Summary
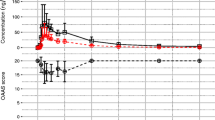
The pharmacokinetics of midazolam and of its main metabolite, 1-hydroxymidazolam, were investigated in intensive care patients after intravenous bolus of 0.2mg/kg followed by a 0.1mg/kg/h intravenous infusion of midazolam over 2 hours. A wide interpatient variability of the main pharmacokinetic parameters of midazolam was found. The mean values of elimination half life and volume of distribution, 4.5±5.4 h and 1.7±0.7l/kg respectively, were higher than those reported in healthy subjects. Total plasma clearance was significantly increased in patients taking drugs that induce hepatic metabolism. Significant concentrations of the unconjugated form of 1-hydroxymidazolam were recovered in plasma. The volume of distribution and the elimination half life of the metabolite were higher than those of the parent drug. These results show that 1-hydroxymidazolam might contribute to the pharmacodynamic effect of midazolam and consequently must be taken into account during pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic studies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dundee J.W., Halliday N.J., Harper K.W., Brogden R.N. (1984): Midazolam, a review of its pharmacological properties and therapeutic use. Drugs 28, 519–543.
Heizmann P., Eckert M., Zeigler W.H. (1983): Pharmacokinetics and bioavailability of midazolam in man. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 16, 435–495.
Ziegler W.H., Schalch E., Leishman B., Eckert M. (1983): Comparison of the effects of intravenously administered midazolam, triazolam and their hydroxy metabolites. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 16, 63S-69S.
Oldenhof H., De Jong M., Steenhoek A., Janknegt R. (1988): Clinical pharmacokinetics of midazolam in intensive care patients, a wide interpatient variability? Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 43, 263–269.
Lehmann B., Boulieu R. (1995): Determination of midazolam and its unconjugated 1-hydroxy metabolite in human plasma by high performance liquid chromatography. J. Chromatogr., 674, 138–142.
Gomeni C., Gomeni R., Siphar. (1987): An integrated computer system for statistical and pharmacokinetic data analysis. Proceedings of seventh International congress of Medical Informatics. Serrio A., OÆWoore R., Tardini A., Roger F. eds. European Federation of Medical Informatics, Rome.
Akaike H. (1974): A new look at the statistical identification model. IEEE Auto Control 19, 716–723.
Brown C.R., Sarnquist F.H., Canup C.A., Pedley T.A. (1979): Clinical electroencephalographic and pharmacokinetic studies of a water-soluble benzodiazepine, midazolam maleate. Anesthesiology 50, 467–470.
Allonen H., Ziegler G., Klotz U. (1981): Midazolam kinetics. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther., 30, 5, 653–660.
Michalk S., Moncorge C., Fichelle A. et al. (1988): Midazolam infusion for basal sedation in intensive care: absence of accumulation. Int. Care Med. 15, 37–41.
Malacrida R., Fritz M.E., Suter P.M., Crevoisier C. (1991): Pharmacokinetics of midazolam administered by continuous intravenous infusion to intensive care patients. Crit. Care Med. 20, 1123–1126.
Vree T.N., Shimoda M., Driessen J.J. et al. (1989): Decreased plasma albumin concentration results in increased volume of distribution and decreased elimination of midazolam in intensive care patients. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 46, 537–544.
Crevoisier C., Ziegler W.H., Cano J.P. et al. (1986): Relation between the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of intravenously administered midazolam, triazolam and their hydroxy metabolites. In: Second Congress of the Inter American Society for Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics, pp. 47.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boulieu, R., Lehmann, B., Salord, F. et al. Pharmacokinetics of midazolam and its main metabolite 1-hydroxymidazolam in intensive care patients. European Journal of Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 23, 255–258 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189348
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF03189348