer Disease: a review of the literature. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 11 (Suppl. 6): 135–145, 1997.
Schumock G.T.: Economic considerations in the treatment and management of Alzheimer’s Disease. Am. J. Health Syst. Pharm. 55 (Suppl. 2): S17–S21, 1998.
Gutterman E.M., Markowitz J.S., Lewis B., Fillit H.: Cost of Alzheimer’s Disease and related dementia in managed medicare. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 47: 1065–1071, 1999.
Weiner M., Powe N.R., Anderson G.F.: Medicare expenditures for beneficiaries with dementia of the Alzheimer’s type (Letter). J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 47: 1276, 1999.
Arnsberger P., Fox P., Zhang X.: Case manager-defined roles in the Medicare Alzheimer’s Disease Demonstration: relationship to client and caregiver outcomes. Care Manag. J. 1: 29–37, 1999.
Wimo A., Wallin J.O., Lundgren K., Ronnback E., Asplund M., Mattson B., Krakau I.: Impact of day care on dementia patients - costs, well-being and relatives’ views. Fam. Pract. 7: 279–287, 1990.
Wimo A., Mattson B., Krakau I., Eriksson T., Nelvig A.: Cost-effectiveness analysis of day care for patients with dementia disorders. Health Econ. 3: 395–404, 1994.
Knopman D., Schneider L., Davis K., Talwalker S., Smith F., Hoover T., Gracon S.: Long term tacrine (Cognex) treatment: effects on nursing home placements and mortality. Neurology 47: 166–177, 1996.
Thal L.J., Thomas R.G., Sano M.: Tacrine and nursing home placement. Neurology 49: 897–899, 1997.
Leon J., Moyer D.: Potential cost savings in residential care for Alzheimer’s disease patients. Gerontologist 39: 440–449, 1999.
Lewin V.H.I.: National study of assisted living for the frail elderly: literature review update. Report prepared for HHS/ASPE under contract no. DHHS-100-94-0024. Research Triangle Institute, 1996.
Mollica R.L., Snow K.I.: State assisted living policy 1996. A report prepared for HHS/ASPE under contract no. DHHS- 100-94-0024 Portland, ME. National Academy for State Health Policy, 1996.
Neumann P.J., Herrmann R.C., Kuntz K.M., Araki S.S., Duff S.B., Leon J., Berenbaum P.A., Goldman P.A., Williams L.W., Weinstein M.C.: Cost-effectiveness of Donepezil in the treatment of mild or moderate Alzheimer’s Disease. Neurology 52: 1138–1145, 1999.
Fenn P., Gray A.: Estimating long-term cost savings from treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. A modelling approach. Pharmacoeconomics 16: 165–174, 1999.
O’Brien B.J., Goeree R., Hux M., Iskedjian M., Blackhouse G., Gagnon M., Gauthier S.: Economic evaluation of Donepezil for the treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease in Canada. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 47: 570–578, 1999.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Michel, J.P., Zekry, D., Mulligan, R. et al. Economic considerations of Alzheimer’s disease and related disorders. Aging Clin Exp Res 13, 255–260 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03351484
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03351484