Abstract
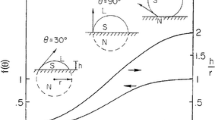
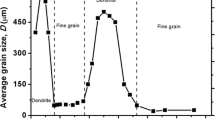
Precision adiabatic recalescence experiments on both pure and binary undercooled melts have been conducted. The adiabatic constraint limits the amount of net phase transformation from the metastable under-cooled state (creating a mushy zone) and also sets bounds on the microstructural parameters of the mushy zone, namely the volume fraction of the phases, their length scales, and the interfacial compositions. As many as three distinct kinetic time scales are observed in these experiments: a short time scale (less than ∼1 s) of rapidly increasing temperature from the initial nucleation temperature, associated with the propagation of the dendrites and release of latent heat; an intermediate time scale (∼103–104 s) of slowly rising temperature, associated with coarsening of the mushy zone; and a long time scale (days) of steadily falling temperature, associated with solid-state diffusional adjustments near the solid-liquid interface.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.K. Trivedi, Lectures on the Theory of Phase Transformations, ed. H.I. Aaronson (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1975), pp. 51–81.
W. Kurz and D.J. Fisher, Fundamentals of Solidification (Switzerland: Trans. Tech. Publications, 1986), p. 13.
O.M. Todes, J. Physical Chem. (Russ.) 20 (1946), p. 630.
I.M. Lifshitz and V.V. Slyozov, J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 19 (1961), p. 315.
C. Wagner, Z. Elektrochem., 65 (1961), p. 581.
J.A. Marqusee and J. Ross, J. Chem. Phys., 80(1) (1984), p. 536.
P.W. Voorhees, J. Stat. Phys., 38 (1985), p. 231.
S.P. Marsh, Ph.D thesis, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (1989).
S.P. Marsh, R.N. Smith, and M.E. Glicksman, Heat Transfer in Phase Change, ed. I.S. Habib, L.S. Yao, and J. Goodman (New York: ASME, 1992), p. 47.
R.T. DeHoff and C.V. Iswaran, Met. Trans. A, 13A (1982), p. 1389.
P.W. Voorhees and M.E. Glicksman, J. Crystal Growth, 72 (1985), p. 599.
S.P. Marsh and M.E. Glicksman, Modeling and Control of Casting and Welding Processes, ed. S. Kou and R. Mehrabian (Warrendale, PA: TMS, 1986), pp. 579–585.
P.W. Voorhees, Met. Trans., 21A (1990), p. 27–37.
L. A. Meloro, M.S. thesis, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (1988).
The International Practical Temperature Scale of 1968, Metrologia, 5 (1969), p. 35.
R. Kuklinski and R.N. Smith, Heat Transfer in Manufacturing and Materials Processing, ed. R.K. Shah (New York: ASME, 1989), pp. 55–61.
R. Kuklinski, Ph.D. thesis, Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute (1990).
M.E. Glicksman et al., Met. Trans., 23A (1992), p. 659–667.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Colucci-Mizenko, L.M., Glicksman, M.E. & Smith, R.N. Thermal recalescence and mushy zone coarsening in undercooled melts. JOM 46, 51–55 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03222538
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03222538