Summary
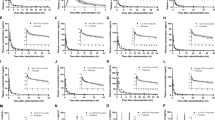
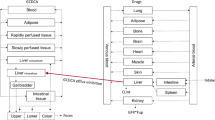
Torcetrapib was the lead candidate belonging to the class of cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor which was being developed for the management of cardiovascular risk factors by raising HDL. The availability of pharmacokinetic parameters (clearance: CL/F, volume of distribution: Vd/F, elimination rate constant: Kel and elimination half-life: t1/2) in mice, rats and monkeys, enabled the prediction of human parameter values using the well accepted tool of allometry. Although allometry work has been largely restricted to intravenous drugs, the present case of torcetrapib showed that allometry may be equally applicable to oral route. Simple allometry appeared to markedly inflate the human parameters for CL/F, Vd/F, Kel and t1/2. However, the application of bile correction factors provided allometric equations of 0.2486W0.877 (R2=0.9416), 1.4723W1.8263 (R2=0.8873), 0.1685W−095 (R2=0.828) and 4.1044W0.9493 (R2=0.9337) for CL/F, Vd/F, Kel, and t1/2, rendering a closer prediction of human parameter values. Accordingly, the predicted (observed) values of torcetrapib were 10.3 L/h (15.8 L/h), 3449 L (4810 L), 0.00298 h−1 (0.00328 h−1) and 211 h (231 h) for CL/F, Vd/F, Kel and t1/2, respectively. In summary, the data suggested that allometry tool with appropriate bile correction factors could be effectively used in a prospective manner for other orally administered CETP inhibitors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barter P.J., Brewer H.B., Chapman J., Hennekens C.H., Radar D.J., Tall A.R. (2003). Cholesteryl ester transfer proteins: a novel target for raising HDL and inhibiting atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vase. Biol., 23, 160–167.
Tall A.R. (1993). Plasma cholesteryl ester transfer proteins. J. Lipid Res., 34, 1255–1274.
Hesler C.B., Swenson T.L., Tall A.R. (1987). Purification and characterization of a human plasma cholesteryl ester transfer protein. J. Biol. Chem., 262, 2275–2282
Barter P.J., Rye K.A. (2001). Cholesteryl ester transfer protein, high density lipoprotein and arterial disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol., 12, 377–382.
McPherson R., Mann C.J., Tall A.R., Hogue M., Martin L., Milne M.W, Marcel Y.L. (1991). Plasma concentrations of cholesteryl ester transfer protein in hyperlipo-proteinemia. Relation to cholesteryl ester transfer protein activity and other lipoprotein variables. Arterioscler. Thromb., 11, 797–804.
Nofer J.R., Kehrel B., Fobker M., Levkau B., Assmann G., von Eckardstein A. (2002). HDL and arteriosclerosis: beyond reverse cholesterol transport. Atherosclerosis, 161, 1–6.
Sacks F.M. (2002). Expert Group on HDL Cholesterol. The role of high density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol in the prevention and treatment of coronary heart disease: expert group recommendations. Am. J. Cardiol., 90, 139–143.
Von Eckardstein A., Nofer J.R., Assmann G. (2001). High density lipoproteins and arteriosclerosis. Role of cholesterol efflux and reverse cholesterol transport. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vase. Biol., 21, 13–27.
Gotto A.M. Jr. (2001). Low high-density lipoprotein cholesterol as a risk factor in coronary heart disease: a working group report. Circulation, 103, 2213–2218.
Krishna R., Anderson M.S., Bergman A.J., Jin B., Fallon M., Cote J., Rosko K, Chavez-Eng C, Lutz R, Bloomfield D.M., Gutierrez M., Doherty J., Bieberdorf F., Chodakewitz J., Gottesdiener K.M., Wagner J.A. (2007). Effect of the cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitor, anacetrapib, on lipoproteins in patients with dyslipidaemia and on 24-h ambulatory blood pressure in healthy individuals; two double-blind, randomised placebo-controlled studies. Lancet, 370, 1907–1924.
de Grooth G.J., Kuivenhoven J.A., Stalenhoef A.F., de Graaf J., Zwinderman A.H., Posma J.L., van Toi A., Kastelein J.J. (2002). Efficacy and safety of a novel cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitor, JTT-705, in humans: a randomized phase II dose-response study. Circulation, 105, 2159–2165.
Howes L.G., Kostner K. (2007). The withdrawal of torcetrapib from drug development: implications for the future of drugs that alter HDL metabolism. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs, 16, 1509–1516.
