Summary
Objective
Randomised clinical trials have demonstrated that rofecoxib has a better gastrointestinal tolerability profile than conventional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) in osteoarthritis, which results in a reduced utilisation of gastroprotective agents (GPA). The aim of this study was to estimate, from the national healthcare system perspective, the total drug costs in patients switched from NSAIDs plus GPAs to rofecoxib.
Design
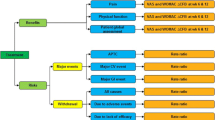
In this longitudinal, observational study, drug prescriptions for symptomatic treatment of osteoarthritis were recorded. A decision tree was used to compare the mean daily drug cost of the following therapeutic options for ostheoarthritis: conventional NSAIDs and rofecoxib/conventional NSAIDs.
Setting
Azienda Unità Sanitaria Locale 110, Ravenna, Italy.
Patients
56,827 patients affected by osteoarthritis were monitored from January 1997 to December 1999. Of this group, we considered the first 2,935 patients who were examined by 21 General Practitioners in the period July 2000-October 2000, in order to point out changes in GPAs co-prescription after the introduction of rofecoxib in the Italian market.
Interventions
Alternative treatments compared were: NSAIDs either alone or combined with GPAs (NSAIDs option), and just after the introduction of rofecoxib, NSAIDs or rofecoxib alone and NSAIDs or rofecoxib combined with GPAs (rofecoxib/NSAIDs option).
Main outcome measures and results
27,511 out of 56,827 patients (48.4%; IC 95%: 48.0–48.8%) treated with NSAIDs also received a GPA co-medication. In the aforementioned subgroup of 2,935 patients, 1,814 (62%) received multiple prescriptions of NSAIDs or rofecoxib. In this subgroup, rofecoxib was associated with a statistically significant reduction of GPAs utilisation of 58.8% (IC 95%: 30.7–80.1; p = 0.012) compared with what was recorded during treatment with NSAIDs. In fact, the mean daily cost per patient of the NSAIDs option was € 1.66 versus € 1.55 of the rofecoxib/NSAIDs option (6.6% lower).
Conclusions
Our preliminary results suggest that the use of rofecoxib is associated with cost savings in terms of total drug costs compared with conventional NSAIDs.
Similar content being viewed by others
Bibliografia
Badley EM, Rasooly I, Webster GK. Relative importance of musculoskeletal disorders as a cause of chronic health problems, disability, and health care utilization: findings from the 1990 Ontario Health Survey. J Rheumatol 1994; 21: 505–14
Leardini G. Dimensioni e costi degli effetti indesiderati FANS-indotti nel paziente affetto da artrosi in Italia. Reumatismo 2000; 52(4): 223–33
Istituto Nazionale di Statistica. Le condizioni di salute degli italiani. Anno 1999. Roma; ISTAT, 2000
Badley EM, Crotty M. An international comparison in the estimated effect of the aging of the population on the major cause of disablement, musculoskeletal disorders. J Rheum 1995; 22: 1934–40
March LM, Bachmeier CJM. Economics of osteoarthritis: a global perspective. Baillières Clin Rheumatol 1997; 11: 817–34
Singh G, Ramey D. NSAID induced gastrointestinal complications: the ARAMIS perspective-1997. Arthritis, Rheumatism, and Aging Medical Information System. J Rheum 1998; 51 (Suppl): 8–16
Blower AL, Brooks A, Fenn GC, et al. Emergency admissions for upper gastrointestinal disease and their relation to NSAID use. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 1997; 12: 283–91
Garcia Rodriguez LA, Cattaruzzi C, Troncon MG, Agostinis L. Risk of hospitalization for upper gastrointestinal tract bleeding associated with ketorolac, other nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, calcium antagonists, and other antihypertensive drugs. Arch Intern Med 1998; 158: 33–9
Langman MJS. Ulcer complications and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. Am J Med 1988; 84 (Suppl 2a): 15–9
Langman MJ, Jensen DM, Watson DJ, et al. Adverse upper gastrointestinal effects of rofecoxib compared with NSAIDs. JAMA 1999; 282: 1929–33
Laine L, Harper S, Simon T, et al. A randomized trial comparing the effect of rofecoxib, a cyclooxygenase 2-specific inhibitor, with that of ibuprofen on the gastroduodenal mucosa of patients with osteoarthritis. Gastroenterology 1999; 117: 776–83
Simon LS, Weaver AL, Graham DY, et al. Anti-inflammatory and upper gastrointestinal effects of celecoxib in rheumatoid arthritis. JAMA 1999; 282: 1921–28
Silverstein FE, Faich G, Goldstein JL, et al. Gastrointestinal toxicity with celecoxib vs nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. The CLASS Study: a randomized controlled trial. JAMA 2000; 284: 1247–55
Bombardier C, Laine L, Reicin A, et al. Comparison of upper gastrointestinal toxicity of rofecoxib and naproxen in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. VIGOR Study Group. N Engl J Med. 2000; 343(21): 1520–28
Watson DJ, Harper S, Zhao P, et al. Treatment with rofecoxib required less gastrointestinal (GI) combination and fewer GI procedures than nonspecific cyclooxygenase inhibitors (NSAIDs). Proceedings of the American College of Rheumatology 1999; S403
IMS-Health Italia. Il mercato farmaceutico. Milano; IMS, 2000: 12
Attanasio E. Implicazioni economiche nelle scelte mediche. In: Torsoli A. (ed.). Manuale di metodologia clinica per studenti e giovani medici. Roma; Il Pensiero Scientifico Editore, 1997: 73–91
Moore N, Montout C, Verschuren X, et al. Use of gastrointestinal (GI) protective agents among patients on non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in France and prevention or treatment of adverse GI effects. 12th EULAR Congress. Glasgow, Scotland, June 6–11, 1999. Rheumatol Europe 1999
Langman M, Kahler KH, Kong SX, et al. Use of gastroprotective agents and other healthcare resources among patients on nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in the United Kingdom (Abstract). 12th EULAR Congress. Glasgow, Scotland, June 6–11, 1999. Rheumatol Europe 1999
Lanas A. Impacto económico de los efectos secundarios gastrointestinales asociados a antiinflamatorios no esteroideos en el Servicio Nacional de Salud. Med Clin (Barc) 2000; 114 (Suppl 3): 46–53
Rahme E, Kong SX, Watson DJ, LeLorier J. Use of concomitant gastro-protective agents, diagnostic tests, and hospitalizations among elderly patients who started nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs in Quebec (Abstract). Arth Rheum 1998; 41 (Suppl): S77
Singh G, Ramey DR, Morfeld D, et al. Gastrointestinal tract complications of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. A prospective observational cohort study. Arch Intern Med 1996; 156: 1530–36
Silverstein FE, Graham DY, Senior JR, et al. Misoprostol reduces serious gastrointestinal complications in patients with rheumatoid arthritis receiving nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs. A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 1995;v123: v241–9
Hogan DB, Campbell NRC, Crutcher R, et al. Prescription of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for elderly people in Alberta. Can Med Assoc J 1994; 151: 315–22
Hunsche E, Chancellor JVM, Bruce N. The burden of arthritis and the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory treatment: a European literature review. PharmacoEconomics 2001; 19 (Suppl 1): 1–15
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russo, P., Attanasio, E., Baio, G. et al. Una prima valutazione economica dell’impiego di rofecoxib versus FANS convenzionali nell’artrosi. Pharmacoeconomics-Ital-Res-Articles 3, 81–89 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03320582
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03320582