Tanne J.H. Pfizer stops clinical trials of heart drug. (2006). Br. Med. J., 333, 1237.
Krishna R., Bergman A.J., Jin B., Fallon M., Cote J., Van Hoydonck P., Laethem T., Gendrano I.N. 3rd., Van Dyck K., Hilliard D., Laterza O., Snyder K., Chavez-Eng C., Lutz R., Chen J., Bloomfield D.M., De Smet M., Van Bortel L.M., Gutierrez M., Al-Huniti N., Dykstra K., Gottesdiener K.M., Wagner J.A. (2008). Multiple-dose pharmacodynamics of anacetrapib, a potent cholesteryl ester transfer protein (CETP) inhibitor, in healthy subjects. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 84, 679–683.
Prakash C., Chen W., Rossulek M., Johnson K., Zhang C., O’Connell T, Potchoiba M., Dalvie D. (2008). Metabolism, pharmacokinetics, and excretion of a cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitor, torcetrapib, in rats, monkeys, and mice: characterization of unusual and novel metabolites by high-resolution liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry and1H nuclear magnetic resonance. Drug Metab. Dispos., 36, 2064–2079.
Dalvie D., Chen W., Zhang C., Vaz A.D., Smolarek T.A., Cox L.M., Lin J., Obach R.S. (2008). Pharmacokinetics, metabolism and excretion of torcetrapib, a CETP inhibitor, in humans. Drug Metab. Dispos., 36, 2185–2198.
Boxembaum H. Interspecies scaling, allometry, physiological time, and the ground plan of pharmacokinetics. (1982). J. Pharmacokinet. Biopharm., 10, 201–227.
Mahmood I., Balian J.D. (1996). Interspecies scaling: Predicting pharmacokinetic parameters of antiepileptic drugs in humans from animals with special emphasis on clearance. J. Pharm. Sci., 85, 411–414.
Mahmood I., Yuan R. (1999). A comparative study of allometric scaling with plasma concentrations predicted by species-invariant time methods. Biopharm. Drug Dispos., 20, 137–144.
Sinha V.K., De Buck S.S., Fenu L.A., Smit J.W., Nijsen M., Guissen R.A., Van Peer A., Lavrijsen K., Mackie C.E. (2008). Predicting oral clearance in humans: How close can we get with allometry. Clin. Pharmacokinet., 47, 35–45.
Ahlawat P., Srinivas N.R. (2008). Allometric prediction of the human pharmacokinetic parameters for naveglitazar. Eur. J. Drug. Metab. Pharmacokinet., 33, 187–190.
Ahlawat P., Srinivas N.R. (2008). Interspecies scaling of a camptothecin analogue: human predictions for intravenous topotecan using animal data. Xenobiotica, 38, 1377–1385.
Bhamidipati R.K., Dravid P.V., Mullangi R., Srinivas N.R. (2004). Prediction of clinical pharmacokinetic parameters of linezolid using animal data by allometric scaling: applicability for the development of novel oxazolidinones. Xenobiotica, 34, 571–579.
Kim S.H., Kim W.B., Lee M.G. (1998). Interspecies pharmacokinetic scaling of a new carbapenem, DA-1131, in mice, rats, rabbits and dogs, and prediction of human pharmacokinetics. Biopharm. Drug Dispos., 19, 231–235.
Mehta S.C., Lu R.D. (1995). Interspecies pharmacokinetic scaling of BSH in mice, rats, rabbits, and humans. Biopharm. Drug Dispos., 16, 735–744.
Pavankumar V.V., Vinu C.A., Mullangi R., Srinivas N.R. (2007). Preclinical pharmacokinetics and interspecies scaling of ragaglitazar, a novel biliary excreted PPAR dual activator. Eur. J. Drug. Metab. Pharmacokinet., 32, 29–37.
Mahmood I. (2005). Interspecies scaling of biliary excreted drugs: a comparison of several methods. J. Pharm. Sci., 94, 883–892.
Mahmood I., Sahawalla C. (2002). Interspecies scaling of biliary excreted drugs. J. Pharm. Sci., 91, 1908–1914.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mullangi, R., Ahlawat, P., Trivedi, R.K. et al. Use of bile correction factors for allometric prediction of human pharmacokinetic parameters of torcetrapib, a facile cholesteryl ester transfer protein inhibitor. Eur. J. Drug Metabol. Pharmacokinet. 34, 57–63 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191385
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03191385